|
Baltic States Under Soviet Rule (1944–1991)
The three Baltic states – Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania – were occupied and ruled by the Soviet Union (USSR) starting in 1944. They regained independence in 1991. In 1944-1945, World War II and the occupation by Nazi Germany ended. Then, re-occupation and annexation by the Soviet Union occurred, as the three countries became constituent "union republics" of the USSR: Estonian SSR, Latvian SSR and Lithuanian SSR. The three countries remained under Soviet rule until regaining their full independence in August 1991, a few months prior to the eventual dissolution of the Soviet Union in December 1991. Soviet rule in the Baltic states led to mass deportations to other parts of the Soviet Union, in order to quell resistance and weaken national identity. Mass migration from other parts of the Soviet Union into the Baltic states had a similar effect. The Soviet Union also required the Baltic states to industrialize in a manner to maximize the Soviet economy, and isolated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
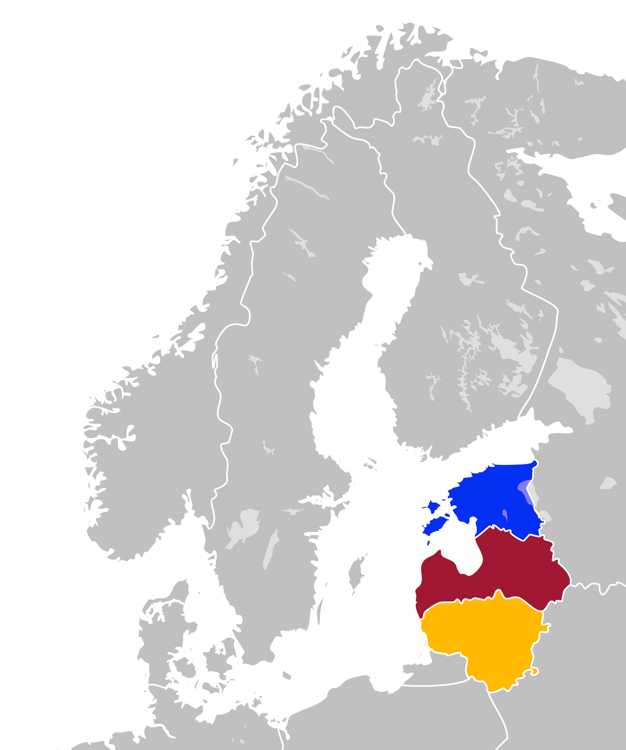
Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. The term "Baltic states" ("countries", "nations", or similar) cannot be used unambiguously in the context of cultural areas, national identity, or language. While the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet politician who served as the 8th and final leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1985 and additionally as head of state beginning in 1988, as Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet from 1988 to 1989, Chairman of the Supreme Soviet from 1989 to 1990 and the only President of the Soviet Union from 1990 to 1991. Ideologically, Gorbachev initially adhered to Marxism–Leninism but moved towards social democracy by the early 1990s. Gorbachev was born in Privolnoye, Stavropol Krai, Privolnoye, Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR, to a poor peasant family of Russian and Ukrainian heritage. Growing up under the rule of Joseph Stalin, in his youth he operated combine harvesters on a Collective farming, collective farm before join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Deportations From Lithuania
Soviet deportations from Lithuania were a series of 35 mass deportations carried out in Lithuania, a country that was occupied as a constituent socialist republic of the Soviet Union, in 1941 and 1945–1952. At least 130,000 people, 70% of them women and children, were forcibly transported to labor camps and other forced settlements in remote parts of the Soviet Union, particularly in the Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai. Among the deportees were about 4,500 Poles. These deportations do not include Lithuanian partisans or political prisoners (approximately 150,000 people) deported to Gulags (prison camps). Deportations of the civilians served a double purpose: repressing resistance to Sovietization policies in Lithuania and providing free labor in sparsely inhabited areas of the Soviet Union. Approximately 28,000 of Lithuanian deportees died in exile due to poor living conditions. After Stalin's death in 1953, the deportees were slowly and gradually released. The last deportee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Deportations From Estonia
Soviet deportations from Estonia were a series of mass deportations by the Soviet Union from Estonia in 1941 and 1945–1951. The two largest waves of deportations occurred in June 1941 and March 1949 simultaneously in all three Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania). The deportations targeted primarily women, children and the elderly calling them 'anti-Soviet elements'. In addition there were deportations based on ethnicity (Germans in 1945 and Ingrian Finns in 1947–1950) and religion (Jehovah's Witnesses in 1951). Estonians residing in the Leningrad Oblast had already been subjected to deportation since 1935. People were deported to remote areas of the Soviet Union, predominantly to Siberia and northern Kazakhstan, by means of railroad cattle cars. Entire families, including children and the elderly, were deported without trial or prior announcement. Of March 1949 deportees, over 70% of people were women and children under the age of 16. About 7,550 families, or 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enemies Of The People
The term enemy of the people or enemy of the nation, is a designation for the political or class opponents of the subgroup in power within a larger group. The term implies that by opposing the ruling subgroup, the "enemies" in question are acting against the larger group, for example against society as a whole. It is similar to the notion of "enemy of the state". The term originated in Roman times as lat, hostis publicus, typically translated into English as the "public enemy". The term in its "enemy of the people" form has been used for centuries in literature (see ''An Enemy of the People'', the play by Henrik Ibsen, 1882; or ''Coriolanus'', the play by William Shakespeare, c. 1605). The Soviet Union made extensive use of the term until 1956, notably by Joseph Stalin. It is routinely used by authoritarian rulers. Former U.S. President Donald Trump used the phrase on multiple occasions since early 2017 to refer to news organizations and journalists whom he perceives as crit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
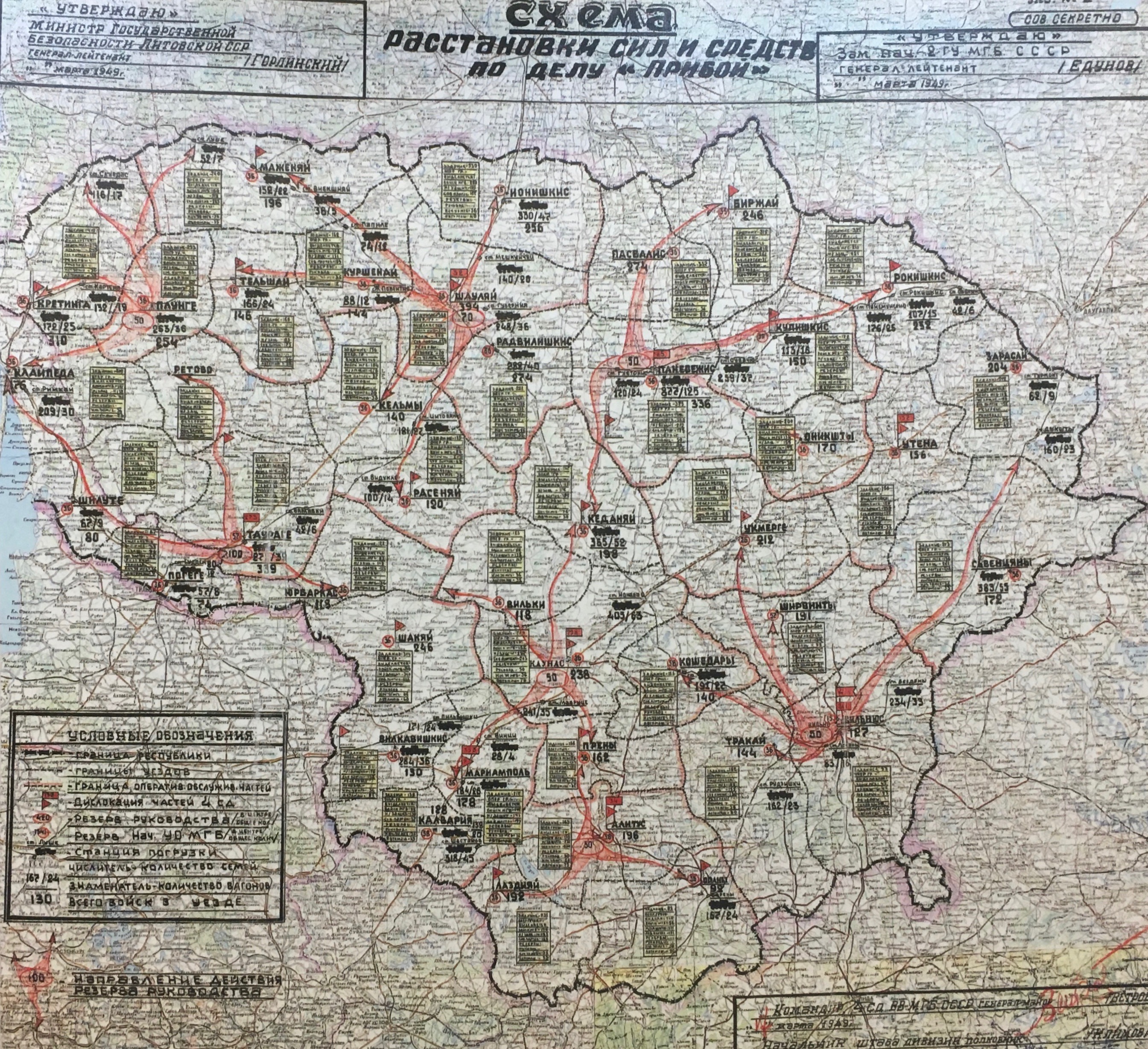
Operation Priboi
Operation Priboi (russian: Операция «Прибой» – "Operation 'Coastal Surf) was the code name for the Soviet mass deportation from the Baltic states on 25–28 March 1949. The action is also known as the March deportation ( et, Märtsiküüditamine; lv, Marta deportācijas; russian: Мартовская депортация) by Baltic historians. More than 90,000 Estonians, Latvians and Lithuanians, labeled as "enemies of the people", were deported to forced settlements in inhospitable areas of the Soviet Union. Over 70% of the deportees were either women or children under the age of 16. Portrayed as a "dekulakization" campaign, the operation was intended to facilitate collectivisation and to eliminate the support base for the armed resistance of the Forest Brothers against the illegal Soviet occupation. The deportation fulfilled its purposes: by the end of 1949, 93% and 80% of the farms were collectivized in Latvia and Estonia. In Lithuania, the progress was sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
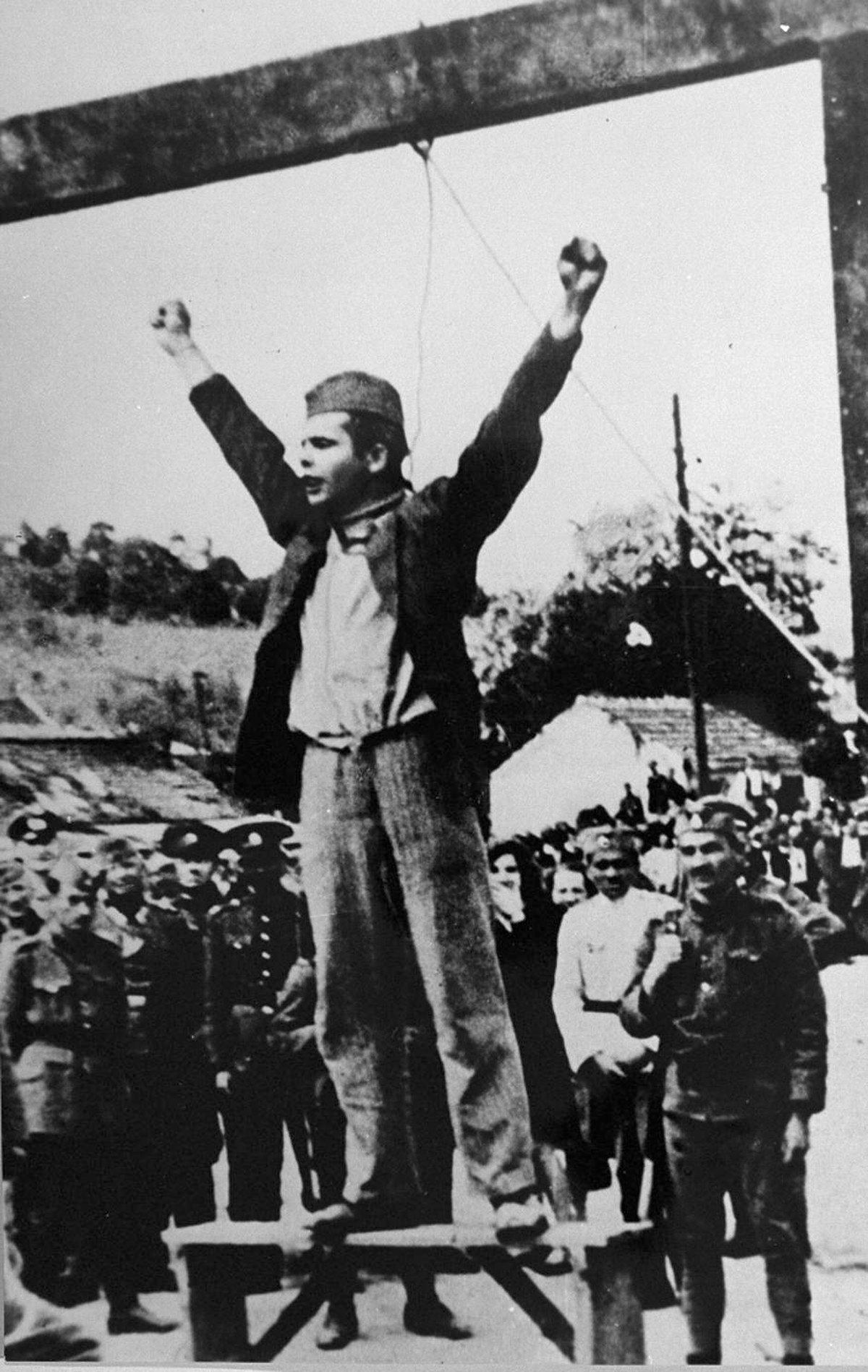
Forest Brothers
The Guerrilla war in the Baltic states was an armed struggle which was waged by the Latvian, Lithuanian, and Estonian partisans, called the Forest Brothers (also: the "Brothers of the Wood" and the "Forest Friars"; et, metsavennad, lv, mežabrāļi, lt, žaliukai), against the Soviet Union during the Soviet invasion and occupation of the three Baltic states both during and after World War II. Similar anti-Soviet Central and Eastern European resistance groups fought against Soviet and communist rule in Bulgaria, Poland, Romania, and western Ukraine. The Red Army occupied the independent Baltic states in 1940–1941 and, after a period of German occupation, it re-occupied them in 1944–1945. As Stalinist repression intensified over the following years, some 50,000 residents of these countries used the heavily forested countryside as a natural refuge and base for armed anti-Soviet insurgency. According to some estimates, 10,000 partisans in Estonia, 10,000 partisans in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partisan (military)
A partisan is a member of an irregular military force formed to oppose control of an area by a foreign power or by an army of military occupation, occupation by some kind of insurgent activity. The term can apply to the field element of resistance movements. The most common use in present parlance in several languages refers to Resistance during World War II, occupation resistance fighters during World War II, especially under the Yugoslav Partisans, Yugoslav partisan leader Josip Broz Tito. History before 1939 The initial concept of partisan warfare involved the use of militia , troops raised from the local population in a war zone (or in some cases regular forces) who would operate behind enemy front line , lines to disrupt communications, seize posts or villages as forward-operating bases, ambush convoys, impose war taxes or contributions, raid logistical stockpiles, and compel enemy forces to disperse and protect their base of operations. George Satterfield has analyse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collectivisation
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member-owners jointly engage in farming activities as a collective, and state farms, which are owned and directly run by a centralized government. The process by which farmland is aggregated is called collectivization. In some countries (including the Soviet Union, the Eastern Bloc countries, China and Vietnam), there have been both state-run and cooperative-run variants. For example, the Soviet Union had both kolkhozy (cooperative-run farms) and sovkhozy (state-run farms). Pre-20th century history A small group of farming or herding families living together on a jointly managed piece of land is one of the most common living arrangements in all of human history, having co-existed and competed with more individualistic forms of ownership (as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
_lead_the_arrested_Commissar_of_the_Red_Army%2C_1941.jpg)

