|
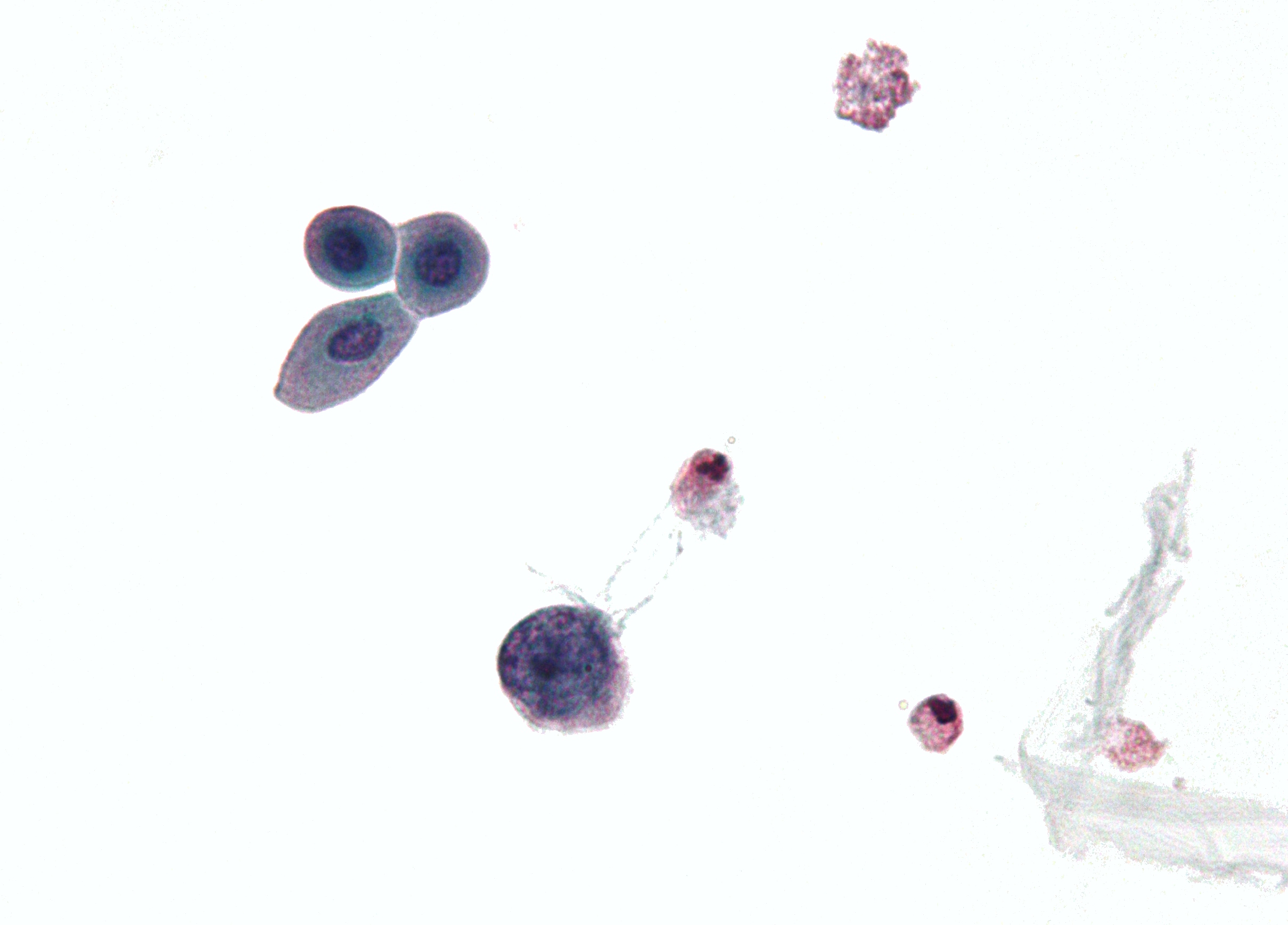
BK Virus
The BK virus is a member of the polyomavirus family. Past infection with the BK virus is widespread, but significant consequences of infection are uncommon, with the exception of the immunocompromised and the immunosuppressed. BK virus is an abbreviation of the name of the first patient, from whom the virus was isolated in 1971 (the patient was then 29 years old). Signs and symptoms The BK virus rarely causes disease but is typically associated with patients who have had a kidney transplant; many people who are infected with this virus are asymptomatic. If symptoms do appear, they tend to be mild: respiratory infection or fever. These are known as primary BK infections. Although without any clinical symptoms, footprints of BK virus have been detected in specimens from females affected by spontaneous abortion. Serum antibodies against BK virus have also been found in spontaneous abortion affected women as well as in women who underwent voluntary interruption of pregnancy. The vir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields such as ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Marrow Transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce additional normal blood cells. It may be autologous (the patient's own stem cells are used), allogeneic (the stem cells come from a donor) or syngeneic (from an identical twin). It is most often performed for patients with certain cancers of the blood or bone marrow, such as multiple myeloma or leukemia. In these cases, the recipient's immune system is usually destroyed with radiation or chemotherapy before the transplantation. Infection and graft-versus-host disease are major complications of allogeneic HSCT. HSCT remains a dangerous procedure with many possible complications; it is reserved for patients with life-threatening diseases. As survival following the procedure has increased, its use has expanded beyond cancer to autoimmune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinolone Antibiotic
A quinolone antibiotic is a member of a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well as in animal husbandry, specifically poultry production. Nearly all quinolone antibiotics in use are fluoroquinolones, which contain a fluorine atom in their chemical structure and are effective against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. One example is ciprofloxacin, one of the most widely used antibiotics worldwide. Medical uses Fluoroquinolones are often used for genitourinary infections and are widely used in the treatment of hospital-acquired infections associated with urinary catheters. In community-acquired infections, they are recommended only when risk factors for multidrug resistance are present or after other antibiotic regimens have failed. However, for serious acute cases of pyelonephritis or bacterial pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leflunomide
Leflunomide, sold under the brand name Arava among others, is an immunosuppressive disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), used in active moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. It is a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor that works by inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Medical use Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are the only indications that have received regulatory approval. Arava was developed by Sanofi Aventis and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1998. Clinical studies regarding the following diseases have been conducted: There has been reports on potential re-purposing of leflunomide for treatment of solid tumors with tumor suppressor, PTEN, loss. In PTEN negative tumors, leflunomide causes synthetic lethality potentially due to increased demand on pyrimidines in these faster growing cells. * Polyoma BK virus Diabetic nephropathy, nephropathy * Kimura's disease * Systemic lupus erythematosus * Felty's syndr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidine Synthesis Inhibitor
Pyrimidine biosynthesis occurs both in the body and through organic synthesis. ''De novo'' biosynthesis of pyrimidine ''De Novo'' biosynthesis of a pyrimidine is catalyzed by three gene products CAD, DHODH and UMPS. The first three enzymes of the process are all coded by the same gene in CAD which consists of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II, aspartate carbamoyltransferase and dihydroorotase. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) unlike CAD and UMPS is a mono-functional enzyme and is localized in the mitochondria. UMPS is a bifunctional enzyme consisting of orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (OPRT) and orotidine monophosphate decarboxylase (OMPDC). Both, CAD and UMPS are localized around the mitochondria, in the cytosol. In Fungi, a similar protein exists but lacks the dihydroorotase function: another protein catalyzes the second step. In other organisms (Bacteria, Archaea and the other Eukaryota), the first three steps are done by three different enzymes. Pyrimidine catab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroquinolone
A quinolone antibiotic is a member of a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well as in animal husbandry, specifically poultry production. Nearly all quinolone antibiotics in use are fluoroquinolones, which contain a fluorine atom in their chemical structure and are effective against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. One example is ciprofloxacin, one of the most widely used antibiotics worldwide. Medical uses Fluoroquinolones are often used for genitourinary infections and are widely used in the treatment of hospital-acquired infections associated with urinary catheters. In community-acquired infections, they are recommended only when risk factors for multidrug resistance are present or after other antibiotic regimens have failed. However, for serious acute cases of pyelonephritis or bacterial pros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin therapy is the use of a mixture of antibodies (normal human immunoglobulin or NHIG) to treat several health conditions. These conditions include primary immunodeficiency, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, Kawasaki disease, certain cases of HIV/AIDS and measles, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and certain other infections when a more specific immunoglobulin is not available. Depending on the formulation it can be given by injection into muscle, a vein, or under the skin. The effects last a few weeks. Common side effects include pain at the site of injection, muscle pain, and allergic reactions. Other severe side effects include kidney problems, anaphylaxis, blood clots, and red blood cell breakdown. Use is not recommended in people with some types of IgA deficiency. Use appears to be relatively safe during pregnancy. Human immunoglobulin is made from human blood plasma. It contains antibodies against many viruses. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
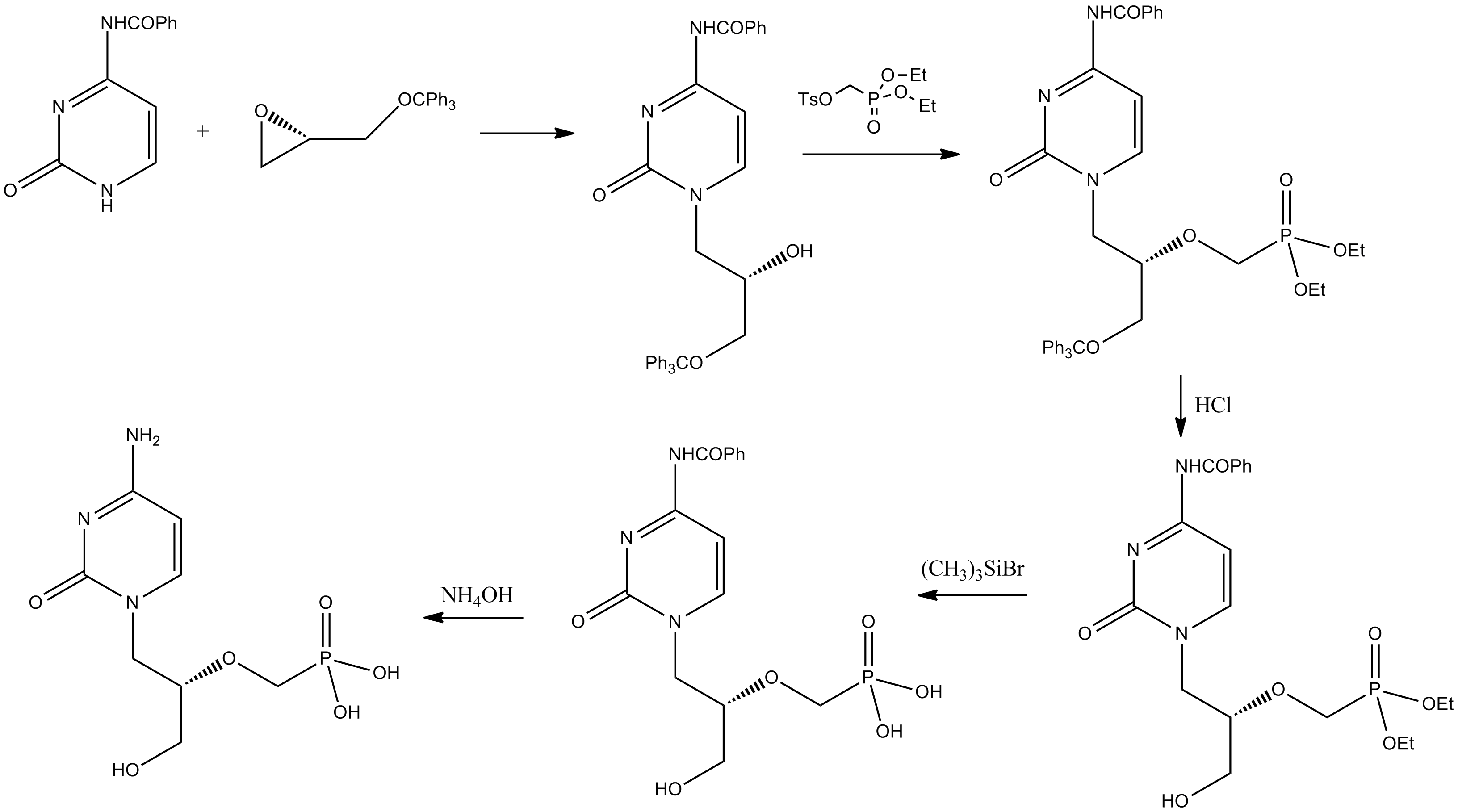
Cidofovir
Cidofovir, brand name Vistide, is a topical or injectable antiviral medication primarily used as a treatment for cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis (an infection of the retina of the eye) in people with AIDS. Cidofovir was approved for medical use in 1996. Medical use DNA virus Its only indication that has received regulatory approval worldwide is cytomegalovirus retinitis. Cidofovir has also shown efficacy in the treatment of aciclovir-resistant HSV infections. Cidofovir has also been investigated as a treatment for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy with successful case reports of its use. Despite this, the drug failed to demonstrate any efficacy in controlled studies. Cidofovir might have anti-smallpox efficacy and might be used on a limited basis in the event of a bioterror incident involving smallpox cases. Brincidofovir, a cidofovir derivative with much higher activity against smallpox that can be taken orally has been developed. It has inhibitory effects on var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leflunomide
Leflunomide, sold under the brand name Arava among others, is an immunosuppressive disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), used in active moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. It is a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor that works by inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Medical use Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are the only indications that have received regulatory approval. Arava was developed by Sanofi Aventis and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1998. Clinical studies regarding the following diseases have been conducted: There has been reports on potential re-purposing of leflunomide for treatment of solid tumors with tumor suppressor, PTEN, loss. In PTEN negative tumors, leflunomide causes synthetic lethality potentially due to increased demand on pyrimidines in these faster growing cells. * Polyoma BK virus Diabetic nephropathy, nephropathy * Kimura's disease * Systemic lupus erythematosus * Felty's syndr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycophenolate Mofetil
Mycophenolic acid (MPA) is an immunosuppressant medication used to prevent rejection following organ transplantation and to treat autoimmune conditions such as Crohn's disease and lupus. Specifically it is used following kidney, heart, and liver transplantation. It can be given by mouth or by injection into a vein. It comes as mycophenolate sodium and mycophenolate mofetil. Common side effects include nausea, infections, and diarrhea. Other serious side effects include an increased risk of cancer, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, anemia, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. It works by blocking inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH), which is needed by lymphocytes to make guanosine. Mycophenolic acid was initially discovered by Italian Bartolomeo Gosio in 1893. It was rediscovered in 1945 and 1968. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1995 following the discovery of its immunosuppressive properties in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacrolimus
Tacrolimus, sold under the brand name Prograf among others, is an immunosuppressive drug. After allogeneic organ transplant, the risk of organ rejection is moderate. To lower the risk of organ rejection, tacrolimus is given. The drug can also be sold as a topical medication in the treatment of T-cell-mediated diseases such as eczema and psoriasis. For example, it is prescribed for severe refractory uveitis after a bone marrow transplant, exacerbations of minimal change disease, Kimura's disease, and vitiligo. It can be used to treat dry eye syndrome in cats and dogs. Tacrolimus inhibits calcineurin, which is involved in the production of interleukin-2, a molecule that promotes the development and proliferation of T cells, as part of the body's learned (or adaptive) immune response. Chemically, it is a macrolide lactone that was first discovered in 1987, from the fermentation broth of a Japanese soil sample that contained the bacterium ''Streptomyces tsukubensis''. It is on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunosuppressant Drug
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system. Classification Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into five groups: * glucocorticoids * cytostatics * antibodies * drugs acting on immunophilins * other drugs Glucocorticoids In pharmacologic (supraphysiologic) doses, glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, dexamethasone, and hydrocortisone are used to suppress various allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune disorders. They are also administered as posttransplantory immunosuppressants to prevent the acute transplant rejection and graft-versus-host disease. Nevertheless, they do not prevent an infection and also inhibit later reparative processes. Immunosuppressive mechanism Glucocorticoids suppress cell-mediated immunity. They act by inhibiting genes that code for the cytokines Interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |