|
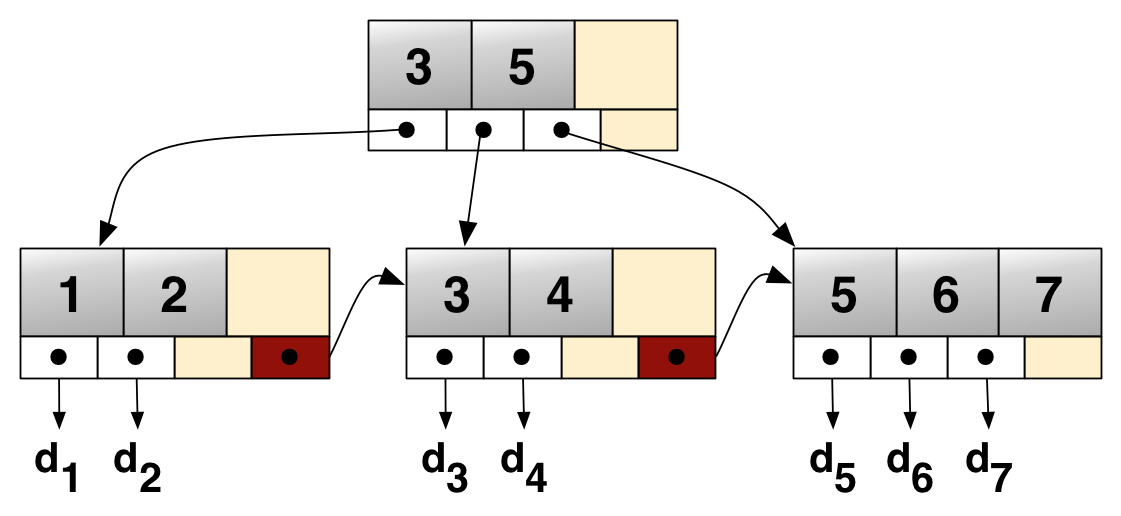
B Tree
A B+ tree is an m-ary tree with a variable but often large number of children per node. A B+ tree consists of a root, internal nodes and leaves. The root may be either a leaf or a node with two or more children. A B+ tree can be viewed as a B-tree in which each node contains only keys (not key–value pairs), and to which an additional level is added at the bottom with linked leaves. The primary value of a B+ tree is in storing data for efficient retrieval in a Block (data storage), block-oriented storage context—in particular, filesystems. This is primarily because unlike binary search trees, B+ trees have very high fanout (number of pointers to child nodes in a node, typically on the order of 100 or more), which reduces the number of I/O operations required to find an element in the tree. History There is no single paper introducing the B+ tree concept. Instead, the notion of maintaining all data in leaf nodes is repeatedly brought up as an interesting variant of the B- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree (data Structure)
In computer science, a tree is a widely used abstract data type that represents a hierarchical tree structure with a set of connected nodes. Each node in the tree can be connected to many children (depending on the type of tree), but must be connected to exactly one parent, except for the ''root'' node, which has no parent (i.e., the root node as the top-most node in the tree hierarchy). These constraints mean there are no cycles or "loops" (no node can be its own ancestor), and also that each child can be treated like the root node of its own subtree, making recursion a useful technique for tree traversal. In contrast to linear data structures, many trees cannot be represented by relationships between neighboring nodes (parent and children nodes of a node under consideration, if they exist) in a single straight line (called edge or link between two adjacent nodes). Binary trees are a commonly used type, which constrain the number of children for each parent to at most two. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branching Factor
In computing, tree data structures, and game theory, the branching factor is the number of children at each node, the outdegree. If this value is not uniform, an ''average branching factor'' can be calculated. For example, in chess, if a "node" is considered to be a legal position, the average branching factor has been said to be about 35, and a statistical analysis of over 2.5 million games revealed an average of 31. This means that, on average, a player has about 31 to 35 legal moves at their disposal at each turn. By comparison, the average branching factor for the game Go is 250. Higher branching factors make algorithms that follow every branch at every node, such as exhaustive brute force searches, computationally more expensive due to the exponentially increasing number of nodes, leading to combinatorial explosion. For example, if the branching factor is 10, then there will be 10 nodes one level down from the current position, 102 (or 100) nodes two levels down, 103 ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O'Reilly Media
O'Reilly Media, Inc. (formerly O'Reilly & Associates) is an American learning company established by Tim O'Reilly that provides technical and professional skills development courses via an online learning platform. O'Reilly also publishes books about programming and other technical content. Its distinctive brand features a woodcut of an animal on many of its book covers. The company was known as a popular tech conference organizer for more than 20 years before closing the live conferences arm of its business. Company Early days The company began in 1978 as a private consulting firm doing technical writing, based in the Cambridge, Massachusetts area. In 1984, it began to retain publishing rights on manuals created for Unix vendors. A few 70-page "Nutshell Handbooks" were well-received, but the focus remained on the consulting business until 1988. After a conference displaying O'Reilly's preliminary Xlib manuals attracted significant attention, the company began increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastopol, California
Sebastopol ( ) is a city in Sonoma County, California, with a recorded population of 7,521, per the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. Census. Sebastopol was once primarily a plum- and apple-growing region. Wine grapes are the predominant agriculture crop, and nearly all lands once used for orchards are now vineyards. The creation of The Barlow, a $32 million mall on a floodplain in Sebastopol, has converted old agricultural warehouses into a marketplace for dining, tasting rooms, and art, and has made Sebastopol a Wine Country destination. Horticulturist Luther Burbank had gardens in this region. The city hosts an annual Apple Blossom Festival in April, Gravenstein Apple Fair in August, and is home to the Sebastopol Documentary Film Festival. History Etymology The settlement was originally named Pine Grove. The name change to Sebastopol has historically been attributed to a bar fight in the late 1850s, which was allegedly compared by a bystander to the long Allied Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relational Database
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured format using rows and columns. Many relational database systems are equipped with the option of using SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and updating the database. History The concept of relational database was defined by E. F. Codd at IBM in 1970. Codd introduced the term ''relational'' in his research paper "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks". In this paper and later papers, he defined what he meant by ''relation''. One well-known definition of what constitutes a relational database system is composed of Codd's 12 rules. However, no commercial implementations of the relational model conform to all of Codd's rules, so the term has gradually come to describe a broader class of database systems, which at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Page Cache
In computing, a page cache, sometimes also called disk cache, is a transparent cache for the pages originating from a secondary storage device such as a hard disk drive (HDD) or a solid-state drive (SSD). The operating system keeps a page cache in otherwise unused portions of the main memory (RAM), resulting in quicker access to the contents of cached pages and overall performance improvements. A page cache is implemented in kernels with the paging memory management, and is mostly transparent to applications. Usually, all physical memory not directly allocated to applications is used by the operating system for the page cache. Since the memory would otherwise be idle and is easily reclaimed when applications request it, there is generally no associated performance penalty and the operating system might even report such memory as "free" or "available". When compared to main memory, hard disk drive read/writes are slow and random accesses require expensive disk seeks; as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database Index
A database index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure. Indexes are used to quickly locate data without having to search every row in a database table every time said table is accessed. Indexes can be created using one or more columns of a database table, providing the basis for both rapid random lookups and efficient access of ordered records. An index is a copy of selected columns of data, from a table, that is designed to enable very efficient search. An index normally includes a "key" or direct link to the original row of data from which it was copied, to allow the complete row to be retrieved efficiently. Some databases extend the power of indexing by letting developers create indexes on column values that have been transformed by functions or expressions. For example, an index could be created on upper(last_name), which would o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seek Time
Higher performance in hard disk drives comes from devices which have better performance characteristics. These performance characteristics can be grouped into two categories: #Access time, access time and #Data transfer rate, data transfer time (or rate). Access time The ''access time'' or ''response time'' of a rotating drive is a measure of the time it takes before the drive can actually Data transmission, transfer data. The factors that control this time on a rotating drive are mostly related to the mechanical nature of the rotating disks and moving Disk read-and-write head, heads. It is composed of a few independently measurable elements that are added together to get a single value when evaluating the performance of a storage device. The access time can vary significantly, so it is typically provided by manufacturers or measured in benchmarks as an average. The key components that are typically added together to obtain the access time are: * #Seek time, Seek time * #Rotati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Search
In computer science, binary search, also known as half-interval search, logarithmic search, or binary chop, is a search algorithm that finds the position of a target value within a sorted array. Binary search compares the target value to the middle element of the array. If they are not equal, the half in which the target cannot lie is eliminated and the search continues on the remaining half, again taking the middle element to compare to the target value, and repeating this until the target value is found. If the search ends with the remaining half being empty, the target is not in the array. Binary search runs in Time complexity#Logarithmic time, logarithmic time in the Best, worst and average case, worst case, making O(\log n) comparisons, where n is the number of elements in the array. Binary search is faster than linear search except for small arrays. However, the array must be sorted first to be able to apply binary search. There are specialized data structures designed fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big O Notation
Big ''O'' notation is a mathematical notation that describes the asymptotic analysis, limiting behavior of a function (mathematics), function when the Argument of a function, argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a member of a #Related asymptotic notations, family of notations invented by German mathematicians Paul Gustav Heinrich Bachmann, Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation. The letter O was chosen by Bachmann to stand for '':wikt:Ordnung#German, Ordnung'', meaning the order of approximation. In computer science, big O notation is used to Computational complexity theory, classify algorithms according to how their run time or space requirements grow as the input size grows. In analytic number theory, big O notation is often used to express a bound on the difference between an arithmetic function, arithmetical function and a better understood approximation; one well-known exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Statistic Tree
In computer science, an order statistic tree is a variant of the binary search tree (or more generally, a B-tree) that supports two additional operations beyond insertion, lookup and deletion: * Select(''i'') – find the ''i''-th smallest element stored in the tree * Rank(''x'') – find the rank of element ''x'' in the tree, i.e. its index in the sorted list of elements of the tree Both operations can be performed in worst case time when a self-balancing tree is used as the base data structure. Augmented search tree implementation To turn a regular search tree into an order statistic tree, the nodes of the tree need to store one additional value, which is the size of the subtree rooted at that node (i.e., the number of nodes below it). All operations that modify the tree must adjust this information to preserve the invariant that size = size eft[x + size[right[x + 1 where size[nil">">eft[x<_a>_+_size[right[x.html" ;"title=".html" ;"title="eft[x">eft[x + size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B+ Tree
A B+ tree is an m-ary tree with a variable but often large number of children per node. A B+ tree consists of a root, internal nodes and leaves. The root may be either a leaf or a node with two or more children. A B+ tree can be viewed as a B-tree in which each node contains only keys (not key–value pairs), and to which an additional level is added at the bottom with linked leaves. The primary value of a B+ tree is in storing data for efficient retrieval in a Block (data storage), block-oriented storage context—in particular, filesystems. This is primarily because unlike binary search trees, B+ trees have very high fanout (number of pointers to child nodes in a node, typically on the order of 100 or more), which reduces the number of I/O operations required to find an element in the tree. History There is no single paper introducing the B+ tree concept. Instead, the notion of maintaining all data in leaf nodes is repeatedly brought up as an interesting variant of the B- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |