|
B1 Road (Kenya)
B1, B.I, B.1 or B-1 may refer to: Biology and chemistry * Bradykinin receptor B1, a human protein * Cinnamtannin B1, a condensed tannin found in cinnamon * Combretastatin B-1, a stilbenoid found in ''Combretum sp.'' * Fumonisin B1, a toxins produced by several species of ''Fusarium'' molds * B-1 cell, a lymphocyte type * Arecatannin B1, a tannin found in the betel nut * Proanthocyanidin B1, a B type proanthocyanidin * Vitamin B1, also known as thiamine Media * B1 TV, a Romanian TV network * A class of FM radio broadcasting in North America Roads Vehicles * Rockwell B-1 Lancer, a United States Air Force strategic bomber * B1 (New York City bus) serving Brooklyn * B1 type submarine, a World War II Imperial Japanese Navy submarine class * Alsace-Lorraine B 1, an Alsace-Lorraine P 1 class steam locomotive * Marussia B1, a high-performance luxury sports coupé built by Russian automaker Marussia Motors * GS&WR Class B1, a Great Southern and Western Railway Irish ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradykinin Receptor B1
Bradykinin receptor B1 (B1) is a G-protein coupled receptor encoded by the BDKRB1 gene in humans. Its principal ligand is bradykinin, a 9 amino acid peptide generated in pathophysiologic conditions such as inflammation, trauma, burns, shock, and allergy. The B1 receptor is one of two of G protein-coupled receptors that have been found which bind bradykinin and mediate responses to these pathophysiologic conditions. B1 protein is synthesized ''de novo'' following tissue injury and receptor binding leads to an increase in the cytosolic calcium ion concentration, ultimately resulting in chronic and acute inflammatory responses. Classical agonist of this receptor includes bradykinin1-8 (bradykinin with the first 8 amino acid) and antagonist includes [Leu8]-bradykinin1-8. Antagonists * LF22-0542 See also * Bradykinin receptor References External links * * * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranerecepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS B1
HMS ''B1'' was the lead boat of the B-class submarines built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. The boat survived the First World War and was sold for scrap in 1921. Design and description The B class was an enlarged and improved version of the preceding A class. The submarines had a length of overall, a beam of and a mean draft of . They displaced on the surface and submerged. The B-class submarines had a crew of two officers and thirteen ratings.Gardiner & Gray, p. 87 For surface running, the boats were powered by a single 16-cylinder Vickers petrol engine that drove one propeller shaft. When submerged the propeller was driven by a electric motor. They could reach on the surface and underwater. On the surface, the B class had a range of at .Akermann, p. 123 The boats were armed with two 18-inch (450 mm) torpedo tubes in the bow. They could carry a pair of reload torpedoes, but generally did not as they would have to remove an equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B1 (classification)
B1 is a medical-based Paralympic classification for blind sport. Athletes in this classification are totally or almost totally blind. It is used by a number of blind sports including blind tennis, para-alpine skiing, para-Nordic skiing, blind cricket, blind golf, five-a-side football, goalball and judo. Some other sports, including adaptive rowing, athletics and swimming, have equivalents to this class. The B1 classification was first created by the IBSA in the 1970s, and has largely remained unchanged since despite an effort by the International Paralympic Committee (IPC) to move towards a more functional and evidence-based classification system. Classification is often handled on the international level by the International Blind Sports Federation (IBSA) but it sometimes handled by national sport federations. There are exceptions for sports like athletics and cycling, where classification is handled by their own governing bodies. Equipment utilized by competitors in this cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B1 (archive Format)
B1 is an open archive file format that supports data compression and archiving. B1 files use the file extension ".b1" or ".B1" and the MIME media type application/x-b1. B1 incorporates the LZMA compression algorithm. B1 archive combines a number of files and folders into one or more volumes, optionally adding compression and encryption. Construction of the B1 archive involves creating a binary stream of records and building volumes of that stream. The B1 archive format supports password-based AES-256 encryption. B1 files are created and opened with its native open-source B1 Pack Tool, as well as B1 Free Archiver utility. B1 Pack Project B1 Pack is an open-source software project that produces a cross-platform command-line tool and a Java library for creating and extracting file archives in the B1 archive format. Source code of the project is published at GitHub. B1 Pack Project is released under the Apache License. The B1 Pack Tool module builds a single executable JAR file ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Steam Locomotive Class B1
The Finnish Steam Locomotive Class B1 is an built by Beyer, Peacock & Company, at its Gorton Foundry in Manchester, England. Nine were constructed between 1868 and 1890. They were designed for use as shunting locomotives. Number 9 is Finland's oldest preserved locomotive and is preserved at the Finnish Railway Museum The Finnish Railway Museum ( fi, Suomen Rautatiemuseo) is located in Hyvinkää, Finland. It was founded in 1898 and located in Helsinki. The museum was moved to Hyvinkää in 1974. The museum is on the original station and yard site of the Hank .... The B1 was nicknamed “Ram”. They were numbered 9–10, 53–56, 150–151. B1 locomotives were withdrawn in the 1920s. The last was withdrawn in 1928. References * Sakari K. Salo: Höyryveturikirja, s. 14. Helsinki: Kustantaja Laaksonen, 2009. . External links Finnish Railway Museum {{Fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boom XB-1 Baby Boom
The Boom XB-1 "Baby Boom" is a one-third-scale trijet supersonic demonstrator designed by Boom Technology ( dba "Boom Supersonic") as part of development of the Boom Overture supersonic transport airliner. Powered by three General Electric J85s, it is planned to maintain Mach 2.2, with over of range. Taxi tests began in December 2022, with flight tests expected in 2023. Development The design was unveiled in Denver on November 15, 2016, and it was initially intended to make its first subsonic flight in late 2017, powered by three General Electric CJ610 turbojets (a civilian J85), with subsequent supersonic flight testing at Edwards Air Force Base. By April 2017, enough financing was secured to build and fly it. Its preliminary design review was completed by June 2017, with a switch of engine to the military version of the J85 to take advantage of its extra thrust. It was then anticipated that flight tests would start late 2018. In 2017, the composite wing spar was load tested ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B1 Centauro
The Centauro is a family of Italian military vehicles originating from a wheeled tank destroyer for light to medium territorial defense and tactical reconnaissance. It was developed by a consortium of manufacturers, the Società Consortile Iveco Fiat - OTO Melara (CIO). Iveco Fiat was tasked with developing the hull and propulsion systems while Oto Melara was responsible for developing the turrets and weapon systems. Over the years, the Centauro platform has been developed into multiple variants to fulfill other combat roles, such as infantry fighting vehicle or self-propelled howitzer. Description The vehicle was developed in response to an Italian Army requirement for a tank destroyer with the firepower of the old Leopard 1 main battle tank then in service with the Italian Army, but with greater strategic mobility. The main mission of the Centauro is to protect other, lighter, elements of the cavalry, using its good power-to-weight ratio, excellent range and cross country abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
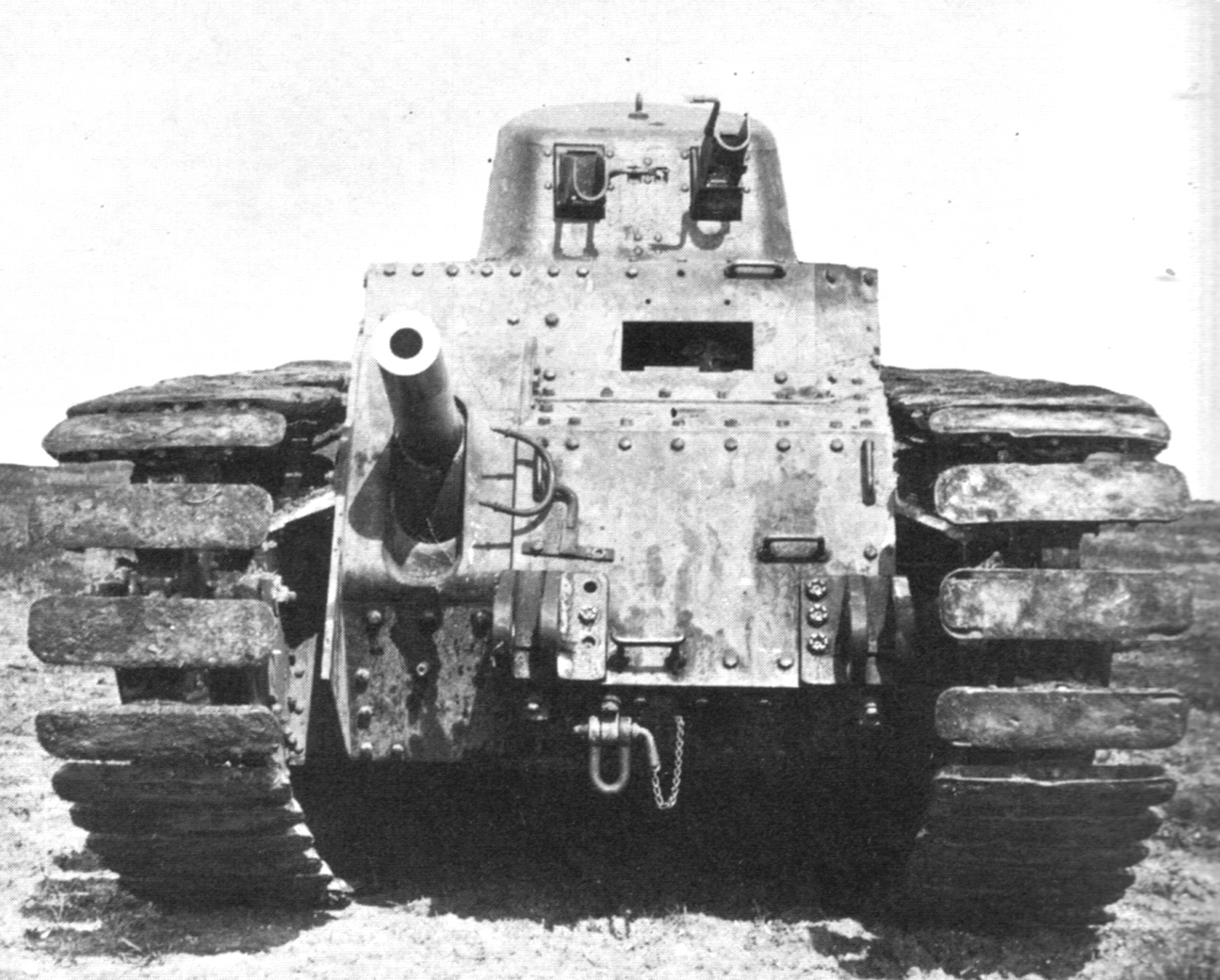
Char B1
The Char B1 was a French heavy tank manufactured before World War II. The Char B1 was a specialised break-through vehicle, originally conceived as a self-propelled gun with a 75 mm howitzer in the hull; later a 47 mm gun in a turret was added, to allow it to function also as a , a "battle tank" fighting enemy armour, equipping the armoured divisions of the Infantry Arm. Starting in the early twenties, its development and production were repeatedly delayed, resulting in a vehicle that was both technologically complex and expensive, and already obsolescent when real mass-production of a derived version, the Char B1 "bis", started in the late 1930s. A further up-armoured version, the Char B1 "ter", was only built in two prototypes. Among the most powerfully armed and armoured tanks of its day, the type was very effective in direct confrontations with German armour in 1940 during the Battle of France, but low speed and high fuel consumption made it ill-adapted to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brasilsat B1
Brasilsat B1 is a Brazilian communications satellite launched on August 10, 1994, by an Ariane rocket model 44LP at Guiana Space Centre which is located in Kourou, French Guiana. History It was constructed by the United States and Brazil and is classified as a second generation satellite. It is larger and more powerful than the previous generation of satellites. The Boeing Company (which chose to expand its presence in another aerospace field of satellite communications by purchasing Hughes Electronics Corporation, the builder of Brasilsat B1 and B2) contracted the acquisition of three satellites from Hughes. As part of the contract, Hughes would divide the work with Promon Engenharia SA of São Paulo. Brasilsat B1 and B2 were tested by the Institute of Space Research - INPE of São José dos Campos, Brasilsat B3 and B4 were tested in the Hughes laboratories. The contract also included renovation of sensor equipment and telemetry, provided by Guaratiba Center for Satellite Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS B-1 (SS-10)
USS ''B-1'' (SS-10) was the lead ship of her class of submarines built for the United States Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. Description The B-class submarines were enlarged versions of the preceding ''Plunger'' class. They had a length of overall, a beam of and a mean draft of . They displaced on the surface and submerged. The B-class boats had a crew of one officer and nine enlisted men. They had a diving depth of .Friedman, p. 306 For surface running, they were powered by one gasoline engine that drove the single propeller shaft. When submerged the propeller was driven by a electric motor. The boats could reach on the surface and underwater. On the surface, they had a range of at and at submerged. The B-class boats were armed with two 18 inch (450 mm) torpedo tubes in the bow. They carried two reloads, for a total of four torpedoes.Gardiner & Gray, p. 127 Construction and career ''B-1'' was laid down by Fore River Shipbuilding Company in Qui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn B-1
Studied in 1959, the ''Saturn B-1'', was a four-stage concept rocket similar to the Jupiter-C, and consisted of a Saturn IB first stage, a cluster of four Titan I first stages used for a second stage, a S-IV third stage and a Centaur high-energy liquid-fueled fourth stage. Like its proposed predecessors, the Saturn B-1 never flew and neither did the Titan cluster stage. The S-IV however flew on the Saturn I. See also *List of space launch system designs Even before the launch of Sputnik 1, there were various types of launch vehicle designs. The launch vehicle designs described below are either canceled or never left the drawing board. 20th century 21st century See also *Comparison of or ... References * Koelle, Heinz Hermann, ''Handbook of Astronautical Engineering'', McGraw-Hill,New York, 1961. The only such comprehensive handbook ever produced, and at the dawn of the space age. * Bilstein, Roger E, ''Stages to Saturn'', US Government Printing Office, 1980. . Excellen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania Railroad Class B1
The Pennsylvania Railroad's class B1 comprised 42 switcher-type electric locomotives built between 1926 and 1935. They were of 0-6-0 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation with 700 horsepower. As built, the first 28 locomotives in the 1926 order formed semi-permanently coupled pairs grouped in three classes. The first, class BB1, were AC powered and served as prototypes. The second, class BB2, were DC powered and served in the New York Terminal district, specifically between Sunnyside Yard and New York Penn Station. The third, class BB3, was AC powered and built for the Long Island Rail Road's electrified freight operation on the Bay Ridge Branch. In 1934 a follow-up order of 14 locomotives were built as single unit class B1 for the expanding main line AC electrification system. In addition to these new units all previous BB classes were split into single units and the BB2 class were re-powered for AC operation as that system replaced the old 650 V DC system in the New York ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |