|
Banded Demoiselle
The banded demoiselle (''Calopteryx splendens'') is a species of damselfly belonging to the family Calopterygidae. It is often found along slow-flowing streams and rivers. It is a Eurasian species occurring from the Atlantic coast eastwards to Lake Baikal and northwestern China. This is a common species throughout much of its range. Description This is a large damselfly with a total length of up to and a hindwing length of up to . Male and female are variable in color and pattern. The male has translucent wings which each have a broad, dark iridescent blue-black spot (or band) across the outer part. On immature individuals the spot is dark brown. The body can be a metallic blue or bluish green or a combination of both colours, depending on the time of year and location. The dark wing patch of the male starts at the nodus (the slight dip midway down the upper edge of the wing) but can reach up to the wing-tip in southern races. In the very similar beautiful demoiselle ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
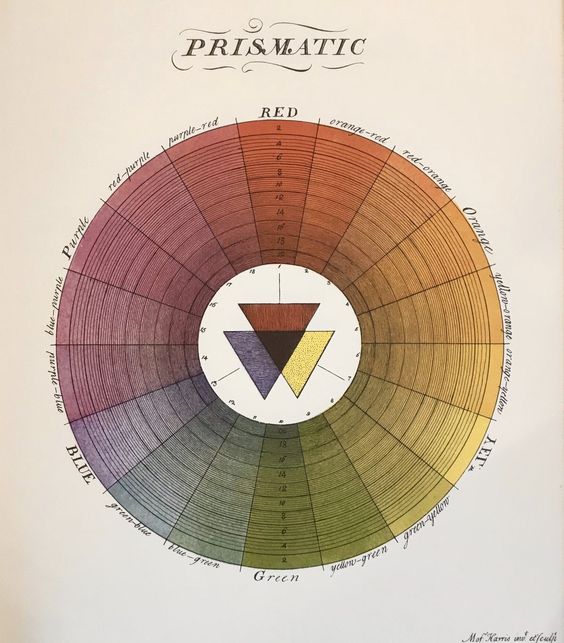
Moses Harris
Moses Harris (15 April 1730 – 1787) was an English entomologist and engraver. Life and work Harris was encouraged in entomology from a young age by his uncle, a member of the Society of the Aurelians. In 1762 he became secretary of a second Society of Aurelians. He was a skilled artist, displaying some of his insect drawings at the Royal Academy in 1785. He drew and engraved illustrations for books including Dru Drury's ''Illustrations of Natural History'' (3 volumes, 1770–1782) and John Coakley Lettsom's ''The Naturalist's and Traveller's Companion'' (1772). Colour theory In "The Natural System of Colours" published in 1766, Harris discussed the multitude of colours that can be created using three "grand or principle" colours: red, yellow and blue. As a naturalist and an engraver, Harris focussed on the relationships between colours and how they are coded and created. He explained how three colours can be íntermixed, tinted and shaded to create 660 colours "materially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Territory (animal)
In ethology, territory is the sociographical area that an animal consistently defends against conspecific competition (or, occasionally, against animals of other species) using agonistic behaviors or (less commonly) real physical aggression. Animals that actively defend territories in this way are referred to as being territorial or displaying territorialism. Territoriality is only shown by a minority of species. More commonly, an individual or a group of animals occupies an area that it habitually uses but does not necessarily defend; this is called its home range. The home ranges of different groups of animals often overlap, and in these overlap areas the groups tend to avoid each other rather than seeking to confront and expel each other. Within the home range there may be a ''core area'' that no other individual group uses, but, again, this is as a result of avoidance. Function The ultimate function of animals inhabiting and defending a territory is to increase the indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insects Described In 1780
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; In: potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within. Nearly all insects hatch from eggs. Insect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damselflies Of Europe
Damselflies are flying insects of the suborder Zygoptera in the order Odonata. They are similar to dragonflies, which constitute the other odonatan suborder, Anisoptera, but are smaller and have slimmer bodies. Most species fold the wings along the body when at rest, unlike dragonflies which hold the wings flat and away from the body. An ancient group, damselflies have existed since at least the Lower Permian, and are found on every continent except Antarctica. All damselflies are predatory insects; both nymphs and adults actively hunt and eat other insects. The nymphs are aquatic, with different species living in a variety of freshwater habitats including acidic bogs, ponds, lakes and rivers. The nymphs moult repeatedly, at the last moult climbing out of the water to undergo metamorphosis. The skin splits down the back, they emerge and inflate their wings and abdomen to gain their adult form. Their presence on a body of water indicates that it is relatively unpolluted, but their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odonata Of Asia
Odonata is an order of flying insects that includes the dragonflies and damselflies. Members of the group first appeared during the Triassic, though members of their total group, Odonatoptera, first appeared in Late Carboniferous. The two common groups are distinguished with dragonflies, placed in the suborder Epiprocta, usually being larger, with eyes together and wings up or out at rest, while damselflies, suborder Zygoptera, are usually smaller with eyes placed apart and wings along body at rest. All Odonata have aquatic larvae called naiads (nymphs), and all of them, larvae and adults, are carnivorous. The adults can land, but rarely walk. Their legs are specialised for catching prey. They are almost entirely insectivorous. Etymology and terminology Fabricius coined the term ''Odonata'' in 1793 from the Ancient Greek ( Ionic form of ) 'tooth'. One hypothesis is that it was because their maxillae are notably toothed. Most insects also have toothed mandibles. The wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The British Dragonfly Society
The ''Journal of the British Dragonfly Society'' is a scientific journal published twice-yearly by the British Dragonfly Society since 1983. It contains material relevant to Odonata recorded from the United Kingdom. The editor-in-chief is P. J. Mill. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in ''The Zoological Record''. Further reading * Merritt, R., 1987. The origins and early history of the British Dragonfly Society. ''Journal of the British Dragonfly Society'' 3: 21–37. * Corbet, P.S., 1993. The first ten years of the British Dragonfly Society. ''Journal of the British Dragonfly Society'' 9: 25–37. References External links * {{Official website, http://www.british-dragonflies.org.uk/content/journal-0 Entomology journals and magazines Publications established in 1983 Biannual journals English-language journals 1983 establishments in the United Kingdom Academic journals published by learned and professional societies of the United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Scots replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands. The term is also used for the area north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault, although the exact boundaries are not clearly defined, particularly to the east. The Great Glen divides the Grampian Mountains to the southeast from the Northwest Highlands. The Scottish Gaelic name of ' literally means "the place of the Gaels" and traditionally, from a Gaelic-speaking point of view, includes both the Western Isles and the Highlands. The area is very sparsely populated, with many mountain ranges dominating the region, and includes the highest mountain in the British Isles, Ben Nevis. During the 18th and early 19th centuries the population of the Highlands rose to around 300,000, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, and over six thousand smaller islands."British Isles", ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. They have a total area of and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland (which covers roughly five-sixths of Ireland), and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Channel Islands, off the north coast of France, are normally taken to be part of the British Isles, even though they do not form part of the archipelago. The oldest rocks are 2.7 billion years old and are found in Ireland, Wales and the northwest of Scotland. During the Silurian period, the north-western regions collided with the south-east, which had been part of a separate continental landmass. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest, and claims a border with Albania through the Political status of Kosovo, disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia without Kosovo has about 6.7 million inhabitants, about 8.4 million if Kosvo is included. Its capital Belgrade is also the List of cities in Serbia, largest city. Continuously inhabited since the Paleolithic Age, the territory of modern-day Serbia faced Slavs#Migrations, Slavic migrations in the 6th century, establishing several regional Principality of Serbia (early medieval), states in the early Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
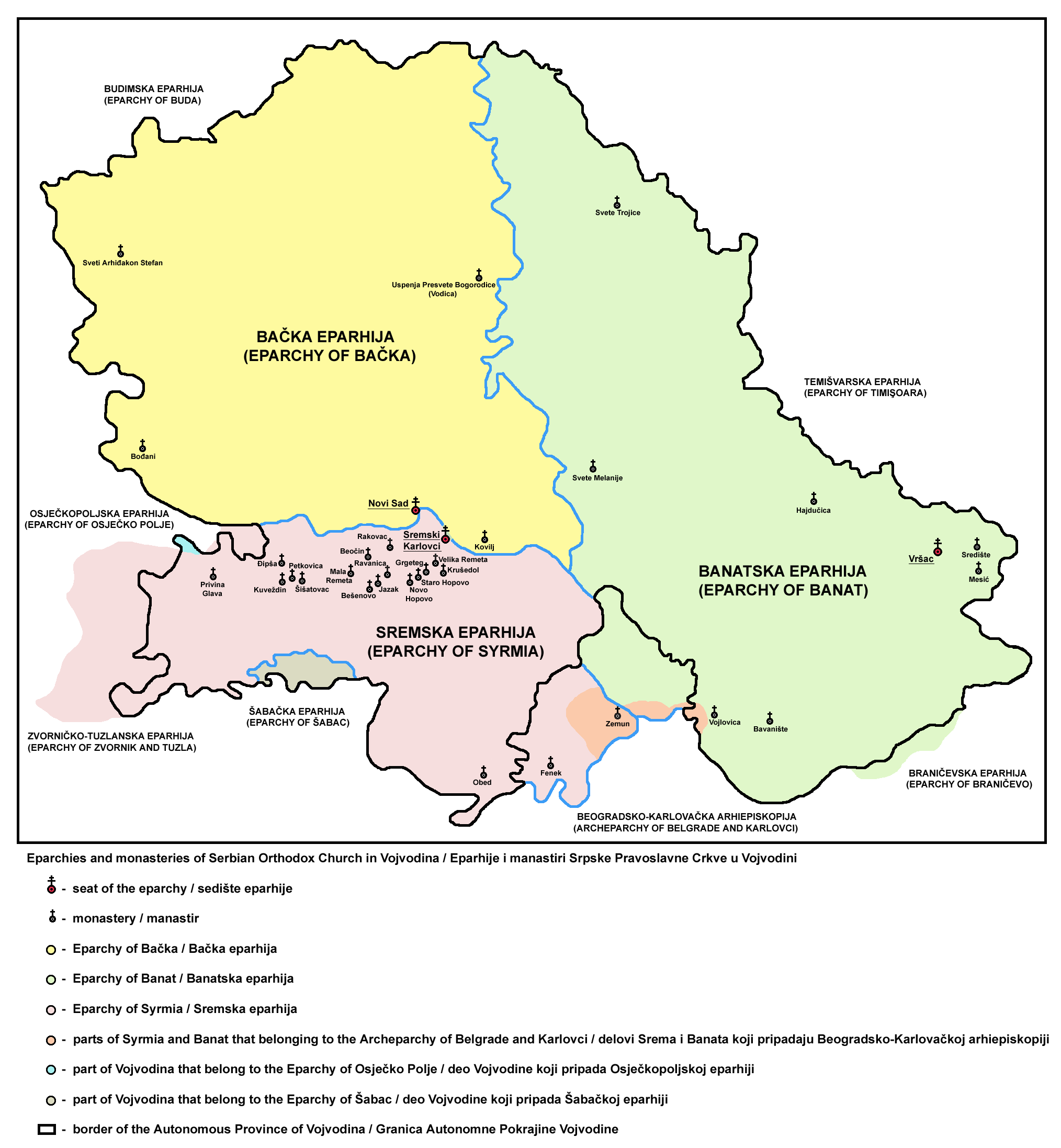
Fruška Gora
Fruška gora ( sr-Cyrl, Фрушка гора; hu, Tarcal-hegység) is a mountain in Syrmia, administratively part of Serbia with a part of its western side extending into eastern Croatia. The area under Serbian administration forms the country's oldest national park. Sometimes also referred to as the ''Jewel of Serbia'', due to its largely pristine landscape and protection effort, or the ''Serbian Mount Athos'', being the home of a large number of historical Serbian Orthodox monasteries. Name In Serbian, it is known as ''Fruška gora'' (, Фрушка гора), in Hungarian as ''Tarcal'' (also ''Almus-hegy'' or ''Árpatarló''), in German as ''Frankenwald'', and in Latin as ''Alma Mons''. In Medieval Greek, it was known as ''Frangochoria''. The mountain's name originates in the old Serbian word ''"Fruzi"'' derived from the singular form ''"Frug"''; and its adjective is ''Fruški'', used for naming the Frankish people. The name of ''"Fruška Gora"'' is ''"Frankish mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zyuratkul' National Park
Zyuratkul National Park (russian: Зюраткуль (национальный парк)) is a Russian national park established in 1993 in the southern part of Satkinsky Raion (Chelyabinsk Oblast, Urals). The park lies about 30 km south of Satka and 200 km west of Chelyabinsk. Description Notable features include Zyuratkul lake, a rare mountainous body of water for the Urals 754 m above sea level, with a surface area of 13,2 km2 and a maximum depth of 8 m. Water is slightly mineralised (≈50 mg/L). Because of its clear water and spectacular landscape around, Zyuratkul' is often called "Ural Ritsa". Also remarkable is a number of mountain ranges, among them Zyuratkul' range (8 km in length, rising 1175 m in its highest point). Another range, Nurgush, is the highest point of Chelyabinsk Oblast with a height of 1406 m. See also * Southern Ural * Zyuratkul Geoglyph The Russian geoglyph refers to a geoglyph on slopes of the Zyuratkul Mountains in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
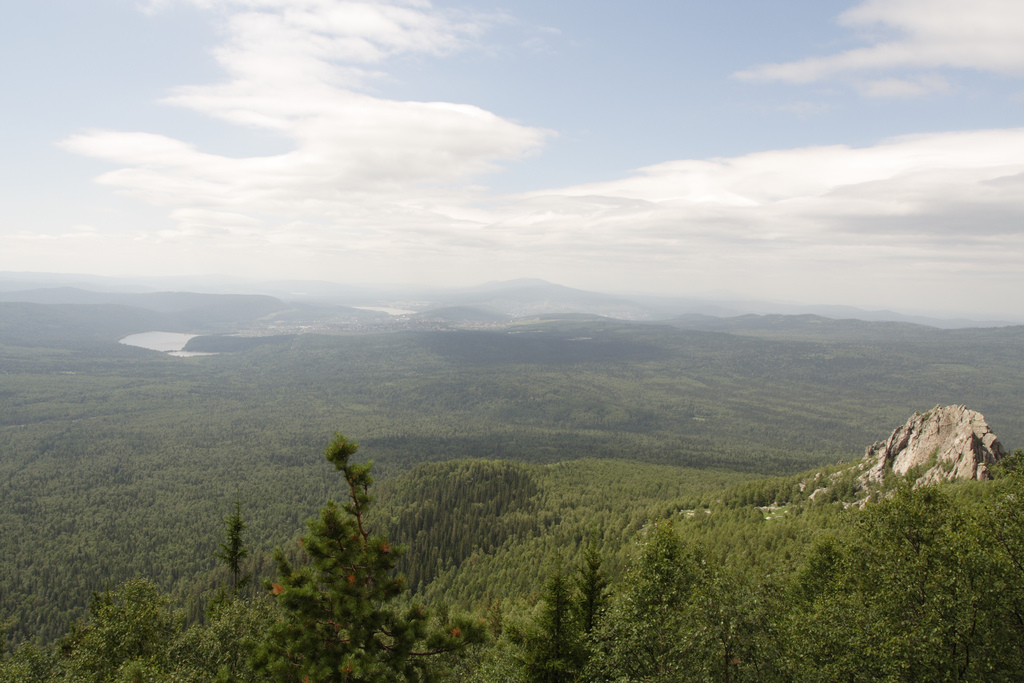
Taganay
Taganay (russian: Таганай, ba, Тағанай) is a group of mountain ridges in the Southern Urals, on the territory of Chelyabinsk Oblast, with the highest point rising 1178 m. above sea level. Taganay National Park was established in 1991, with its south-western border reaching down to the outskirts of Zlatoust Zlatoust ( rus, Златоуст, p=zlətɐˈust) is a city in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Ay River (in the Kama basin), west of Chelyabinsk. Population: 181,000 (1971); 161,000 (1959); 99,000 (1939); 48,000 (1926); 21,000 (19 .... Total area of the park is about , with the distance of from north to south and width of about . The vast majority of the park is covered with forests of Siberian spruce, pine, larch, aspen, willow, lime and alder. Over 750 species of plants have been recorded, some of which are listed in the Red Book. This is also home to many animal species, wolves, lynxes, brown bears, martens, moose and otters. The park is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |