|
A─čdaban
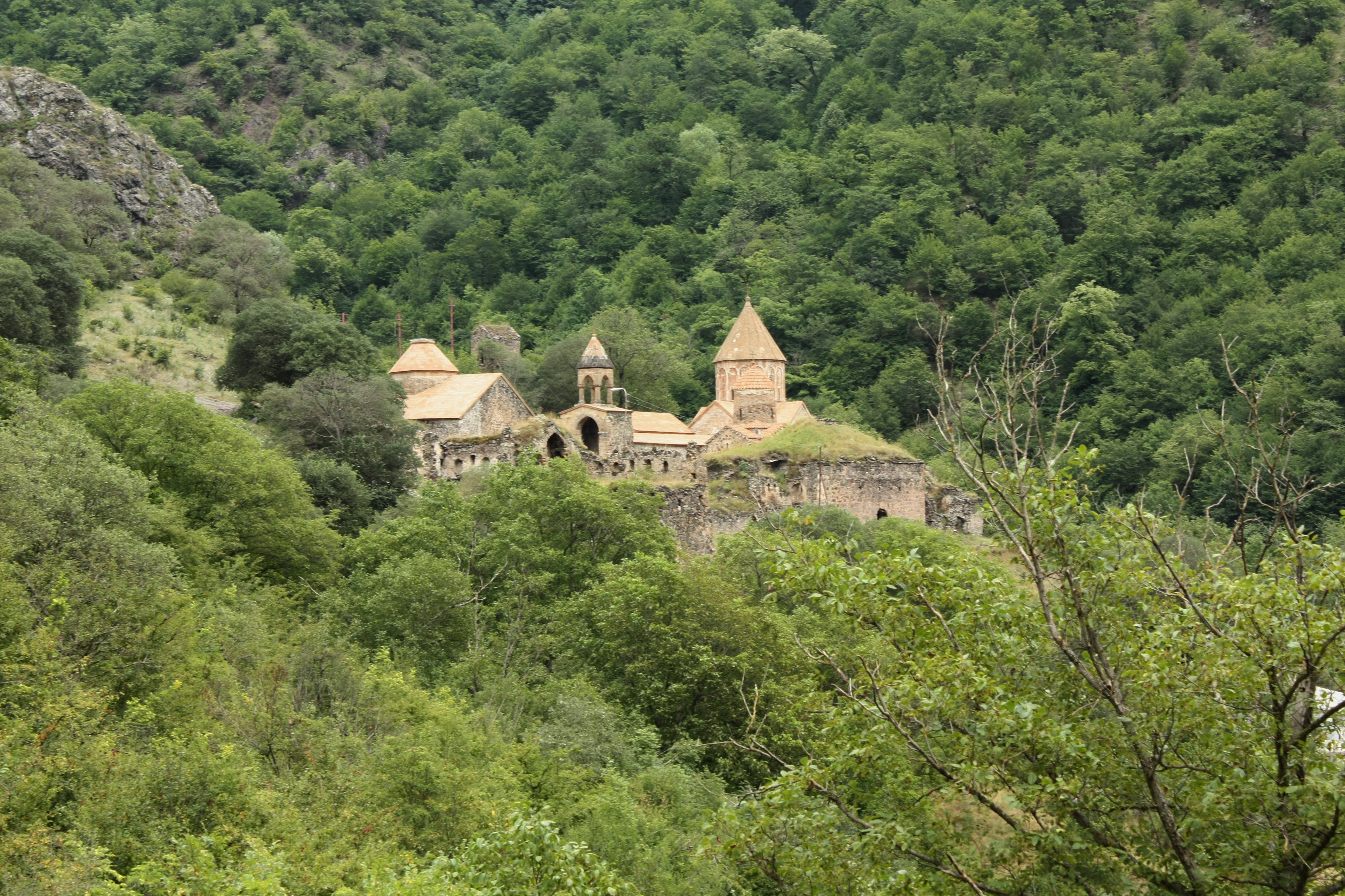
A─čdaban () is a village in the Kalbajar District of Azerbaijan. A─čdaban was one of two villages of Kalbajar forming an enclave inside of the Mardakert District of the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast of the Azerbaijan SSR Azerbaijan ( az, đÉđĚËÖĐÇđ▒đ░ĐśĎ╣đ░đŻ, Az╔Örbaycan, italics=no), officially the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic (Azerbaijan SSR; az, đÉđĚËÖĐÇđ▒đ░ĐśĎ╣đ░đŻ đíđżđ▓đÁĐé đíđżĐüđŞđ░đ╗đŞĐüĐé đáđÁĐüđ┐Đâđ▒đ╗đŞđ║đ░ĐüĐő, Az╔Örbaycan Sovet Sosialist R .... Aghdaban attack On March 26 1993, Armenian forces attacked Aghdaban Melkonian. ''My Brother's Road'', 243. References External links * Populated places in Kalbajar District {{DEFAULTSORT:Agdaban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally recognized. Examples Between 1805 and 1914, the ruling dynasty of Egypt were subject to the rulers of the Ottoman Empire, but acted as de facto independent rulers who maintained a polite fiction of Ottoman suzerainty. However, starting from around 1882, the rulers had only de jure rule over Egypt, as it had by then become a British puppet state. Thus, by Ottoman law, Egypt was de jure a province of the Ottoman Empire, but de facto was part of the British Empire. In U.S. law, particularly after ''Brown v. Board of Education'' (1954), the difference between de facto segregation (segregation that existed because of the voluntary associations and neighborhoods) and de jure segregation (segregation that existed because of local laws that m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by law"), which refers to things that happen according to official law, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. History In jurisprudence, it mainly means "practiced, but not necessarily defined by law" or "practiced or is valid, but not officially established". Basically, this expression is opposed to the concept of "de jure" (which means "as defined by law") when it comes to law, management or technology (such as standards) in the case of creation, development or application of "without" or "against" instructions, but in accordance with "with practice". When legal situations are discussed, "de jure" means "expressed by law", while "de facto" means action or what is practiced. Similar expressions: "essentially", "unofficial", "in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
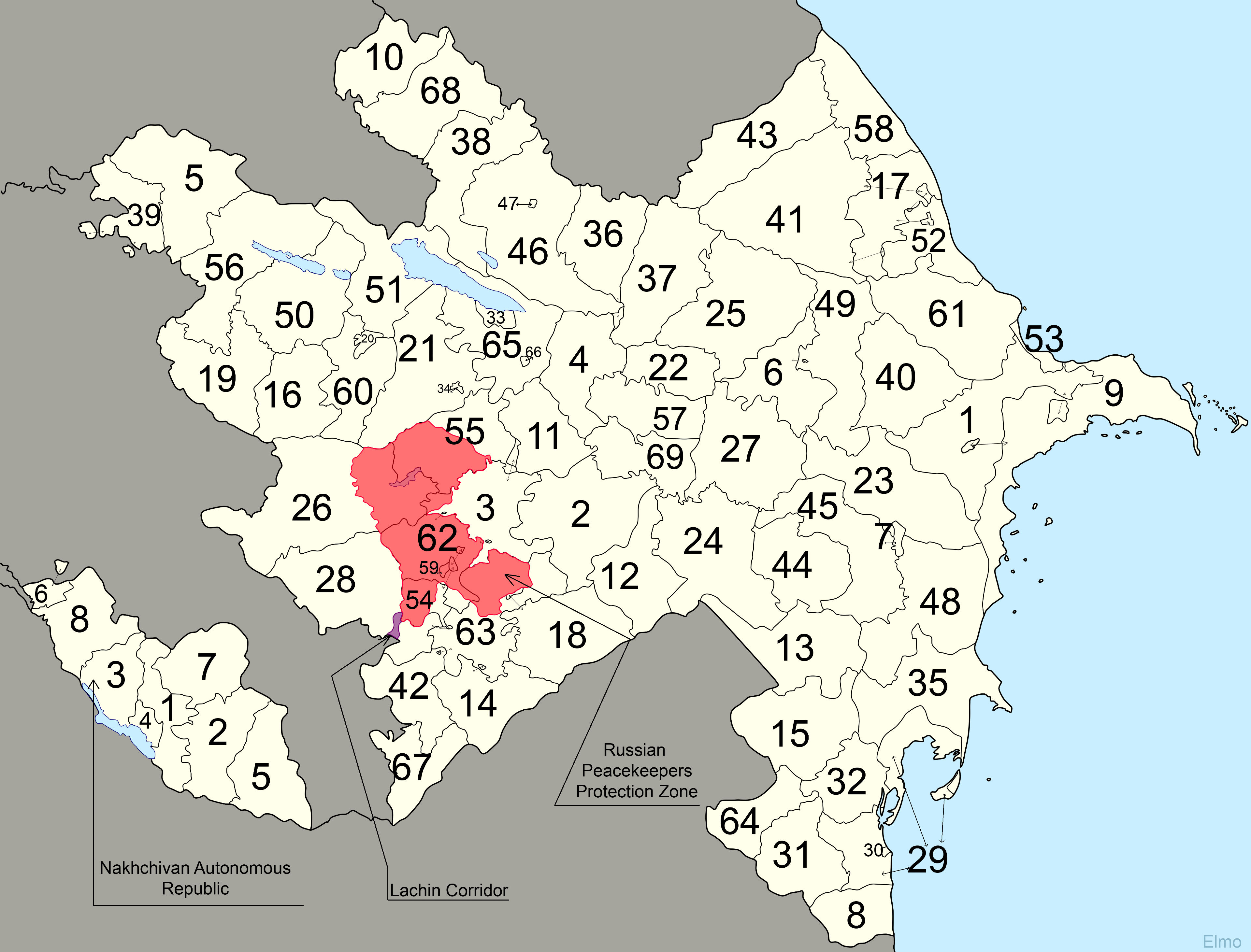
Administrative Divisions Of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 66 districts () and 11 cities () that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these, 7 districts and 1 city is located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into municipalities (). Additionally, the districts of Azerbaijan are grouped into 14 Economic Regions (). On July 7, 2021, the President of Azerbaijan Ilham Aliyev signed Decree "On the new division of economic regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan". Administrative divisions Contiguous Azerbaijan The territory of former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast presently consists of the districts of Khojavend, Shusha, Khojaly, the eastern portion of Kalbajar and the western portion of Tartar. The Autonomous Oblast was abolished on 26 November 1991, by the Supreme Soviet of the Azerbaijan SSR. Since then, the territory of the autonomous oblast has been administratively split between the aforementioned districts. As a result of the First N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalbajar District
Kalbajar District ( az, K╔Ölb╔Öc╔Ör rayonu) is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the west of the country and belongs to the East Zangezur Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Lachin, Khojaly, Agdam, Tartar, Goranboy, Goygol and Dashkasan districts of Azerbaijan, as well as the Gegharkunik and Vayots Dzor provinces of Armenia. Its capital and largest city is Kalbajar. As of 2020, the district had a nominal population of 94,100. History In Turkic ''Kalbajar'' means ''"Castle on the mouth of the river"''. The city of Kalbajar was renamed to ''Karvachar'' ( hy, ŇöŇíÍÇŇżŇíŇ│ŇíŇ╝) after its occupation in the First Nagorno-Karabakh war, which corresponds to the ancient district of Vaykunik, one of 12 cantons of Artsakh. Robert H. Hewsen, ''Armenia: A Historical Atlas''. The University of Chicago Press, 2001, pp. 40, 101ÔÇô102, 264ÔÇô265. It was also known as ''Upper-Khachen'' or ''Tsar'' ( after its chief town) and was ruled by one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of The Republic Of Artsakh
The administrative divisions of the Republic of Artsakh are of two types; provinces and cities. There are six provinces and one special administrative city - the capital of the Republic. Municipalities in Artsakh are divided into 2 categories: urban communities and rural communities. Before the 2020 war, there were 10 towns (urban) and 322 villages (rural) in Artsakh. Administrative divisions These divisions include territory controlled by Azerbaijan, which are officially considered occupied by Artsakh. : Totally under Azerbaijani control. : Partially under Azerbaijani control. Azerbaijan divisions and claimed territories Before the Artsakh republic was established, the territory was organized by the Republic of Azerbaijan into a number of rayons (districts). Artsakh extended its provinces across the border of the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast (NKAO), removing the administrative distinction between the two areas. The following districts, which were not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martakert Province
Martakert Province ( hy, ŇäŇíÍÇŇ┐ŇíһҹÍÇŇ┐) is a province of the Republic of Artsakh, ''de jure'' part of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The population is mainly Armenian. The province has 43 communities of which one is considered urban and 42 are rural. Cultural sites The Gandzasar monastery, the Yeghishe Arakyal Monastery and the 17th century Armenian monastery Yerits Mankants are located in the province. The Vankasar Monastery is just outside the town of Martakert. The archaeological site of Tigranakert of Artsakh Tigranakert ( hy, ď▒ÍÇÍüŇíҺҟ ŇĆŇźŇúÍÇŇíŇÂŇíһҹÍÇŇ┐, ''Arts'akhi Tigranakert''), also known as Tigranakert-Artsakh, is a ruined Armenian city dating back to the Hellenistic period, located in the Aghdam District of what is today Azerbaijan. I ... is also located in the province, thought to have been founded in the 2nd-1st century B.C, it has been undergoing excavation since 2005. Some of the walls of the city, with Hellenistic-style towers, as well as Arme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijan Time
Azerbaijan Time ( az, Azərbaycanda vaxt), abbreviated as AZT, is the standard time zone in Azerbaijan, four hours ahead of UTC ( UTC+04:00). The daylight saving time adjustment, Azerbaijan Summer Time (AZST), was one hour ahead at UTC+05:00 and was introduced in 1997 and discontinued in March 2016. Azerbaijan Time is the same as Samara Time (Russia), United Arab Emirates Standard Time, Georgia Time, Armenia Time and Seychelles Time. IANA time zone database The IANA time zone database The tz database is a collaborative compilation of information about the world's time zones, primarily intended for use with computer programs and operating systems. Paul Eggert is its current editor and maintainer, with the organizational backi ... contains one zone for Azerbaijan in the file zone.tab, named Asia/Baku. References Time in Azerbaijan {{Azerbaijan-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia (Republic of Dagestan) to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. Baku is the capital and largest city. The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic proclaimed its independence from the Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic in 1918 and became the first secular democratic Muslim-majority state. In 1920, the country was incorporated into the Soviet Union as the Azerbaijan SSR. The modern Republic of Azerbaijan proclaimed its independence on 30 August 1991, shortly before the dissolution of the Soviet Union in the same year. In September 1991, the ethnic Armenian majority of the Nagorno-Karabakh region formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mardakert District (NKAO)
Mardakert District ( az, Mardakert rayonu, đťđ░ĐÇđ┤đ░đ║đÁĐÇĐé ĐÇđ░ĐśđżđŻĐâ; hy, ŇäŇíÍÇŇĄŇíһҹÍÇŇ┐Ňź ŇĚÍÇŇ╗ŇíŇÂ) was an administrative unit within the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast (NKAO) of the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic. History The district was formed on 8 August 1930, as the ''Jrabert district''. It was renamed to Mardakert district on 17 September 1939. The administrative centre of the district was Mardakert. 3 urban-type settlements existed in the region: Madagiz (gained urban status in 1943), Mardakert (since 1960), Leninavan (since 1966). The district was the largest one in NKAO in terms of area and population. The Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast was abolished on 26 November 1991 and the district was renamed Aghdara ( az, A─čd╔Ör╔Ö). On 13 October 1992, the Aghdara district was also abolished and split between the three neighbouring districts, with the western part being incorporated into Kalbajar District, the northeastern part into the Tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast
The Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast (NKAO), DQMV, hy, ď╝ŇąŇ╝ŇÂŇíŇÁҟҠŇéŇíÍÇŇíŇóŇíŇ▓Ňź ď╗ŇÂÍäŇÂŇíŇżŇíÍÇ ŇäŇíÍÇŇŽ, ď╝Ňéď╗Ňä was an autonomous oblast within the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic that was created on July 7, 1923. Its capital was the city of Stepanakert. The leader of the oblast was the First Secretary of the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast Committee of the Communist Party of Azerbaijan. The majority of the population were ethnic Armenians. History The area was disputed between Armenia and Azerbaijan during their short-lived independence from 1918 and 1920. After the Sovietization of Armenia and Azerbaijan, the Kavbiuro organisation decided to keep the area within the Azerbaijan SSR whilst granting it broad regional autonomy. Initially, the principal city of Karabakh, Shusha, and its surrounding villages were to be excluded from the autonomy as they were predominantly Azerbaijani, particularly after the massacre and expulsion of the majority Armeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic
Azerbaijan ( az, đÉđĚËÖĐÇđ▒đ░ĐśĎ╣đ░đŻ, Az╔Örbaycan, italics=no), officially the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic (Azerbaijan SSR; az, đÉđĚËÖĐÇđ▒đ░ĐśĎ╣đ░đŻ đíđżđ▓đÁĐé đíđżĐüđŞđ░đ╗đŞĐüĐé đáđÁĐüđ┐Đâđ▒đ╗đŞđ║đ░ĐüĐő, Az╔Örbaycan Sovet Sosialist Respublikas─▒, italics=no, links=no; russian: đÉđĚđÁĐÇđ▒đ░đ╣đ┤đÂđ░đŻĐüđ║đ░ĐĆ đíđżđ▓đÁĐéĐüđ║đ░ĐĆ đíđżĐćđŞđ░đ╗đŞĐüĐéđŞĐçđÁĐüđ║đ░ĐĆ đáđÁĐüđ┐Đâđ▒đ╗đŞđ║đ░ ÉđĚđíđíđáAzerbaydzhanskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Respublika zSSR}), also referred to as Soviet Azerbaijan, was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union between 1922 and 1991. Created on 28 April 1920 when the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic brought pro-Soviet figures to power in the region, the first two years of the Azerbaijani SSR were as an independent country until incorporation into the Transcausasian SFSR, along with the Armenian SSR and the Georgian SSR. In December 1922, the Transcaucasian SFSR became part of the newly established Soviet Union. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |