|
Banu Thabit
The Banu Thabit or Banu 'Ammar were a Berbers, Berber dynasty that ruled Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli in present-day Libya during the 14th century. The dynasty's founder, Thabit ibn 'Ammar, was a member of the Zakūğa tribe from the Hawwara, Huwwara tribal confederation. History After the collapse of Almohad Caliphate, Almohad rule in the Maghreb during the early 13th century, Tripoli came under the authority of the Hafsid dynasty, Hafsids of Tunis. Thabit ibn 'Ammar, took power in the city toward 1324. According to historian Jamil Abun-Nasr, he took power following a rebellion in the city that expelled the Hafsid prince, Ibn Abi 'Umran, whom the Hafsid caliph Abu Yahya Abu Bakr II had appointed there as governor. According to historian Dominique Valérian, Thabit came to power with the assassination of Sa'id ibn Ṭahir al-Mazughi, the city's previous ruler. Thabit was murdered six months later by Sa'id's son, Ahmad, before the latter was assassinated in turn by the Banu Thabit famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Tripoli (1350) As Reported By The "Book Of All Kingdoms"
A flag is a piece of textile, fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the Maritime flag, maritime environment, where Flag semaphore, semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as "vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Yahya Abu Bakr II
Abu Yahya Abu Bakr II ( ; died 19 October 1346) was the Hafsid caliph of Ifriqiya from 1318 to 1346. He was the son of Abu-Zakariyya Yahya III, emir of Béjaïa and grandson of Abu Ishaq Ibrahim I. Under his rule the former unity of the Hafsid domains was restored. Rise to power After 1309 his brother Abu-l-Baqa Khalid An-Nasr came to power in Tunis and made him governor of Constantine. Shortly after this he revolted. In 1311 his brother was overthrown and Abu-Yahya Abu-Bakr seized the opportunity to take Bejaïa in 1312 with the new ruler of Tunis, Abd al-Wahid Zakariya ibn al-Lihyani, powerless to respond. In 1315 or 1316 the attacks on Tunis began; in 1317 al-Lihyaní fled the country and abdicated in favor of his son Abu-Darba Muhammad who resisted for another nine months, but in early 1318 Abu-Yahya Abu-Bakr II made his entrance into the capital. Early challenges The earlier part of his reign was largely devoted to suppressing rebellions. Abu-Darba tried to encourage rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berber Dynasties
Berber or Berbers may refer to: Ethnic group * Berbers Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connec ..., an ethnic group native to Northern Africa * Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages Places * Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile People with the surname * Ady Berber (1913–1966), Austrian film actor * Alejandro Berber (born 1987), Mexican footballer * Anita Berber (1899–1928), German dancer, actress, and writer * Fatiha Berber (1945–2015), Algerian actress * Felix Berber (1871–1930), German violinist * Fritz Berber (1898–1984), member of the Nazi administration in Germany until 1943 * Kübra Berber (born 1996), Turkish women's footballer * Mersad Berber (1940–2012), Bosnian painter * Oğuzhan Berber (born 1992), Turkish footballer * Philip Berber (born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Faris Abd Al-Aziz II
Abu Faris Abd al-Aziz II () (reigned 1394–1434) was a Hafsid Caliph of Ifriqiya. Life He proceeded to further consolidate the kingdom after his father Abu al-Abbas Ahmad II had restored its integrity. A strong monarch and an orthodox Muslim he abolished some taxes he deemed incompatible with the teachings of Qur'an, using instead privateer actions against Christian shipping as a way to raise state income. He intervened against his western neighbors, the Zayyanid dynasty of the Kingdom of Tlemcen, and in Andalusia Andalusia ( , ; , ) is the southernmost autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Peninsular Spain, located in the south of the Iberian Peninsula, in southwestern Europe. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomou ... as well. References * Year of birth unknown 1434 deaths 14th-century Hafsid caliphs 15th-century Hafsid caliphs {{Africa-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin I Of Sicily
Martin I of Sicily (c. 1374/1376 – 25 July 1409), called the Younger, was King of Sicily from his marriage to Maria, Queen of Sicily, Queen Maria in 1390 until his death in 1409. Martin's father was the future King Martin I of Aragon, and his grandparents were King Peter IV of Aragon and Eleanor of Sicily. In February 1390 he married Maria of Sicily, born in 1362/1363. In 1392 he returned with Maria to Sicily with a military force and defeated a group of opposing barons. In 1394 the couple had their only son Peter of Aragon, Heir of Sicily, Peter, crown prince of Sicily, who died in 1400. He ruled Sicily jointly with Maria until her death at Lentini on 25 May 1401. At that time, he repudiated the Treaty of Villeneuve (1372) and ruled Sicily alone. After his death in 1409 in Cagliari, Sardinia, his father, by then king of Aragon, ruled Sicily as Martin II. After Maria's death Martin I the Younger married at Catania on 21 May 1402 by proxy and on 26 December 1402 in person Blan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was a successor state of the County of Sicily, which had been founded in 1071 during the Norman conquest of southern Italy, Norman conquest of the southern peninsula. The island was divided into Three valli of Sicily, three regions: Val di Mazara, Val Demone and Val di Noto. After a brief rule by Charles of Anjou, a revolt in 1282 known as the Sicilian Vespers threw off Capetian House of Anjou, Angevin rule in the island of Sicily. The Angevins managed to maintain control in the mainland part of the kingdom, which became a separate entity also styled ''Kingdom of Sicily'', although it is retroactively referred to as the Kingdom of Naples. Sicily (officially known as the Kingdom of Trinacria between 1282 and 1442) at the other hand, remained a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
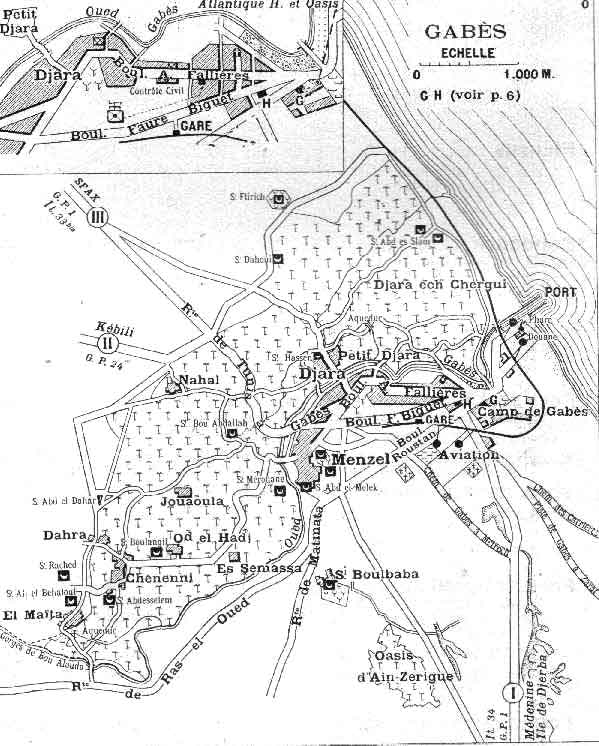
Gabès
Gabès (, ; ), also spelled Cabès, Cabes, and Kabes, is the capital of the Gabès Governorate in Tunisia. Situated on the coast of the Gulf of Gabès, the city has a population of 167,863, making it the 6th largest city in Tunisia. Located 327 km southeast of Tunis and 113 km from Sfax, Gabès lies at the delta of the Wadi Qabis, which originates 10 kilometers upstream at Ras El Oued, Algeria, Ras al-Oued and serves as its primary water source. Historically, the town was a Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian settlement known as Tacapae before falling under Roman Empire, Roman control. It was later ruined during the 7th-century Arab invasion but was recovered by Sidi Boulbaba, a revered companion of the Muhammad, Prophet Muhammad and a patron of the town. Although it experienced decline under the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, Gabès saw significant growth under French rule from 1881 to 1955, with the development of key infrastructure, including a railway, road network, and port. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Makki
Banu Makki was a Muslim dynasty that ruled over Gabès from 1282 until 1394. History The Banu Makki were one of the notable families in Gabès during the rule of the Hafsids in Ifriqiya (the region around modern-day Tunisia). While the Hafsids appointed governors to the main cities of their provinces, powerful local families often exercised great influence. In the case of the Banu Makki, they were able to get one of their own members to be appointed as governor in Gabès. At their height, sometime the early 14th century, their domain extended from Gabès to Tripoli and the nearby Jabal Nafusa (in present-day Libya). By the mid-1350s, they had extended their control to both Tripoli and Sfax. During the second half of the 14th century they had formed an effectively independent state in this region. The region was only brought back under direct Hafsid control during the reign of Abu al-Abbas Ahmad II (), who progressively reasserted Hafsid authority across former territories. See al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in both the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Black Sea. Between the 16th and 17th centuries, it was one of the major financial centres of Europe. Throughout its history, the Genoese Republic established Genoese colonies, numerous colonies throughout the Mediterranean and the Black Sea, including Corsica from 1347 to 1768, Monaco, Gazaria (Genoese colonies), Southern Crimea from 1266 to 1475, and the islands of Lesbos and Chios from the 14th century to 1462 and 1566, respectively. With the arrival of the early modern period, the Republic had lost many of its colonies, and shifted its focus to banking. This was successful for Genoa, which remained a hub of capitalism, with highly developed banks and trading companies. Genoa was known as ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunis
Tunis (, ') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Tunisia. The greater metropolitan area of Tunis, often referred to as "Grand Tunis", has about 2,700,000 inhabitants. , it is the third-largest city in the Maghreb region (after Casablanca and Algiers) and the List of largest cities in the Arab world, eleventh-largest in the Arab world. Situated on the Gulf of Tunis, behind the Lake of Tunis and the port of La Goulette (Ḥalq il-Wād), the city extends along the coastal plain and the hills that surround it. At its core lies the Medina of Tunis, Medina, a World Heritage Site. East of the Medina, through the Sea Gate (also known as the ''Bab el Bhar'' and the ''Porte de France''), begins the modern part of the city called "Ville Nouvelle", traversed by the grand Avenue Habib Bourguiba (often referred to by media and travel guides as "the Tunisian Champs-Élysées"), where the colonial-era buildings provide a clear contrast to smaller, older structures. Further east by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berbers
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connections are identified by their usage of Berber languages, most of them mutually unintelligible, which are part of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They are indigenous peoples, indigenous to the Maghreb region of North Africa, where they live in scattered communities across parts of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and to a lesser extent Tunisia, Mauritania, northern Mali and northern Niger. Smaller Berber communities are also found in Burkina Faso and Egypt's Siwa Oasis. Descended from Stone Age tribes of North Africa, accounts of the Imazighen were first mentioned in Egyptian hieroglyphs, Ancient Egyptian writings. From about 2000 BC, Berber languages spread westward from the Nile, Nile Valley across the northern Sahara int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hafsid Dynasty
The Hafsid dynasty ( ) was a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Berbers, Berber descentC. Magbaily Fyle, ''Introduction to the History of African Civilization: Precolonial Africa'', (University Press of America, 1999), 84. that ruled Ifriqiya (modern day Tunisia, western Libya, and eastern Algeria) from 1229 to 1574. The dynasty was founded by Abu Zakariya Yahya, who was initially appointed governor of the region by the Almohad caliph before declaring his independence. Under the reigns of Abu Zakariya and his successor, Muhammad I al-Mustansir, al-Mustansir (), the Hafsids consolidated and expanded their power, with Tunis as their capital. After al-Mustansir's death, internal conflicts resulted in a division between an eastern branch of the dynasty ruling from Tunis and a Hafsids of Béjaïa, western branch ruling from Béjaïa and Constantine, Algeria, Consantine. A reunification took place under Abu Yahya Abu Bakr II (), but his death was followed by another crisis during which the Marinid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |