|
BFKL Pomeron
In physics, the pomeron is a Regge trajectory — a family of particles with increasing spin — postulated in 1961 to explain the slowly rising cross section of hadronic collisions at high energies. It is named after Isaak Pomeranchuk. Overview While other trajectories lead to falling cross sections, the pomeron can lead to logarithmically rising cross sections — which, experimentally, are approximately constant ones. The identification of the pomeron and the prediction of its properties was a major success of the Regge theory of strong interaction phenomenology. In later years, a BFKL pomeron was derived in further kinematic regimes from perturbative calculations in QCD, but its relationship to the pomeron seen in soft high energy scattering is still not fully understood. One consequence of the pomeron hypothesis is that the cross sections of proton–proton and proton–antiproton scattering should be equal at high enough energies. This was demonstrated by the Soviet physicis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pion
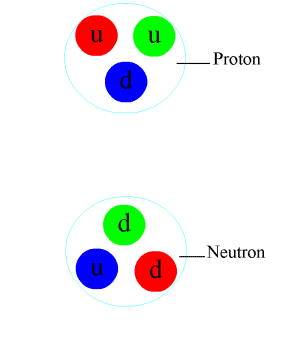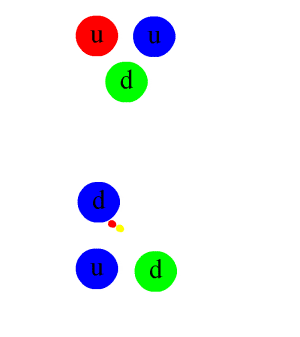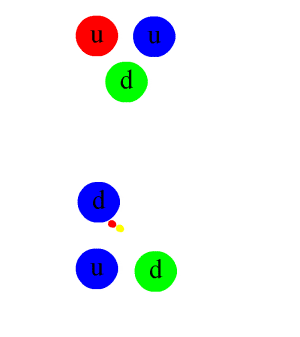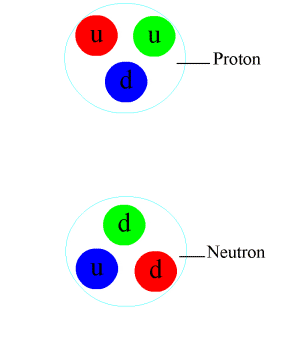
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual pions, along with vector, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some matter–antimatter annihilation events. All types of pions are also produced in natural processes wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subatomic Particles
In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that composes an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). Particle physics and nuclear physics study these particles and how they interact. Experiments show that light could behave like a stream of particles (called photons) as well as exhibiting wave-like properties. This led to the concept of wave–particle duality to reflect that quantum-scale behave like both particles and waves; they are sometimes called wavicles to reflect this. Another concept, the uncertainty principle, states that some of their properties taken together, such as their simultaneous position and momentum, cannot be measured exactly. The wave–particle duality has been shown to apply n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamás Csörgő
Tamás () is a Hungarian, masculine given name. It is a Hungarian equivalent of the name Thomas. The given name may refer to: * Tamás Bognár (born 1978), Hungarian footballer * Tamás Gábor (1932–2007), Hungarian Olympic champion épée fencer * Tamás Mendelényi (1936–1999), Hungarian fencer * Tamás Varga (rower) (born 1978), Hungarian rower * Tamás Varga (water polo) (born 1975), Hungarian water polo player * Tamás Wichmann Tamás Wichmann (4 February 1948 – 12 February 2020) was a Hungarian sprint canoeist who competed from 1966 to 1983. Competing in four Summer Olympics, he won three medals. This included two silver (C-1 1000 m: 1972 ... (1948–2020), Hungarian canoer Tamás is also used as a surname. Notable holders of the surname include: * G.M. Tamás (born 1948), Hungarian philosopher, critic, and former politician See also * All Wikipedia pages beginning with Tamás {{DEFAULTSORT:Tamas (name) Hungarian masculine giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giuseppe Cocconi
Giuseppe Cocconi (1914–2008) was an Italian physicist who was director of the Proton Synchrotron at CERN in Geneva. He is known for his work in particle physics and for his involvement with SETI where he wrote, " e probability of success is difficult to estimate; but if we never search, the chance of success is zero." Life Cocconi was born in Como, Kingdom of Italy in 1914. He went to study physics at the University of Milan, and then in February 1938, went to the Sapienza University of Rome on the invitation of Edoardo Amaldi. There he met physicists Enrico Fermi, and Gilberto Bernardini. With Fermi, he built a Wilson chamber to study the disintegration of mesons. In August of that year, Cocconi laid the foundation of cosmic ray research in Milan. While at Milan, Cocconi supervised Vanna Tongiorgi, who picked cosmic rays as her thesis' subject, and later married her in 1945. In 1942, Cocconi was nominated professor at University of Catania, but was engaged by the Italian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open String (physics)
Open or OPEN may refer to: Music * Open (band), Australian pop/rock band * The Open (band), English indie rock band * ''Open'' (Blues Image album), 1969 * ''Open'' (Gotthard album), 1999 * ''Open'' (Cowboy Junkies album), 2001 * ''Open'' (YFriday album), 2001 * ''Open'' (Shaznay Lewis album), 2004 * ''Open'' (Jon Anderson EP), 2011 * ''Open'' (Stick Men album), 2012 * ''Open'' (The Necks album), 2013 * ''Open'', a 1967 album by Julie Driscoll, Brian Auger and the Trinity * ''Open'', a 1979 album by Steve Hillage * "Open" (Queensrÿche song) * "Open" (Mýa song) * "Open", the first song on The Cure album ''Wish'' Literature * ''Open'' (Mexican magazine), a lifestyle Mexican publication * ''Open'' (Indian magazine), an Indian weekly English language magazine featuring current affairs * ''OPEN'' (North Dakota magazine), an out-of-print magazine that was printed in the Fargo, North Dakota area of the U.S. * Open: An Autobiography, Andre Agassi's 2009 memoir Computin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed String
In physics, a string is a physical entity postulated in string theory and related subjects. Unlike elementary particles, which are zero-dimensional or point-like by definition, strings are one-dimensional extended entities. Researchers often have an interest in string theories because theories in which the fundamental entities are strings rather than point particles automatically have many properties that some physicists expect to hold in a fundamental theory of physics. Most notably, a theory of strings that evolve and interact according to the rules of quantum mechanics will automatically describe quantum gravity. Overview In string theory, the strings may be open (forming a segment with two endpoints) or closed (forming a loop like a circle) and may have other special properties. Prior to 1995, there were five known versions of string theory incorporating the idea of supersymmetry, which differed in the type of strings and in other aspects. Today these different string theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gizmodo
''Gizmodo'' ( ) is a design, technology, science and science fiction website. It was originally launched as part of the Gawker Media network run by Nick Denton, and runs on the Kinja platform. ''Gizmodo'' also includes the subsite ''io9'', which focuses on science fiction and futurism. ''Gizmodo'' is now part of G/O Media, owned by private equity firm Great Hill Partners. History The blog, launched in 2002, was originally edited by Peter Rojas, who was later recruited by Weblogs, Inc. to launch their similar technology blog, ''Engadget''. By mid-2004, ''Gizmodo'' and ''Gawker'' together were bringing in revenue of approximately $6,500 per month. Gizmodo then launched in other locations: *In 2005, VNU and Gawker Media formed an alliance to republish ''Gizmodo'' across Europe, with VNU translating the content into French, German, Dutch, Spanish, Italian and Portuguese, and adding local European-interest material. *In 2006, ''Gizmodo Japan'' was launched by Mediagene, with add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tevatron
The Tevatron was a circular particle accelerator (active until 2011) in the United States, at the Fermilab, Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (also known as ''Fermilab''), east of Batavia, Illinois, and is the second highest energy particle collider ever built, after the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) of the CERN, European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) near Geneva, Switzerland. The Tevatron was a synchrotron that accelerated protons and antiprotons in a ring to energies of up to 1 TeV, hence its name. The Tevatron was completed in 1983 at a cost of $120 million and significant upgrade investments were made during its active years of 1983–2011. The main achievement of the Tevatron was the discovery in 1995 of the top quark—the last Elementary particle#Fundamental fermions, fundamental fermion predicted by the Standard Model of particle physics. On July 2, 2012, scientists of the Collider Detector at Fermilab, CDF and D0 experiment, DØ collider experiment teams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DØ Experiment
The DØ experiment (sometimes written D0 experiment, or DZero experiment) was a worldwide collaboration of scientists conducting research on the fundamental nature of matter. DØ was one of two major experiments (the other was the CDF experiment) located at the Tevatron Collider at Fermilab in Batavia, Illinois. The Tevatron was the world's highest-energy accelerator from 1983 until 2009, when its energy was surpassed by the Large Hadron Collider. The DØ experiment stopped taking data in 2011, when the Tevatron shut down, but data analysis is still ongoing. The DØ detector is preserved in Fermilab's DØ Assembly Building as part of a historical exhibit for public tours. DØ research is focused on precise studies of interactions of protons and antiprotons at the highest available energies. These collisions result in "events" containing many new particles created through the transformation of energy into mass according to the relation E=mc2. The research involves an inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |