|
BL22
An anti-CD22 immunotoxin is a monoclonal antibody (targeting CD22) linked to a cytotoxic agent. They are being studied in the treatment of some types of B-cell cancer. They bind to CD22, a receptor protein on the surface of normal B cells and B-cell tumors, and, upon internalization, kill the cells. Therapeutic immunotoxins that use Pseudomonas exotoxin As of August 2009, several anti-CD22 immunotoxins are undergoing clinical trials. CAT-3888 and CAT-8015 CAT-3888 (or BL22) is an anti-CD22 immunotoxin and completed a Phase I clinical (human) trial for the treatment of hairy cell leukemia at the NIH in the U.S. Technically, CAT-3888 is an anti-CD22 immunotoxin fusion protein between a murine anti-CD22 disulfide-linked Fv (dsFv) antibody fragment and an edited copy of bacterial Pseudomonas exotoxin PE38. The toxin is activated intracellularly, by the low pH of the lysosome into which the entire protein was internalized via the CD22 receptor. The toxin kills the targeted ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
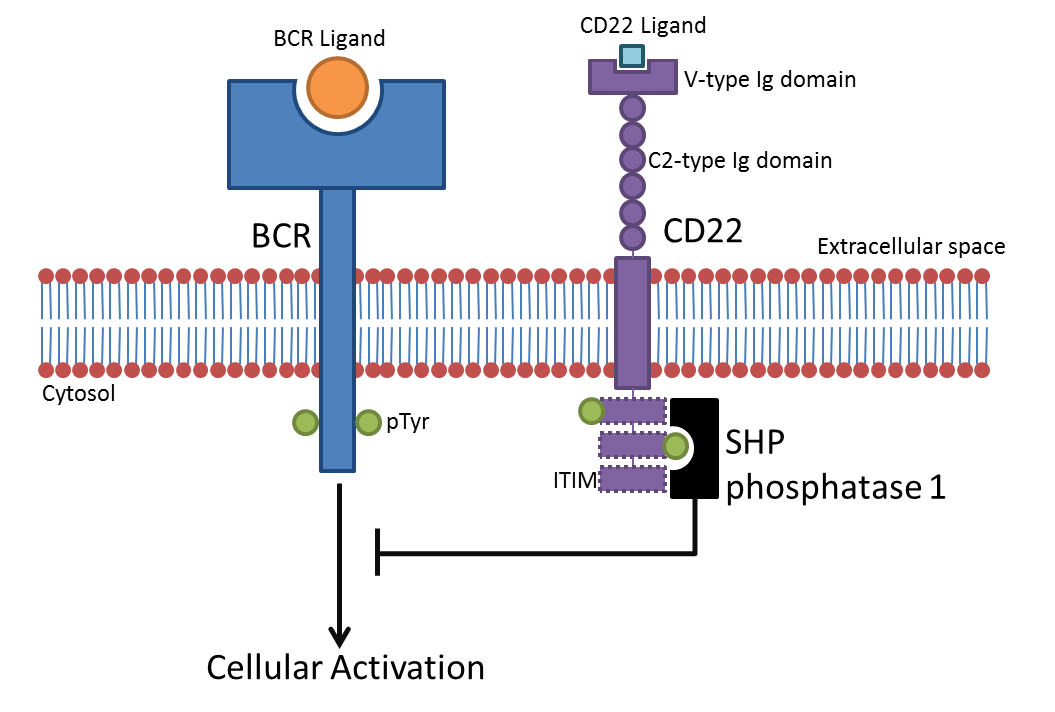
CD22
CD22, or cluster of differentiation-22, is a molecule belonging to the SIGLEC family of lectins. It is found on the surface of mature B cells and to a lesser extent on some immature B cells. Generally speaking, CD22 is a regulatory molecule that prevents the overactivation of the immune system and the development of autoimmune diseases. CD22 is a sugar binding transmembrane protein, which specifically binds sialic acid with an immunoglobulin (Ig) domain located at its N-terminus. The presence of Ig domains makes CD22 a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD22 functions as an inhibitory receptor for B cell receptor (BCR) signaling. It is also involved in the B cell trafficking to Peyer's patches in mice. In mice, it has been shown that CD22 blockade restores homeostatic microglial phagocytosis in aging brains. Structure CD22 is a transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of 140 kDa. The extracellular part of CD22 consists of seven immunoglobulin domains and the intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairy Cell Leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia is an uncommon hematological malignancy characterized by an accumulation of abnormal B lymphocytes. It is usually classified as a subtype of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Hairy cell leukemia makes up about 2% of all leukemias, with fewer than 2,000 new cases diagnosed annually in North America and Western Europe combined. Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) was originally described as histiocytic leukemia, malignant reticulosis, or lymphoid myelofibrosis in publications dating back to the 1920s. The disease was formally named leukemic reticuloendotheliosis, and its characterization was significantly advanced by Bertha Bouroncle and colleagues at the Ohio State University College of Medicine in 1958. Its common name, which was coined in 1966, is derived from the "hairy" appearance of the malignant B cells under a microscope. Signs and symptoms In HCL, the "hairy cells" (malignant B lymphocytes) accumulate in the bone marrow, interfering with the production of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunotoxin
An immunotoxin is an artificial protein consisting of a targeting portion linked to a toxin. When the protein binds to that cell, it is taken in through endocytosis, and the toxin kills the cell. They are used for the treatment of some kinds of cancer and a few viral infections. Design These chimeric proteins are usually made of a modified antibody or antibody fragment, attached to a fragment of a toxin. The targeting portion is composed of the Fab portion of an antibody that targets a specific cell type. The toxin is usually an AB toxin, a cytotoxic protein derived from a bacterial or plant protein, from which the natural binding domain has been removed so that the Fv directs the toxin to the antigen on the target cell. Sometimes recombinant fusion proteins containing a toxin and a growth factor are also referred to as recombinant immunotoxins, although they do not contain an antibody fragment. A more specific name for this latter kind of protein is recombinant fusion toxin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge Antibody Technology
Cambridge Antibody Technology (officially Cambridge Antibody Technology Group Plc, informally CAT) was a biotechnology company headquartered in Cambridge, England, United Kingdom. Its core focus was on antibody therapeutics, primarily using Phage Display and Ribosome Display technology. Phage Display Technology was used by CAT to create adalimumab, the first fully human antibody blockbuster drug. Humira, the brand name of adalimumab, is an anti-TNF antibody discovered by CAT as D2E7, then developed in the clinic and marketed by Abbvie, formerly Abbott Laboratories. CAT was also behind belimumab, the anti-BlyS antibody drug marketed as Benlysta and the first new approved drug for systemic lupus in more than 50 years. In 2018, the Nobel Prize organisation awarded one quarter of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to a founding member of CAT, Sir Greg Winter FRS "for the phage display of peptides and antibodies.". Founded in 1989, CAT was acquired by AstraZeneca for £702m in 2006. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas Exotoxin
The Pseudomonas exotoxin (or exotoxin A) is an exotoxin produced by ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''. ''Vibrio cholerae'' produces a similar protein called the Cholix toxin (). It inhibits elongation factor-2. It does so by ADP-ribosylation of EF2 using NAD+. This then causes the elongation of polypeptides to cease. This mechanism is similar to that of diphtheria toxin. It has been investigated as a treatment for hepatitis B Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection. Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ... and cancer. References External links *P11439 (eta)in InterPro domain view {{Toxins Bacterial toxins Proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drugs Acting On The Blood And Blood Forming Organs
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption via a patch on the skin, suppository, or dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to treat, cure, prevent, or diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used for a limited duration, or on a regular basis for chronic disorders. Pharmaceutical drugs are often classified into drug classes—groups of related drugs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancreatic cancer are known. The most common, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, accounts for about 90% of cases, and the term "pancreatic cancer" is sometimes used to refer only to that type. These adenocarcinomas start within the part of the pancreas that makes digestive enzymes. Several other types of cancer, which collectively represent the majority of the non-adenocarcinomas, can also arise from these cells. About 1–2% of cases of pancreatic cancer are neuroendocrine tumors, which arise from the hormone-producing neuroendocrine cell, cells of the pancreas. These are generally less aggressive than pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Signs and symptoms of the most-common form of pancreatic cancer may include jaundice, ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different cell types including epithelial cells, germ cells, and stromal cells. When these cells become abnormal, they have the ability to divide and form tumors. These cells can also invade or spread to other parts of the body. When this process begins, there may be no or only vague symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms may include bloating, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, constipation, and loss of appetite, among others. Common areas to which the cancer may spread include the lining of the abdomen, lymph nodes, lungs, and liver. The risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. Most cases of ovarian cancer develop after menopause. It is also more common in women who have ovulated m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleural
The pleural cavity, pleural space, or interpleural space is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication between the membranes, and also to create a pressure gradient. The serous membrane that covers the surface of the lung is the visceral pleura and is separated from the outer membrane the parietal pleura by just the film of pleural fluid in the pleural cavity. The visceral pleura follows the fissures of the lung and the root of the lung structures. The parietal pleura is attached to the mediastinum, the upper surface of the diaphragm, and to the inside of the ribcage. Structure In humans, the left and right lungs are completely separated by the mediastinum, and there is no communication between their pleural cavities. Therefore, in cases of a unilateral pneumothorax, the contralateral lung will remain functioning normally unless there is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are also often glycosylated. Glycoproteins are also often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. It is important to distinguish endoplasmic reticulum-based glycosylation of the secretory system from reversible cytosolic-nuclear glycosylation. Glycoproteins of the cytosol and nucleus can be modified through the reversible addition of a single GlcNAc residue that is considered reciprocal to phosphorylation and the functions of these are likely to be an additional regulatory mechanism that controls phosphorylation-based signalling. In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesothelin
Mesothelin, also known as MSLN, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MSLN'' gene. Function Mesothelin is a 40 kDa protein that is expressed in mesothelial cells. The protein was first identified by its reactivity with monoclonal antibody K1. Subsequent cloning studies showed that the mesothelin gene encodes a precursor protein that is processed to yield mesothelin which is attached to the cell membrane by a glycophosphatidylinositol linkage and a 31-kDa shed fragment named megakaryocyte-potentiating factor (MPF). Although it has been proposed that mesothelin may be involved in cell adhesion, its biological function is not known. A knockout mouse line that lacks mesothelin reproduces and develops normally. Mesothelin is over expressed in several human tumors, including mesothelioma, ovarian cancer, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, and cholangiocarcinoma. Mesothelin binds MUC16 (also known as CA125), indicating that the interaction of mesothelin and MU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |