|
Bangstad Syndrome
Bangstad syndrome is a severe, inherited congenital disorder associated with abnormalities of the cell membrane. It was characterized in 1989. Presentation Presenting at birth, features of the disorder include moderately severe IUGR, microcephaly, craniosynostosis, moderately severe post uterine growth retardation, deafness, deep set eyes, cryptorchidism, truncal obesity and acanthosis nigricans, small teeth, prognathism, dislocated radial heads without generalized skeletal dysplasia, however, tall vertebrae, moderate mental retardation, hypothyroidism, insulin resistance, hypoparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism is decreased function of the parathyroid glands with underproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH). This can lead to low levels of calcium in the blood, often causing cramping and twitching of muscles or tetany (involuntary m .... Diagnosis Treatment References External links Congenital disorders Genetic disorders with OMIM but no gene Syndromes affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUGR
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's birth weight percentile. The causes of IUGR are broad and may involve maternal, fetal, or placental complications. At least 60% of the 4 million neonatal deaths that occur worldwide every year are associated with low birth weight (LBW), caused by intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), preterm delivery, and genetic abnormalities, demonstrating that under-nutrition is already a leading health problem at birth. Intrauterine growth restriction can result in a baby being small for gestational age (SGA), which is most commonly defined as a weight below the 10th percentile for the gestational age. At the end of pregnancy, it can result in a low birth weight. Types There are two major categories of IUGR: pseudo IUGR and true IUGR With pseu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcephaly
Microcephaly (from New Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it may develop in the first few years of life. Since brain growth is correlated with head growth, people with this disorder often have an intellectual disability, poor motor function, poor speech, abnormal facial features, seizures and dwarfism. The disorder is caused by a disruption to the genetic processes that form the brain early in pregnancy, though the cause is not identified in most cases. Many genetic syndromes can result in microcephaly, including chromosomal and single-gene conditions, though almost always in combination with other symptoms. Mutations that result solely in microcephaly (primary microcephaly) exist but are less common. External toxins to the embryo, such as alcohol during pregnancy or vertically transmitted infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
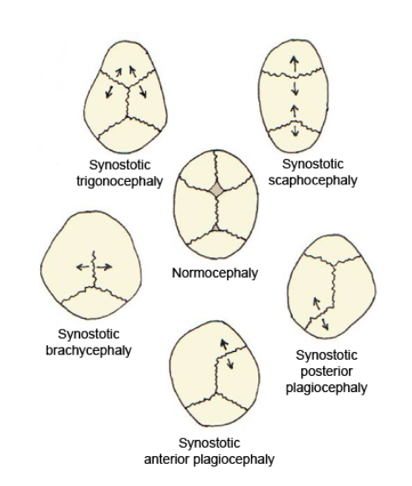
Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in a young infant's skull prematurely fuses by turning into bone (ossification), thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull. Because the skull cannot expand perpendicular to the fused suture, it compensates by growing more in the direction parallel to the closed sutures. Sometimes the resulting growth pattern provides the necessary space for the growing brain, but results in an abnormal head shape and abnormal facial features. In cases in which the compensation does not effectively provide enough space for the growing brain, craniosynostosis results in increased intracranial pressure leading possibly to visual impairment, sleeping impairment, eating difficulties, or an impairment of mental development combined with a significant reduction in IQ. Craniosynostosis occurs in one in 2000 births. Craniosynostosis is part of a syndrome in 15% to 40% of affected patients, but it usually occurs as an isol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Uterine Growth Retardation
Post or POST commonly refers to: *Mail, the postal system, especially in Commonwealth of Nations countries **An Post, the Irish national postal service **Canada Post, Canadian postal service **Deutsche Post, German postal service **Iraqi Post, Iraqi postal service **Russian Post, Russian postal service **Hotel post, a service formerly offered by remote Swiss hotels for the carriage of mail to the nearest official post office **United States Postal Service or USPS **Parcel post, a postal service for mail that is heavier than ordinary letters *Post, a job or occupation Post, POST, or posting may also refer to: Architecture and structures *Lamppost, a raised source of light on the edge of a road *Post (structural), timber framing *Post and lintel, a building system * Steel fence post *Trading post *Utility pole or utility post Military *Military base, an assigned station or a guard post **Outpost (military), a military outpost **Guardpost, or guardhouse Geography *Post, Iran, a vil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptorchidism
Cryptorchidism, also known as undescended testis, is the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum. The word is from Greek () 'hidden' and () 'testicle'. It is the most common birth defect of the male genital tract. About 3% of full-term and 30% of premature infant boys are born with at least one undescended testis. However, about 80% of cryptorchid testes descend by the first year of life (the majority within three months), making the true incidence of cryptorchidism around 1% overall. Cryptorchidism may develop after infancy, sometimes as late as young adulthood, but that is exceptional. Cryptorchidism is distinct from monorchism, the condition of having only one testicle. Though the condition may occur on one or both sides, it more commonly affects the right testis. A testis absent from the normal scrotal position may be: # Anywhere along the "path of descent" from high in the posterior (retroperitoneal) abdomen, just below the kidney, to the inguinal ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truncal Obesity
Abdominal obesity, also known as central obesity and truncal obesity, is a condition when excessive visceral fat around the stomach and abdomen has built up to the extent that it is likely to have a negative impact on health. Abdominal obesity has been strongly linked to cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer's disease, and other metabolic and vascular diseases. Visceral and central abdominal fat and waist circumference show a strong association with type 2 diabetes. Visceral fat, also known as organ fat or ''intra-abdominal fat'', is located inside the peritoneal cavity, packed in between internal organs and torso, as opposed to subcutaneous fat, which is found underneath the skin, and intramuscular fat, which is found interspersed in skeletal muscle. Visceral fat is composed of several adipose depots including mesenteric, epididymal white adipose tissue (EWAT), and perirenal fat. An excess of adipose visceral fat is known as central obesity, the "pot belly" or "beer belly" effect, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthosis Nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans is a medical sign characterised by brown-to-black, poorly defined, velvety hyperpigmentation of the skin. It is usually found in body folds, such as the posterior and lateral folds of the neck, the armpits, groin, navel, forehead and other areas. It is associated with endocrine dysfunction, especially insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia, as seen in diabetes mellitus. This activates the insulin-like growth factor receptors, which leads to proliferation of keratinocytes, fibroblasts and other cells in the skin. Activation of other growth factor receptors such as fibroblast growth factor receptors or epidermal growth factor receptor can also be responsible. Signs and symptoms Acanthosis nigricans may present with thickened, velvety, relatively darker areas of skin on the neck, armpit and in skin folds. Causes It typically occurs in individuals younger than age 40, is associated with insulin resistance, Type 2 diabetes, obesity or endocrinopathies, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prognathism
Prognathism, also called Habsburg jaw or Habsburgs' jaw primarily in the context of its prevalence amongst members of the House of Habsburg, is a positional relationship of the mandible or maxilla to the skeletal base where either of the jaws protrudes beyond a predetermined imaginary line in the coronal plane of the skull. In general dentistry, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and orthodontics, this is assessed clinically or radiographically ( cephalometrics). The word ''prognathism'' derives from Greek πρό (''pro'', meaning 'forward') and γνάθος (''gnáthos'', 'jaw'). One or more types of prognathism can result in the common condition of malocclusion, in which an individual's top teeth and lower teeth do not align properly. Presentation Prognathism in humans can occur due to normal variation among phenotypes. In human populations where prognathism is not the norm, it may be a malformation, the result of injury, a disease state or a hereditary condition. Prognathism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
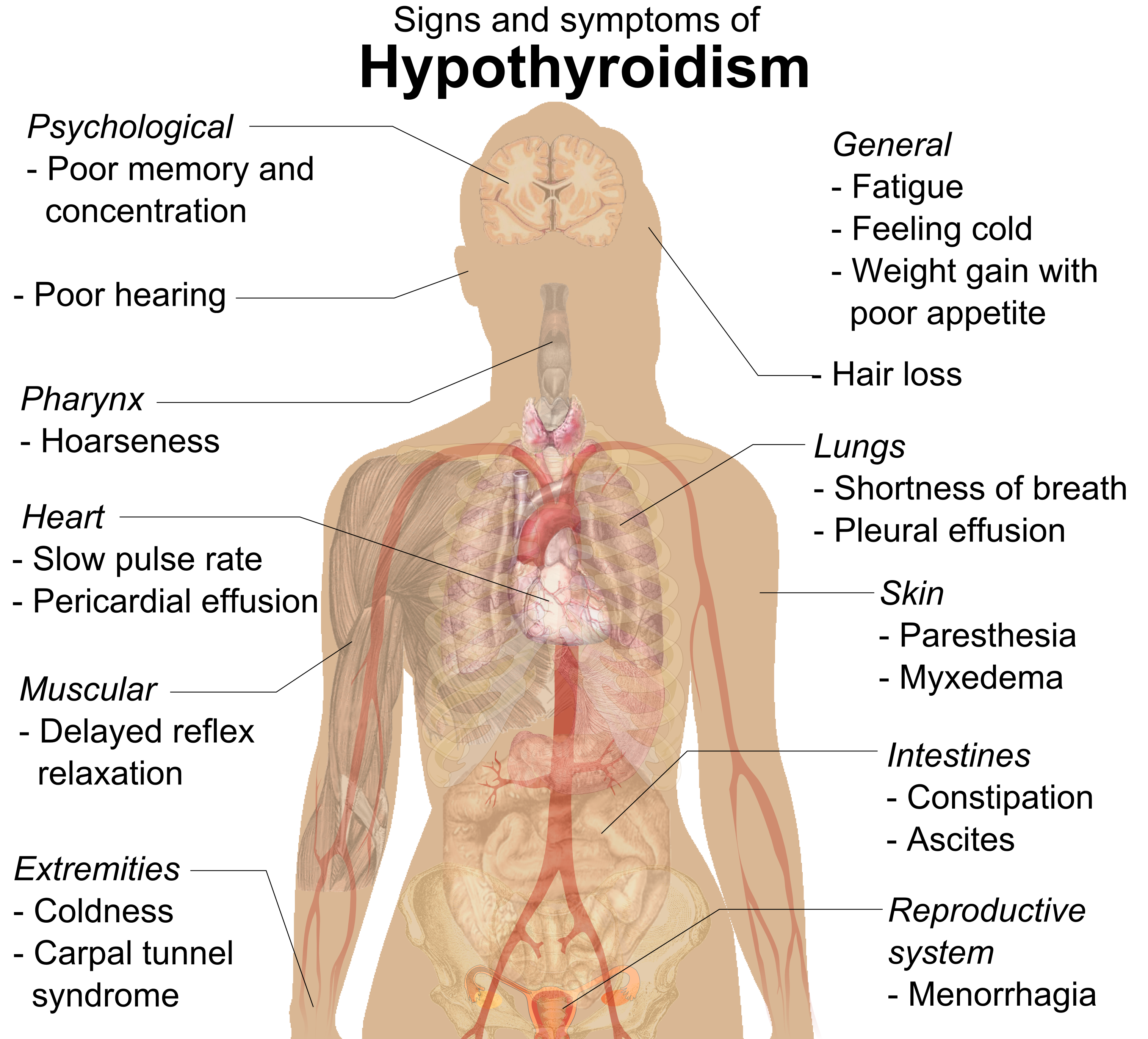
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus or the anterior pituitary gland, certain medications, a lack of a functioning thyroid at bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cell (biology), cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood sugar). Insulin is released by the pancreas in response to carbohydrates consumed in the diet. In states of insulin resistance, the same amount of insulin does not have the same effect on glucose transport and blood sugar levels. There are many causes of insulin resistance and the underlying process is still not completely understood, but sulfate depletion may be the important factor. Risk factors for insulin resistance include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, various health conditions, and certain medications. Insulin resistance is considered a component of the metabolic syndrome. There are multiple ways to measure insulin resistance such as fasting insulin levels or glucose tolerance tests, but these are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |