|
Bainbridge Reflex
The Bainbridge reflex or Bainbridge effect, also called the atrial reflex, is an increase in heart rate due to an increase in central venous pressure. Increased blood volume is detected by stretch receptors (Cardiac Receptors) located in both sides of atria at the venoatrial junctions. History Francis Arthur Bainbridge described this as a reflex in 1918 when he was experimenting on dogs. Bainbridge found that infusing blood or saline into the animal increased heart rate. This phenomenon occurred even if arterial blood pressure did not increase. He further observed that heart rate increased when venous pressure rose high enough to distend the right atrium, but denervation of the vagi to the heart eliminated these effects. Subsequent work demonstrated that a stretch-induced increase in cardiac beating rate can also be observed in isolated hearts or even the fully separated SAN. Thus, the positive chronotropic (from Χρόνος, Greek for 'time', and τρέπειν, Greek for 'to ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide, but is also modulated by numerous factors, including, but not limited to, genetics, physical fitness, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness as well as the interaction between and among these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse measured at any peripheral point. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. Tachycardia is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. Bradycardia is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. When a human sleeps, a heartbeat with rates around 40–50 bpm is common and is considered normal. When the heart is not beating in a regular pattern, this is ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanoreceptors
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are innervated by sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals that, in animals, are sent to the central nervous system. Vertebrate mechanoreceptors Cutaneous mechanoreceptors Cutaneous mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical stimuli that result from physical interaction, including pressure and vibration. They are located in the skin, like other cutaneous receptors. They are all innervated by Aβ fibers, except the mechanorecepting free nerve endings, which are innervated by Aδ fibers. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors can be categorized by what kind of sensation they perceive, by the rate of adaptation, and by morphology. Furthermore, each has a different receptive field. By sensation *The Slowly Adapting type 1 (SA1) mechanoreceptor, with the Merkel corpuscle end-organ (also known as Merkel discs) detect sustained pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Arthur Bainbridge
Francis Arthur Bainbridge FRS FRCP (29 July 1874 – 27 October 1921) was an English physiologist. History Bainbridge was born in Stockton-on-Tees, County Durham, in 1874 and educated at The Leys School. He entered Trinity College, Cambridge, in 1893, graduating BA in 1896, earning an M.B. in 1901,Bainbridge, Francis Arthur. Oxford Dictionary of National Biography 1912-1921. Oxford University Press. 1927. p. 17 and finally a doctorate in 1904. Medicine did not appeal to him, and for a while he focused on Pathology and Bacteriology. In 1905, he became a lecturer of Pathology at Guy's Hospital, and in 1907, he went on as assistant Bacteriologist to the Lister Institute of Preventive Medicine. His work on food-poisoning bacilli gained wide recognition, and was embodied in his lectures at the Royal College of Physicians. In 1911 he became a professor of physiology at Durham University. In 1915 he attained the chair of physiology at St. Bartholomew's Hospital, where he remained fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given intravenously or by injection into a muscle. Eye drops are also available which are used to treat uveitis and early amblyopia. The intravenous solution usually begins working within a minute and lasts half an hour to an hour. Large doses may be required to treat some poisonings. Common side effects include a dry mouth, large pupils, urinary retention, constipation, and a fast heart rate. It should generally not be used in people with angle closure glaucoma. While there is no evidence that its use during pregnancy causes birth defects, that has not been well studied. It is likely safe during breastfeeding. It is an antimuscarinic (a type of anticholinergic) that works by inhibiting the parasympathetic nervous system. Atropine occurs n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves—but they are typically referred to collectively as a single subsystem. The vagus is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion, whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus. The vagus was also historically called the pneumogastric nerve. Structure Upon leaving the medulla oblongata between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle, the vagus nerve extends through the jugular foramen, then passes into the carotid sheath between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein down to the neck, chest, and abdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroreceptor Reflex
The baroreflex or baroreceptor reflex is one of the body's homeostatic mechanisms that helps to maintain blood pressure at nearly constant levels. The baroreflex provides a rapid negative feedback loop in which an elevated blood pressure causes the heart rate to decrease. Decreased blood pressure decreases baroreflex activation and causes heart rate to increase and to restore blood pressure levels. Their function is to sense pressure changes by responding to change in the tension of the arterial wall The baroreflex can begin to act in less than the duration of a cardiac cycle (fractions of a second) and thus baroreflex adjustments are key factors in dealing with postural hypotension, the tendency for blood pressure to decrease on standing due to gravity. The system relies on specialized neurons, known as baroreceptors, chiefly in the aortic arch and carotid sinuses, to monitor changes in blood pressure and relay them to the medulla oblongata. Baroreceptors are stretch receptors and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
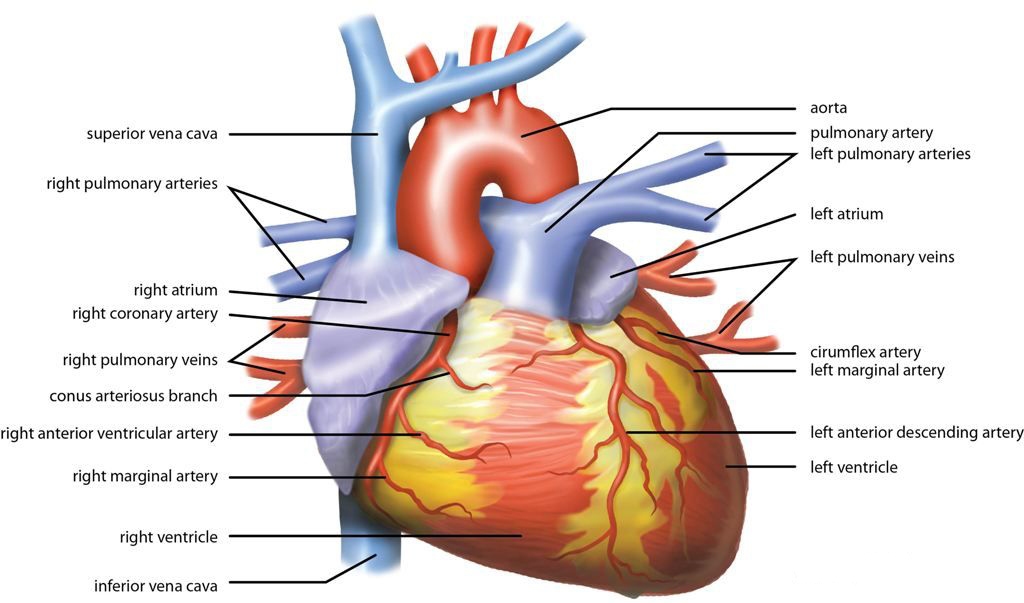
Inferior Vena Cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra. The inferior vena cava is the lower (" inferior") of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart: the inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower half of the body whilst the superior vena cava carries blood from the upper half of the body. Together, the venae cavae (in addition to the coronary sinus, which carries blood from the muscle of the heart itself) form the venous counterparts of the aorta. It is a large retroperitoneal vein that lies posterior to the abdominal cavity and runs along the right side of the vertebral column. It enters the right auricle at the lower right, back side of the heart. The name derives from la, vena, "vei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial Stretch Receptors
Low pressure baroreceptors are baroreceptors that relay information derived from blood pressure within the autonomic nervous system. They are stimulated by stretching of the vessel wall. They are located in large systemic veins and in the walls of the atria of the heart, and pulmonary vasculature. Low pressure baroreceptors are also referred to as volume receptors and cardiopulmonary baroreceptors.Armstrong, Maggie, et al. ''Physiology, Baroreceptors - Statpearls - NCBI Bookshelf''. 9 Mar. 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538172/. Structure There are two types of cardiopulmonary baroreceptors. Type A receptors and Type B receptors are both within the atria of the heart. Type A receptors are activated by wall tension, which develops by atrial contraction during ventricular diastole. Type B receptors are activated by wall stretch, which develops by atrial filling during ventricular systole. In the right atrium, the stretch receptors occur at the junction of the ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Pressure Receptor Zones
Low pressure baroreceptors are baroreceptors that relay information derived from blood pressure within the autonomic nervous system. They are stimulated by stretching of the vessel wall. They are located in large systemic veins and in the walls of the atria of the heart, and pulmonary vasculature. Low pressure baroreceptors are also referred to as volume receptors and cardiopulmonary baroreceptors.Armstrong, Maggie, et al. ''Physiology, Baroreceptors - Statpearls - NCBI Bookshelf''. 9 Mar. 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538172/. Structure There are two types of cardiopulmonary baroreceptors. Type A receptors and Type B receptors are both within the atria of the heart. Type A receptors are activated by wall tension, which develops by atrial contraction during ventricular diastole. Type B receptors are activated by wall stretch, which develops by atrial filling during ventricular systole. In the right atrium, the stretch receptors occur at the junction of the ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia
Vagal tone is activity of the vagus nerve, the 10th cranial nerve and a fundamental component of the parasympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system. This branch of the nervous system is not under conscious control and is largely responsible for the regulation of several body compartments at rest. Vagal activity results in various effects, including: heart rate reduction, vasodilation/constriction of vessels, glandular activity in the heart, lungs, and digestive tract, liver, immune system regulation as well as control of gastrointestinal sensitivity, motility and inflammation. In this context, tone specifically refers to the continual nature of baseline parasympathetic action that the vagus nerve exerts. While baseline vagal input is constant, the degree of stimulation it exerts is regulated by a balance of inputs from sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system, with parasympathetic activity generally being dominant. Vagal tone is frequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhalation
Inhalation (or Inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs. Inhalation of air Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions in some disease states) and does not need conscious control or effort. However, breathing can be consciously controlled or interrupted (within limits). Breathing allows oxygen (which humans and a lot of other species need for survival) to enter the lungs, from where it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Other substances – accidental Examples of accidental inhalation includes inhalation of water (e.g. in drowning), smoke, food, vomitus and less common foreign substances (e.g. tooth fragments, coins, batteries, small toy parts, needles). Other substances – deliberate Recreational use Legal – helium, nitrous oxide ("laughing gas") Illegal – various gaseous, vaporised or aerosolized recreational drugs Medical use Diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valsalva Maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is performed by a forceful attempt of exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut while expelling air out as if blowing up a balloon. Variations of the maneuver can be used either in medical examination as a test of cardiac function and autonomic nervous control of the heart, or to clear the ears and sinuses (that is, to equalize pressure between them) when ambient pressure changes, as in scuba diving, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, or air travel. A modified version is done by expiring against a closed glottis. This will elicit the cardiovascular responses described below but will not force air into the Eustachian tubes. History The technique is named after Antonio Maria Valsalva, a 17th-century physician and anatomist from Bologna whose principal scientific interest was the human ear. He described the Eustachian tube and the maneuver to test its patency (openness). He also described the use of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |