|
Baltimore Railroad Strike Of 1877
The Baltimore railroad strike of 1877 involved several days of work stoppage and violence in Baltimore, Maryland, in 1877. It formed a part of the Great Railroad Strike of 1877, during which widespread civil unrest spread nationwide following the global depression and economic downturns of the mid-1870s. Strikes broke out along the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) on July 16, the same day that 10% wage reductions were scheduled. Violence erupted in Baltimore on July 20, with police and soldiers of the Maryland National Guard clashing with crowds of thousands gathered throughout the city. In response, President Rutherford B. Hayes ordered federal troops to Baltimore, local officials recruited 500 additional police, and two new national guard regiments were formed. Peace was restored on July 22. Between 10 and 22 were killed, more than 150 were injured, and many more were arrested. Negotiations between strikers and the B&O were unsuccessful, and most strikers quit rather than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Railroad Strike Of 1877
The Great Railroad Strike of 1877, sometimes referred to as the Great Upheaval, began on July 14 in Martinsburg, West Virginia, after the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) cut wages for the third time in a year. This strike finally ended 52 days later, after it was put down by unofficial militias, the National Guard, and federal troops. Because of economic problems and pressure on wages by the railroads, workers in numerous other cities, in New York, Pennsylvania and Maryland, into Illinois and Missouri, also went out on strike. An estimated 100 people were killed in the unrest across the country. In Martinsburg, Pittsburgh, Philadelphia and other cities, workers burned down and destroyed both physical facilities and the rolling stock of the railroads—engines and railroad cars. Local populations feared that workers were rising in revolution such as the Paris Commune of 1871. At the time, the workers were not represented by trade unions. The city and state governments were ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking ages, and there is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is most famous as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chapel, Cavendish Laboratory, and the Cambridge University Library, one of the largest legal deposit libraries in the world. The city's skyline is dominated by several college buildings, along with the spire of the Our Lady and the English Martyrs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits (such as holiday, health care, and retirement), improving working conditions, improving safety standards, establishing complaint procedures, developing rules governing status of employees (rules governing promotions, just-cause conditions for termination) and protecting the integrity of their trade through the increased bargaining power wielded by solidarity among workers. Trade unions typically fund their head office and legal team functions through regularly imposed fees called ''union dues''. The delegate staff of the trade union representation in the workforce are usually made up of workplace volunteers who are often appointed by members in democratic elections. The trade union, through an elected leadership and bargaining committee, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railroad Car
A railroad car, railcar (American and Canadian English), railway wagon, railway carriage, railway truck, railwagon, railcarriage or railtruck (British English and UIC), also called a train car, train wagon, train carriage or train truck, is a vehicle used for the carrying of cargo or passengers on a rail transport system (a railroad/railway). Such cars, when coupled together and hauled by one or more locomotives, form a train. Alternatively, some passenger cars are self-propelled in which case they may be either single railcars or make up multiple units. The term "car" is commonly used by itself in American English when a rail context is implicit. Indian English sometimes uses "bogie" in the same manner, though the term has other meanings in other variants of English. In American English, "railcar" is a generic term for a railway vehicle; in other countries "railcar" refers specifically to a self-propelled, powered, railway vehicle. Although some cars exist for the railroa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
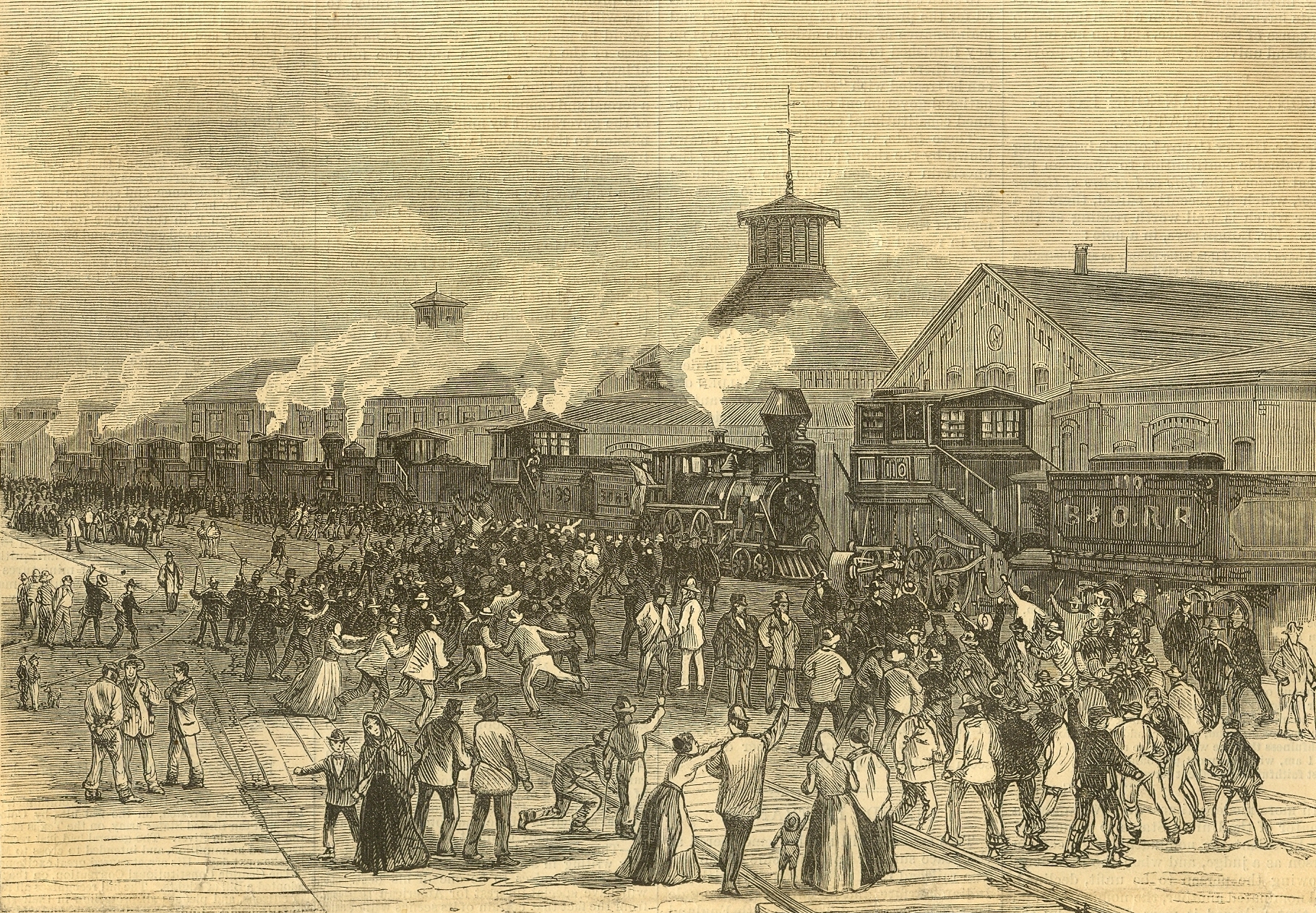
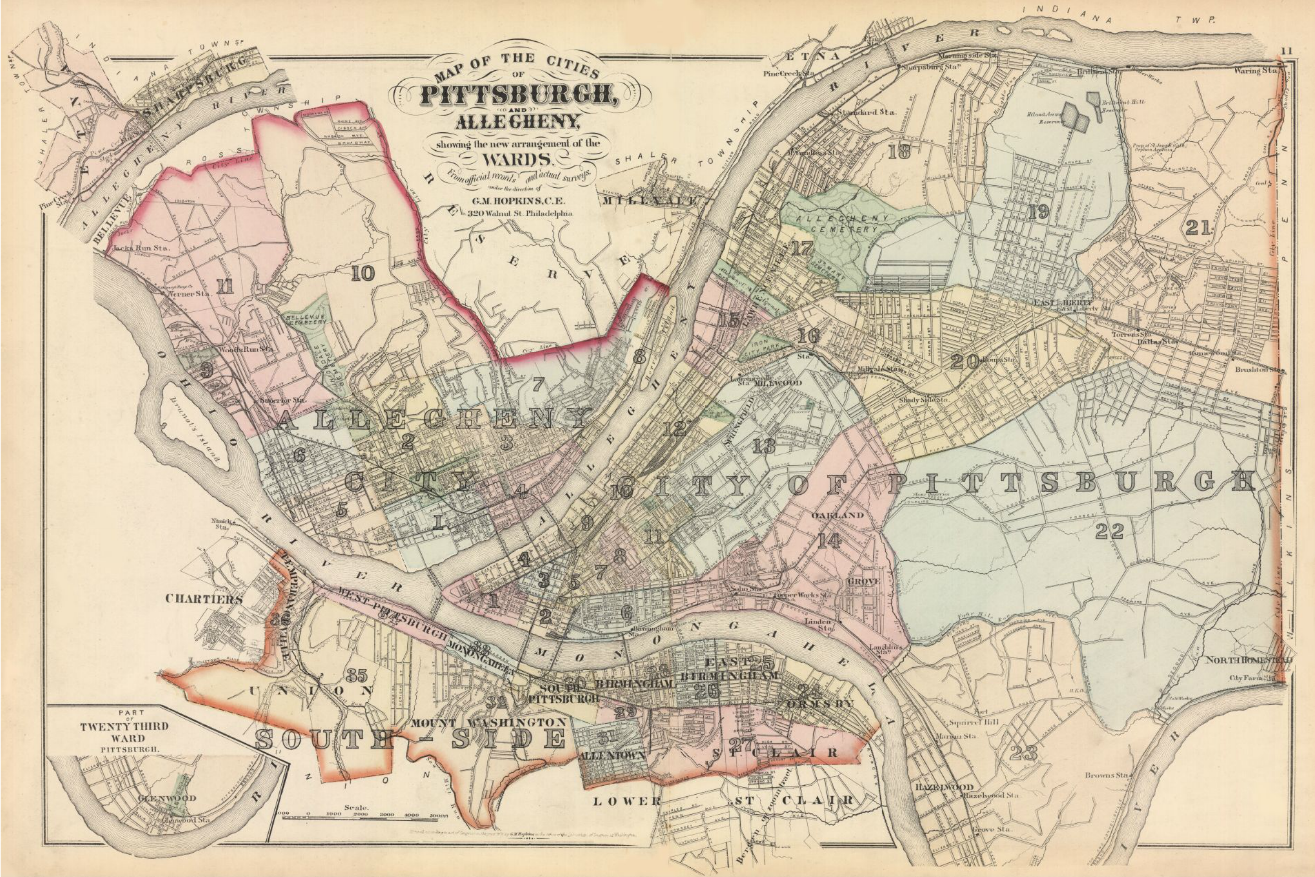
Pittsburgh Railway Riots
The Pittsburgh railway strike occurred in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania as part of the Great Railroad Strike of 1877. It was one of many incidents of strikes, labor unrest and violence in cities across the United States, including several in Pennsylvania. Other cities dealing with similar unrest included Philadelphia, Reading Railroad Massacre, Reading, 1877 Shamokin Uprising, Shamokin and Scranton General Strike, Scranton. The incidents followed repeated reductions in wages and sometimes increases in workload by railroad companies, during a period of economic recession following the Panic of 1873. Between July 21 and 22 in Pittsburgh, a major center of the Pennsylvania Railroad, some 40 people (including women and children) were killed in the ensuing riots; strikers burned the Union Depot and 38 other buildings at the yards. In addition, more than 120 locomotives and more than 1,200 rail cars were destroyed. Due to track damage, trains did not run for a week following the cessation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago Railroad Strike Of 1877
The Chicago railroad strike of 1877 was a series of work stoppages and civil unrest in Chicago, Illinois, which occurred as part of the larger national strikes and rioting of the Great Railroad Strike of 1877. Meetings of working men in Chicago on July 26 led to workers from a number of industries striking on the following morning, and over the next few days, large crowds gathered throughout the city, resulting in violent clashes with police. By the time order was restored on the evening of July 26, 14 to 30 rioters were dead or dying, and 35 to 100 civilian and nine to 13 policemen were wounded. The Long Depression and the Great Strikes The Long Depression, sparked in the United States by the Panic of 1873, had far-reaching implications for US industry, closing more than a hundred railroads in the first year and cutting construction of new rail lines from of track in 1872 to in 1875. Approximately 18,000 businesses failed between 1873 and 1875, production in iron and steel d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1877 St
Events January–March * January 1 – Queen Victoria is proclaimed ''Empress of India'' by the ''Royal Titles Act 1876'', introduced by Benjamin Disraeli, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom . * January 8 – Great Sioux War of 1876 – Battle of Wolf Mountain: Crazy Horse and his warriors fight their last battle with the United States Cavalry in Montana. * January 20 – The Conference of Constantinople ends, with Ottoman Turkey rejecting proposals of internal reform and Balkan provisions. * January 29 – The Satsuma Rebellion, a revolt of disaffected samurai in Japan, breaks out against the new imperial government; it lasts until September, when it is crushed by a professionally led army of draftees. * February 17 – Major General Charles George Gordon of the British Army is appointed Governor-General of the Sudan. * March – ''The Nineteenth Century'' magazine is founded in London. * March 2 – Compromise of 1877: The 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1877 Shamokin Uprising
The 1877 Shamokin uprising occurred in Shamokin, Pennsylvania, in July 1877, as one of the several cities in the state where strikes occurred as part of the Great Railroad Strike of 1877. The Great Strike was the first in the United States in which workers across the country united in an action against major companies. In many cities, the railroad workers were joined by other industrial workers in general strikes. Background Railroad workers and miners had perilous jobs in the late 19th century. More than 200 railroad workers and 1000 miners died in accidents every year. The companies often forced both groups to buy goods from company stores at inflated prices and work from sunup to sundown. Companies made engineers pay for all train damages, regardless of fault. Children tore their hands picking rocks from coal in collieries. The first recorded strike in the anthracite coal region of northeastern Pennsylvania occurred in 1842. More followed in 1849, 1869, and 1872. During th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Hub
A transport hub is a place where passengers and cargo are exchanged between vehicles and/or between transport modes. Public transport hubs include railway stations, rapid transit stations, bus stops, tram stops, airports and ferry slips. Freight hubs include classification yards, airports, seaports and truck terminals, or combinations of these. For private transport by car, the parking lot functions as a unimodal hub. History Historically, an interchange service in the scheduled passenger air transport industry involved a "through plane" flight operated by two or more airlines where a single aircraft was used with the individual airlines operating it with their own flight crews on their respective portions of a direct, no-change-of-plane multi-stop flight. In the U.S., a number of air carriers including Alaska Airlines, American Airlines, Braniff International Airways, Continental Airlines, Delta Air Lines, Eastern Airlines, Frontier Airlines (1950-1986), Hughes Airwest, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinsburg, West Virginia
Martinsburg is a city in and the seat of Berkeley County, West Virginia, in the tip of the state's Eastern Panhandle region in the lower Shenandoah Valley. Its population was 18,835 in the 2021 census estimate, making it the largest city in the Eastern Panhandle and the sixth-largest municipality in the state. Martinsburg is part of the Hagerstown-Martinsburg, MD-WV Metropolitan Statistical Area. History Martinsburg was established by an act of the Virginia General Assembly that was adopted in December 1778 during the American Revolutionary War. Founder Major General Adam Stephen named the gateway town to the Shenandoah Valley along Tuscarora Creek in honor of Colonel Thomas Bryan Martin, a nephew of Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron. Aspen Hall, a Georgian mansion, is the oldest house in the city. Part was built in 1745 by Edward Beeson, Sr. Aspen Hall and its wealthy residents had key roles in the agricultural, religious, transportation, and political history of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_(14575208137).jpg)