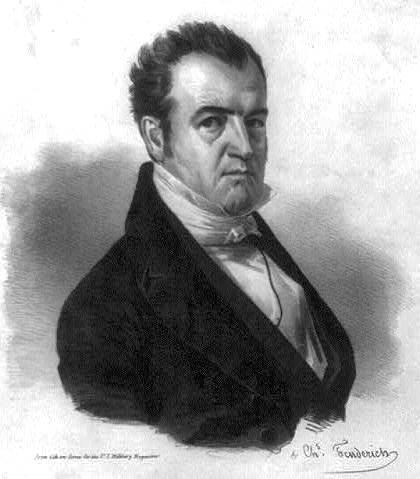|
B. H. Hill
Benjamin Harvey Hill (September 14, 1823 – August 16, 1882) was a politician whose career spanned state and national politics, and the Civil War. He served in the Georgia legislature in both houses. Although he had opposed secession, he stayed with the South and served as a Confederate senator representing Georgia. After the war and near the end of the Reconstruction era, Hill was elected in 1874 to the United States House of Representatives, and in 1877 as a U.S. senator from Georgia. He served in the Senate until his death in 1882. Early life Hill was born September 14, 1823, in Hillsboro, Georgia, in Jasper County. He was of Welsh and Irish American ancestry. He attended the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia, where he was a member of the Demosthenian Literary Society. He graduated in 1844 with first honors. He was admitted to the Georgia bar later in 1844. He married Caroline E. Holt in Athens, Georgia in 1845. Early career As a politician, Hill was affilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (U
Georgia most commonly refers to: * Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia * Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States Georgia may also refer to: Places Historical states and entities * Related to the country in the Caucasus ** Kingdom of Georgia, a medieval kingdom ** Georgia within the Russian Empire ** Democratic Republic of Georgia, established following the Russian Revolution ** Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, a constituent of the Soviet Union * Related to the US state ** Province of Georgia, one of the thirteen American colonies established by Great Britain in what became the United States ** Georgia in the American Civil War, the State of Georgia within the Confederate States of America. Other places * 359 Georgia, an asteroid * New Georgia, Solomon Islands * South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Canada * Georgia Street, in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada * Strait of Georgia, British Columbia, Canada United K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillsboro, Georgia
Hillsboro is an unincorporated community in Jasper County, Georgia, United States, established around 1795. Location and history The community of Hillsboro is located on Georgia State Route 11 (formerly the ''Macon to Athens Road'') south of the county seat of Monticello. Early years The community was established around 1795 and named after John and Isaac Hill, pioneer settlers, and originally spelled Hillsborough. It was the county seat of Baldwin County briefly in 1806 before the county was divided into Jasper and other counties. It is the birthplace of Benjamin Harvey Hill, a United States and later Confederate States Senator. Civil War During the American Civil War, Hillsboro was in the path of Sherman's March to the Sea and suffered damage and plundering from Federal troops. The community was sacked a second time, when cavalry under Major General George Stoneman passed through on their way to Macon, where Stoneman was subsequently captured by the Confederate Army troops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinance Of Secession
An Ordinance of Secession was the name given to multiple resolutions drafted and ratified in 1860 and 1861, at or near the beginning of the Civil War, by which each seceding Southern state or territory formally declared secession from the United States of America. South Carolina, Mississippi, Georgia, and Texas also issued separate documents purporting to justify secession. Adherents of the Union side in the Civil War regarded secession as illegal by any means and President Abraham Lincoln, drawing in part on the legacy of President Andrew Jackson, regarded it as his job to preserve the Union by force if necessary. However, President James Buchanan, in his State of the Union Address of December 3, 1860, stated that the Union rested only upon public opinion and that conciliation was its only legitimate means of preservation; President Thomas Jefferson also had suggested in 1816, after his presidency but in official correspondence, that secession of some states might be desirabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bell (Tennessee Politician)
John Bell (February 18, 1796September 10, 1869) was an American politician, attorney, and planter who was a candidate for President of the United States in the election of 1860. One of Tennessee's most prominent antebellum politicians,Jonathan Atkins,John Bell" ''Tennessee Encyclopedia of History and Culture'', 2009. Retrieved: October 10, 2012. Bell served in the House of Representatives from 1827 to 1841, and in the Senate from 1847 to 1859. He was Speaker of the House for the 23rd Congress (1834–1835), and briefly served as Secretary of War during the administration of William Henry Harrison (1841). In 1860, he ran for president as the candidate of the Constitutional Union Party, a third party which took a neutral stance on the issue of slavery. and won the electoral votes of three states. Initially an ally of Andrew Jackson, Bell turned against Jackson in the mid-1830s and aligned himself with the National Republican Party and then the Whig Party, a shift that ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union (American Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union, also known as the North, referred to the United States led by President Abraham Lincoln. It was opposed by the secessionist Confederate States of America (CSA), informally called "the Confederacy" or "the South". The Union is named after its declared goal of preserving the United States as a constitutional union. "Union" is used in the U.S. Constitution to refer to the founding formation of the people, and to the states in union. In the context of the Civil War, it has also often been used as a synonym for "the northern states loyal to the United States government;" in this meaning, the Union consisted of 20 free states and five border states. The Union Army was a new formation comprising mostly state units, together with units from the regular U.S. Army. The border states were essential as a supply base for the Union invasion of the Confederacy, and Lincoln realized he could not win the war without control of them, especially Maryla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph E
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the modern-day Nordic countries. In Portuguese and Spanish, the name is "José". In Arabic, including in the Quran, the name is spelled '' Yūsuf''. In Persian, the name is "Yousef". The name has enjoyed significant popularity in its many forms in numerous countries, and ''Joseph'' was one of the two names, along with ''Robert'', to have remained in the top 10 boys' names list in the US from 1925 to 1972. It is especially common in contemporary Israel, as either "Yossi" or "Yossef", and in Italy, where the name "Giuseppe" was the most common male name in the 20th century. In the first century CE, Joseph was the second most popular male name for Palestine Jews. In the Book of Genesis Joseph is Jacob's eleventh son and Rachel's first son, and k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral College (United States)
The United States Electoral College is the group of presidential electors required by the Constitution to form every four years for the sole purpose of appointing the president and vice president. Each state and the District of Columbia appoints electors pursuant to the methods described by its legislature, equal in number to its congressional delegation (representatives and senators). Federal office holders, including senators and representatives, cannot be electors. Of the current 538 electors, an absolute majority of 270 or more ''electoral votes'' is required to elect the president and vice president. If no candidate achieves an absolute majority there, a contingent election is held by the United States House of Representatives to elect the president, and by the United States Senate to elect the vice president. The states and the District of Columbia hold a statewide or districtwide popular vote on Election Day in November to choose electors based upon how they have ple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Know-Nothing
The Know Nothing party was a nativist political party and movement in the United States in the mid-1850s. The party was officially known as the "Native American Party" prior to 1855 and thereafter, it was simply known as the "American Party". Members of the movement were required to say "I know nothing" whenever they were asked about its specifics by outsiders, providing the group with its colloquial name. Supporters of the Know Nothing movement believed that an alleged " Romanist" conspiracy by Catholics to subvert civil and religious liberty in the United States was being hatched. Therefore, they sought to politically organize native-born Protestants in defense of their traditional religious and political values. The Know Nothing movement is remembered for this theme because Protestants feared that Catholic priests and bishops would control a large bloc of voters. In most places, the ideology and influence of the Know Nothing movement lasted only one or two years before it d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore (January 7, 1800March 8, 1874) was the 13th president of the United States, serving from 1850 to 1853; he was the last to be a member of the Whig Party while in the White House. A former member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Upstate New York, Fillmore was elected as the 12th vice president of the United States in 1848, and succeeded to the presidency in July 1850 upon the death of U.S. President Zachary Taylor. Fillmore was instrumental in the passing of the Compromise of 1850, a bargain that led to a brief truce in the battle over the expansion of slavery. He failed to win the Whig nomination for president in 1852 but gained the endorsement of the nativist Know Nothing Party four years later and finished third in the 1856 presidential election. Fillmore was born into poverty in the Finger Lakes area of New York State, and his parents were tenant farmers during his formative years. Though he had little formal schooling, he rose from poverty b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellevue (LaGrange, Georgia)
Bellevue is a historic mansion house at 204 Ben Hill Street in LaGrange, Georgia, United States. Built in 1853–1855, it was the home of Senator Benjamin Harvey Hill, and is one of the state's finest examples of Greek Revival architecture. Now a historic house museum, it was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1973, and is a contributing structure in Broad Street Historic District. Description and history Bellevue is located in central LaGrange, on an oval parcel located at the north end of Ben Hill Street, and flanked on both sides by McLendon Circle. It is a two-story wood-frame structure with a two-story Greek temple front, featuring six fluted Ionic columns with four-sided capitals, and a heavy multi-level entablature below a dentillated cornice. Set within the temple front is a second-floor balcony with a turned balustrade, and a center entrance recessed in an opening flanked by pilasters and topped by an entablature. Ells extend the house, joining it to what was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demosthenian Literary Society
The Demosthenian Literary Society is a literary society focused on extemporaneous debate at the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia. It is among the oldest literary societies in the English-Speaking world and was founded on February 19, 1803 by the first graduating class of the University's Franklin College. The object of the Society is "to promote the cause of science and truth by the cultivation of oratory and the art of debate at weekly meetings." It is named after the Greek orator Demosthenes. The Society meets every Thursday during the academic school year at 7pm and once during the summer in Demosthenian Hall on UGA's North Campus. In addition to its relations with other organizations at the University of Georgia, like the Phi Kappa Literary Society, the Society maintains relationships with other Literary and Debate societies across the United States, including the Philodemic Society at Georgetown University, the Dialectic and Philanthropic Societies at UNC-Chapel Hill a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |