|
Balkan–Danubian Culture
The Balkan–Danubian culture was an early medieval archaeological culture which emerged in the region of the Lower Danube in the 8th century and flourished until the 11th century. In Bulgaria it is usually referred to as the Pliska–Preslav culture, while in Romania it is called the Dridu culture. It is better represented in the territory of modern-day Central and Northern Bulgaria, although it probably spread north of the Danube as well due to the continuous extension of the First Bulgarian Empire over the territory of present-day Romania. Description The Balkan–Danubian culture is described as an early ''Slavic-Bulgar'' culture, but besides Slavic and Bulgar elements it also possesses some ''Romance'' components. However, this only appears in the southern regions of what is now southern Bulgaria, all of which were heavily influenced by the Byzantine Empire. Famous examples of this architecture are the early Bulgarian capitals of Pliska and Preslav, in addition to the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Middle Ages of History of Europe, European history, following the decline of the Roman Empire, decline of the Western Roman Empire, and preceding the High Middle Ages ( 11th to 14th centuries). The alternative term ''Late antiquity#Terminology, late antiquity'', for the early part of the period, emphasizes elements of continuity with the Roman Empire, while ''Early Middle Ages'' is used to emphasize developments characteristic of the earlier medieval period. The period saw a continuation of trends evident since late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, Medieval Warm Period, a small rise in average temperatures in the North Atlantic region and Migration Period, increased m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Omurtag
The Palace of Omurtag or Aul (''Aulē'') of Omurtag (, ''Aul na Omurtag'') is an archaeological site in northeastern Bulgaria dating to Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages located near the village of Han Krum in Shumen Province. The site has been pinpointed as the location of a fort and palace of Omurtag, ruler ('' kanasybigi'') of the First Bulgarian Empire in 815–831, as mentioned in the Chatalar Inscription of 822. Earlier structures in the vicinity of the fortress have been identified as the Arian episcopal see of a Gothic bishop. Gothic episcopal see The earliest ruins at the Palace of Omurtag site include four churches, two of which built on top of each other; a bath; and fortified walls, all dating to Late Antiquity (roughly 250–650 CE). Three of the churches and the bath lie outside the medieval fortification, while one of the churches and the traces of ancient walls have been excavated within its limits. Archaeologists and scholars link the ancient ruins to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures In Romania
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves surveying, excavation, and eventually analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures Of Europe
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Medieval Archaeological Cultures Of Europe
Early may refer to: Places in the United States * Early, Iowa, a city * Early, Texas, a city * Early Branch, a stream in Missouri * Early County, Georgia * Fort Early, Georgia, an early 19th century fort Music * Early B, stage name of Jamaican dancehall and reggae deejay Earlando Arrington Neil (1957–1994) * Early James, stage name of American singer-songwriter Fredrick Mullis Jr. (born 1993) * ''Early'' (Scritti Politti album), 2005 * ''Early'' (A Certain Ratio album), 2002 * Early Records, a record label Other uses * Early (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname * Early effect, an effect in transistor physics * Early, a synonym for ''hotter'' in stellar classification See also * * The Earlies, a 21st century band * Earley (other) * Earlie Earlie is a masculine given name which may refer to: * Earlie Fires (born 1947), American jockey * Earlie Thomas (1945–2022), American National Football League player * Earlie End ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Archaeological Cultures
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to: Peoples * Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia ** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples ** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples ** West Slavic peoples, western group of Slavic peoples * Anti-Slavic sentiment, negative attitude towards Slavic peoples * Pan-Slavic movement, movement in favor of Slavic cooperation and unity * Slavic studies, a multidisciplinary field of studies focused on history and culture of Slavic peoples Languages, alphabets, and names * Slavic languages, a group of closely related Indo-European languages ** Proto-Slavic language, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages ** Old Church Slavonic, 9th century Slavic literary language, used for the purpose of evangelizing the Slavic peoples ** Church Slavonic, a written and spoken variant of Old Church Slavonic, standardized and widely adopted by Slavs in the Middle Ages, which became a liturgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Cyrillic Alphabet
The Romanian Cyrillic alphabet is the Cyrillic alphabet that was used to write the Romanian language and Church Slavonic until the 1830s, when it began to be gradually replaced by a Latin-based Romanian alphabet.Cyrillic remained in occasional use until the 1920s, mostly in Russian-ruled Bessarabia. From the 1830s until the full adoption of the Latin alphabet, the Romanian transitional alphabet was in place, combining Cyrillic and Latin letters, and including some of the Latin letters with diacritics that remain in the modern Romanian alphabet. The Romanian Orthodox Church continued using the alphabet in its publications until 1881. The Romanian Cyrillic alphabet is not the same as the Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet (which is based on the modern Russian alphabet) that was used in the Moldavian SSR for most of the Soviet era and that is still used in Transnistria. Rules The orthographic rules for the Romanian Cyrilic script were relatively inconsistent, especially differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
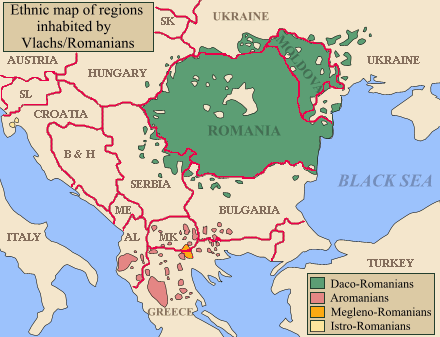
Slavic Influence On Romanian
The Slavic influence on Romanian is noticeable on all linguistic levels: lexis, phonetics, morphology and syntax. Overview Romanian (or Daco-Romanian), Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian and Istro-Romanian form the Eastern Romance branch of the Romance languages. The four languages are descended from a common ancestor developed from the Vulgar Latin spoken in southeastern Europe during Classical Antiquity. The territory where the language formed was a large one, consisting of both the north and the south of the Danube (encompassing the regions of Dacia, Moesia, and possibly Illyria), more precisely to the north of the Jiriček Line. Proto-Slavicthe root from which the modern Slavic languages developedemerged during the first half of the 2nd millennium BC. The Early Slavs lived in the plains north of the Carpathian Mountains or along the middle course of the Dnieper River. Their expansion accelerated after the fall of the Hunnic Empire in the middle of the 5th century AD. Significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
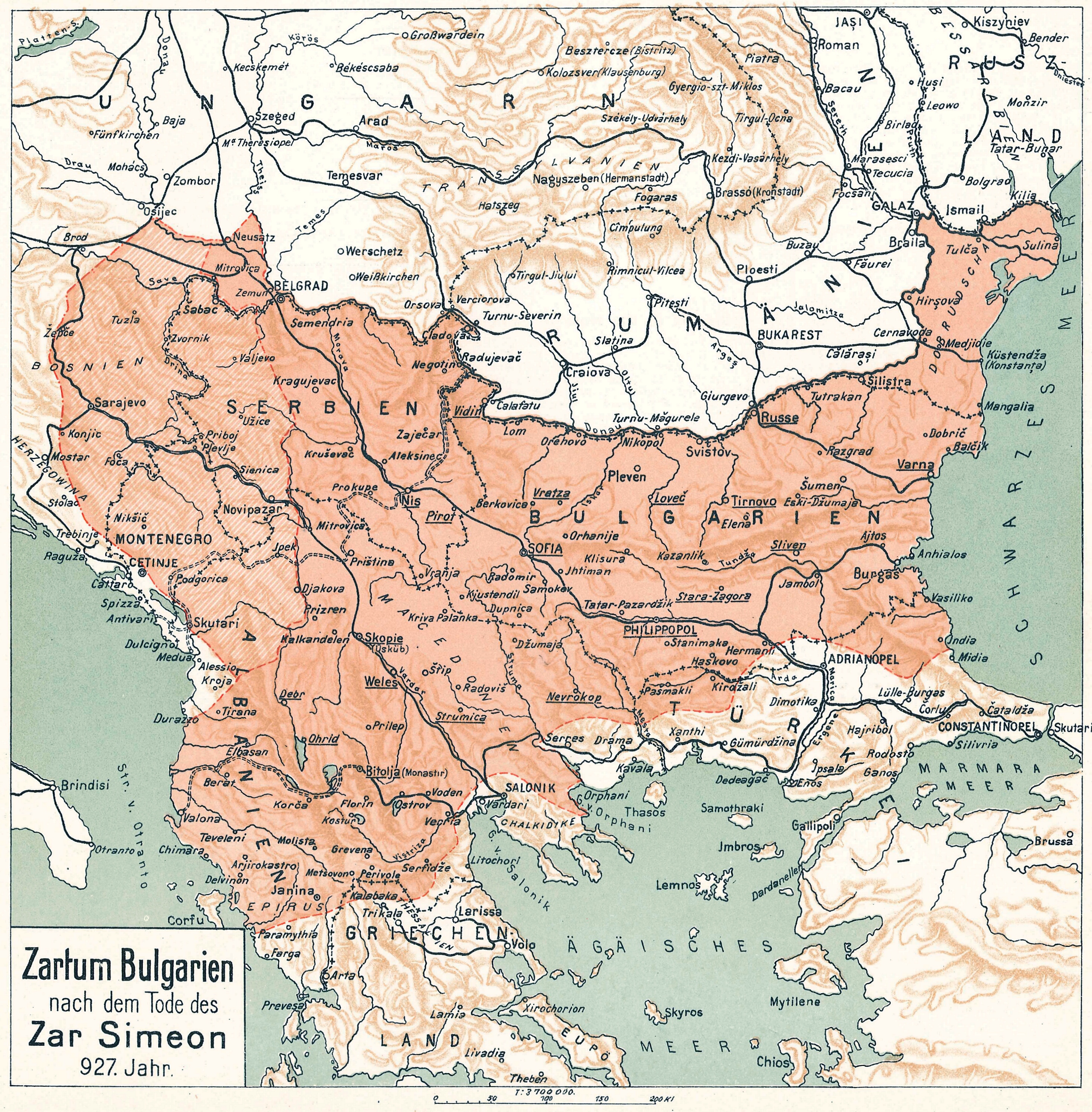
Golden Age Of Bulgaria
The Golden Age (metaphor), Golden Age of First Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria is the period of the Bulgarian culture, Bulgarian cultural prosperity during the reign of emperor Simeon I of Bulgaria, Simeon I the Great (889—927).Kiril Petkiv, The Voices of Medieval Bulgaria, Seventh-Fifteenth Century: The Records of a Bygone Culture', BRILL, 2008, p.89 The term was coined by Spiridon Palauzov in the mid 19th century. During this period there was an increase of Preslav Literary School, literature, Cyrillic script, writing, arts, Round Church, Preslav, architecture and Old Church Slavonic, liturgical reforms. Simeon I achieved spectacular military and political successes, expanding Bulgarian territory and forcing the Byzantine Empire to recognise the imperial title of the Bulgarian monarchs. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murfatlar Cave Complex
The Basarabi-Murfatlar Cave Complex is a medieval Christian monastery located near the town of Murfatlar (known as Basarabi between 1924–1965 and 1975–2007), Constanța County, Northern Dobruja, Romania. The complex is a relict from a widespread monastic phenomenon in 10th century Bulgaria. History The rock churches of Murflatlar, carved into a chalk hill, were discovered in 1957. The excavations conducted in 1957–1960 uncovered a complex of cells-dwellings, 4 small and 2 larger churches, crypts and tombs, all dating from the 9th – 11th century. From the late 7th until beginning of the 11th century this territory was part of the First Bulgarian Empire. Inscriptions There are many inscriptions engraved on the walls – 2 in the Greek alphabet, 2 in the Old Slavonic language (''Bulgarian recension'') using the Glagolitic script and over 30 using the Cyrillic script. The most numerous are the runic inscriptions of Turkic type – over 60 have been found so far. The same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav (, ), former Preslav (; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new Bulgarian: ''obshtina''), which in turn is part of Shumen Province, Bulgaria. Veliki Preslav is situated at an altitude of 132 m (92 m above sea level). A former village, it assumed the name of the medieval capital in 1878 and became a town in 1883. As of December 2009, it had a population of 8,951. Preslav was the capital of the First Bulgarian Empire from 893 to 972 and was one of the most important cities in medieval Southeastern Europe. The ruins of the city are situated in modern northeastern Bulgaria, some 20 kilometres southwest of the regional capital of Shumen, and are currently a national archaeological reserve. History The name of Preslav is of Slavic origin; apparently it was initially founded and functioned as a Slavic settlement until its fortification at the beginning of the ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |