|
Barbera D'Alba
Barbera is a red Italian wine grape variety that, as of 2000, was the third most-planted red grape variety in Italy (after Sangiovese and Montepulciano). It produces good yields and is known for deep color, full body, low tannins and high levels of acidity.J. Robinson (ed) ''The Oxford Companion to Wine'' Third Edition pg 62-63 Oxford University Press 2006 Century-old vines still exist in many regional vineyards and allow for the production of long-aging, robust red wines with intense fruit and enhanced tannic content. The best known appellation is the DOCG (Denominazione di Origine Controllata e Garantita) Barbera d'Asti in the Piedmont region: the highest-quality Nizza DOCG wines are produced within a sub-zone of the Barbera d'Asti production area. When young, the wines offer a very intense aroma of fresh red cherries and blackberries. In the lightest versions notes of cherries, raspberries and blueberries and with notes of blackberry and black cherries in wines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbera (grapes)
Barbera is a name shared by several wine and table grape varieties with the most notable being the red Barbera grape of Piedmont in northwest Italy. Other grapes which are known as Barbera, either as part of their primary name or as a synonym, include: *Barbera Amara *Barbera bianca *Barbera Ciaria *Barbera del Sannio *Barbera di Patrunat *Barbera Sarda *Barbera Selvatico Barbera is a red Italian wine grape variety that, as of 2000, was the third most-planted red grape variety in Italy (after Sangiovese and Montepulciano). It produces good yields and is known for deep color, full body, low tannins and high levels ... * Durasa, known under the synonym of Barbera Rotonda * Ervi, crossing known under the synonym of Barbera x Bonarda 108 * Freisa, known under the synonym of Barbera * Sanches, Brazilian hybrid grape crossing known under the synonym of Barbera Min * Terzi 1, crossing known under the synonym of Barbera x Cabernet Franc N.1 {{SIA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid (wine)
The acids in wine are an important component in both winemaking and the finished product of wine. They are present in both grapes and wine, having direct influences on the color, balance and taste of the wine as well as the growth and vitality of yeast during fermentation and protecting the wine from bacteria. The measure of the amount of acidity in wine is known as the “titratable acidity” or “total acidity”, which refers to the test that yields the total of all acids present, while strength of acidity is measured according to pH, with most wines having a pH between 2.9 and 3.9. Generally, the lower the pH, the higher the acidity in the wine. There is no direct connection between total acidity and pH (it is possible to find wines with a high pH for wine and high acidity). In wine tasting, the term “acidity” refers to the fresh, tart and sour attributes of the wine which are evaluated in relation to how well the acidity balances out the sweetness and bitter componen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dried Fruit
Dried fruit is fruit from which the majority of the original water content has been removed either naturally, through sun drying, or through the use of specialized dryers or dehydrators. Dried fruit has a long tradition of use dating back to the fourth millennium BC in Mesopotamia, and is prized because of its sweet taste, nutritive value, and long shelf life. Today, dried fruit consumption is widespread. Nearly half of the dried fruits sold are raisins, followed by dates, prunes, figs, apricots, peaches, apples, and pears. These are referred to as "conventional" or "traditional" dried fruits: fruits that have been dried in the sun or in heated wind tunnel dryers. Many fruits such as cranberries, blueberries, cherries, strawberries, and mango are infused with a sweetener (e.g. sucrose syrup) prior to drying. Some products sold as dried fruit, like papaya, kiwifruit and pineapple, are most often candied fruit. Dried fruits retain most of the nutritional value of fresh fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla (genus), Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla (''Vanilla planifolia, V. planifolia''). Pollination is required to make the plants produce the fruit from which the vanilla spice is obtained. In 1837, Belgian botanist Charles François Antoine Morren discovered this fact and pioneered a method of artificially pollinating the plant. The method proved financially unworkable and was not deployed commercially. In 1841, Edmond Albius, a 12-year-old enslaved child who lived on the French island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean, discovered that the plant could be hand-pollination, hand-pollinated. Hand-pollination allowed global cultivation of the plant. Noted French botanist and plant collector Jean Michel Claude Richard falsely claimed to have discovered the technique three or four years earlier. By the end of the 20th century, Albius was considered the true discoverer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oak Barrels (wine)
Oak is used in winemaking to vary the color, flavor, tannin profile and texture of wine. It can be introduced in the form of a barrel during the fermentation or aging periods, or as free-floating chips or staves added to wine fermented in a vessel like stainless steel. Oak barrels can impart other qualities to wine through evaporation and low level exposure to oxygen.J. Robinson ''Jancis Robinson's Wine Course'' Third Edition pg 91-93 Abbeville Press 2003 History In early wine history, the amphora was the vessel of choice for the storage and transportation of wine. Due to the perishable nature of wood material it is difficult to trace the usage of barrels in history. The Greek historian Herodotus noted that ancient Mesopotamians used barrels made of palm wood to transport wine along the Euphrates. Palm is a difficult material to bend and fashion into barrels, however, and wine merchants in different regions experimented with different wood styles to find a better wood so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
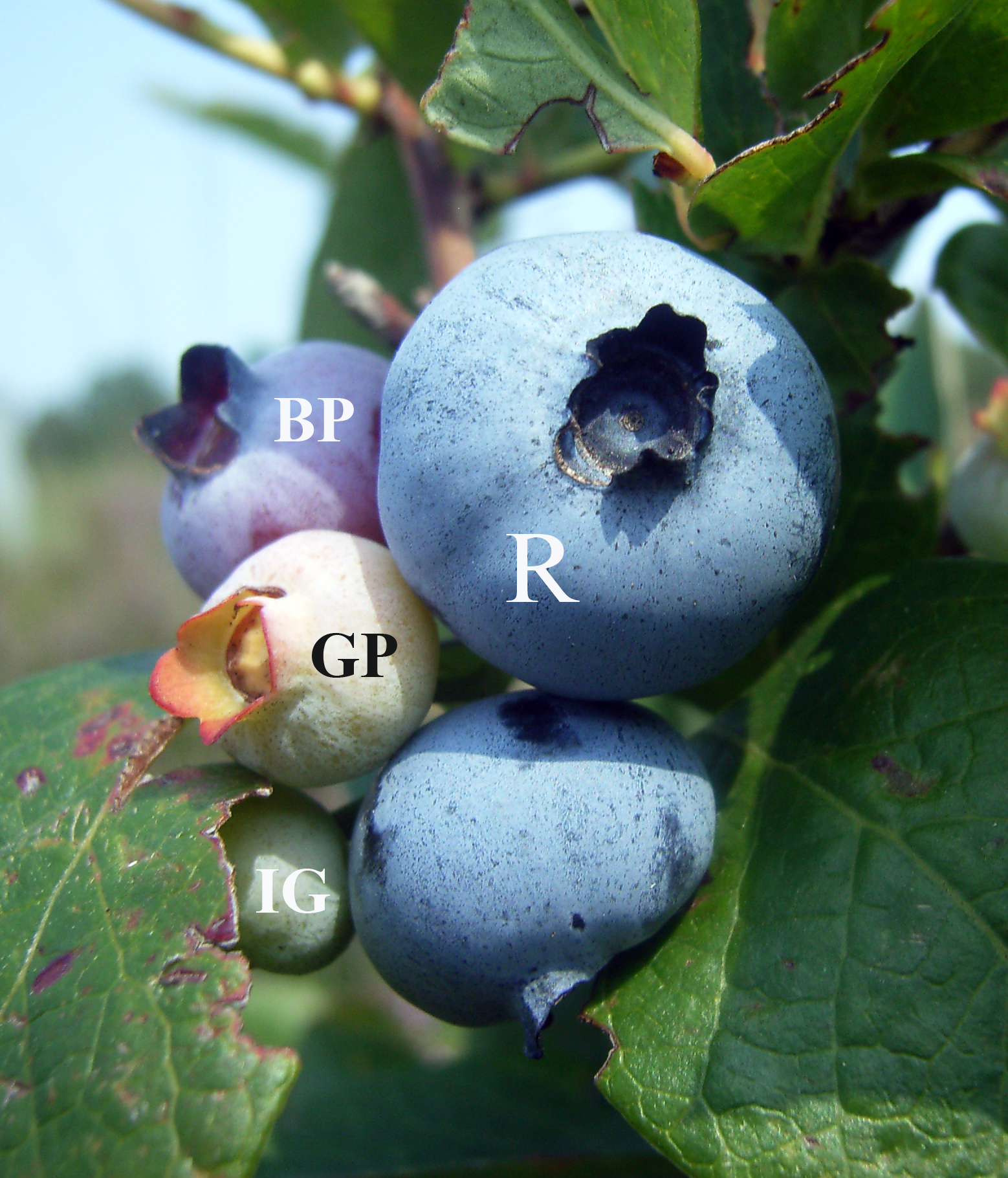
Blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus '' Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s. Blueberries are usually prostrate shrubs that can vary in size from to in height. In commercial production of blueberries, the species with small, pea-size berries growing on low-level bushes are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild"), while the species with larger berries growing on taller, cultivated bushes are known as "highbush blueberries". Canada is the leading producer of lowbush blueberries, while the United States produces some 40% of the world supply of highbush blueberries. Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raspberry
The raspberry is the edible fruit of a multitude of plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the rose family, most of which are in the subgenus '' Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Raspberries are perennial with woody stems. World production of raspberries in 2020 was 895,771 tonnes, led by Russia with 20% of the total. Description A raspberry is an aggregate fruit, developing from the numerous distinct carpels of a single flower. What distinguishes the raspberry from its blackberry relatives is whether or not the torus (receptacle or stem) "picks with" (i.e., stays with) the fruit. When picking a blackberry fruit, the torus stays with the fruit. With a raspberry, the torus remains on the plant, leaving a hollow core in the raspberry fruit. Raspberries are grown for the fresh fruit market and for commercial processing into individually quick frozen (IQF) fruit, purée, juice, or as dried fruit used in a variety of grocery products such as ras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackberries
The blackberry is an edible fruit produced by many species in the genus ''Rubus'' in the family Rosaceae, hybrids among these species within the subgenus ''Rubus'', and hybrids between the subgenera ''Rubus'' and ''Idaeobatus''. The taxonomy of blackberries has historically been confused because of hybridization and apomixis, so that species have often been grouped together and called species aggregates. For example, the entire subgenus ''Rubus'' has been called the ''Rubus fruticosus'' aggregate, although the species ''R. fruticosus'' is considered a synonym of '' R. plicatus''. '' Rubus armeniacus'' ("Himalayan" blackberry) is considered a noxious weed and invasive species in many regions of the Pacific Northwest of Canada and the United States, where it grows out of control in urban and suburban parks and woodlands. Description What distinguishes the blackberry from its raspberry relatives is whether or not the torus (receptacle or stem) "picks with" (i.e., stays with) th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherries
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit). Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour ''Prunus cerasus''. The name 'cherry' also refers to the cherry tree and its wood, and is sometimes applied to almonds and visually similar flowering trees in the genus ''Prunus'', as in "ornamental cherry" or "cherry blossom". Wild cherry may refer to any of the cherry species growing outside cultivation, although ''Prunus avium'' is often referred to specifically by the name "wild cherry" in the British Isles. Botany True cherries ''Prunus'' subg. ''Cerasus'' contains species that are typically called cherries. They are known as true cherries and distinguished by having a single winter bud per axil, by having the flowers in small corymbs or umbels of several together (occasionally solitary, e.g. ''P. serrula''; some species with short racemes, e.g. '' P. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aroma (wine)
The aromas of wine are more diverse than its flavours. The human tongue is limited to the primary tastes perceived by taste receptors on the tongue – sourness, bitterness, saltiness, sweetness and savouriness. The wide array of fruit, earthy, leathery, floral, herbal, mineral, and woodsy flavour present in wine are derived from aroma notes sensed by the olfactory bulb.J. Robinson (ed) ''"The Oxford Companion to Wine"'' Third Edition p. 683 Oxford University Press 2006 In wine tasting, wine is sometimes smelled before taking a sip in order to identify some components of the wine that may be present. Different terms are used to describe what is being smelled. The most basic term is aroma which generally refers to a "pleasant" smell as opposed to odour which refers to an unpleasant smell or possible wine fault. The term aroma may be further distinguished from bouquet which generally refers to the smells that arise from the chemical reactions of fermentation and aging of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piedmont (wine)
Piemonte wine is the range of Italian wines made in the region of Piedmont in the northwestern corner of Italy. The best-known wines from the region include Barolo and Barbaresco. They are made from the Nebbiolo grape. These wines are ideal for storage and a well-aged Barolo for instance may leave a feeling of drinking velvet because the tannins are polished and integrated more and more into the wine. As the wine matures the colour becomes more brownish and rust-red. Other popular grapes used for red wine production are Barbera and Dolcetto. Wine made with the Barbera grape is often fruity, with high acidity. It can be delicate with less tannin than wine made from the Nebbiolo grape. Dolcetto on the other side, is not, as the name indicates, sweet. Dolcetto means "little sweet one". (dolce is Italian for sweet). The grape gives fresh and dry red wines with some tannin. The wines made with the Dolcetto grape are typically consumed relatively young. The sparkling wine Asti s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DOCG
The following four classifications of wine constitute the Italian system of labelling and legally protecting Italian wine: * ''Denominazione di origine'' (DO, rarely used; ; English: “designation of origin”), * ''Indicazione geografica tipica'' (IGT; ; “indication of geographical typicality”), * ''Denominazione di origine controllata'' (DOC; ; “controlled designation of origin”), and * ''Denominazione di origine controllata e garantita'' (DOCG; ; “controlled and guaranteed designation of origin”). The system was introduced in 1963 shortly after the Treaty of Rome established Italy as a founding member of the European Economic Community, and was modelled on the extant French '' Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) laws. It was overhauled in 1992 to match new European Union law on Protected Designation of Origin, introducing the more general ''Denominazione di Origine Protetta'' (DOP) designation for foods and agricultural products, including wines. Furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)


