|
Azimuth Compass
An azimuth compass (or azimuthal compass) is a nautical instrument used to measure the magnetic azimuth, the angle of the arc on the horizon between the direction of the sun or some other celestial object and the magnetic north. This can be compared to the true azimuth obtained by astronomical observation to determine the magnetic declination, the amount by which the reading of a ship's compass must be adjusted to obtain an accurate reading. Azimuth compasses were important in the period before development of the reliable chronometers needed to determine a vessel's exact position from astronomical observations. Theory In navigation, the true azimuth of a heavenly body is the arc of the horizon between the point where a vertical plane containing the observer and the heavenly body intersects the horizon and the direction of true north. The magnetic azimuth is the arc between the point on the horizon below the heavenly body and the direction of magnetic north. When the latitude and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boussole Marine
{{dab ...
Boussole (French "compass") may refer to: *La Boussole, French ship Boussole (1781) *Boussole Rock, Jukdo (island) * Boussole Strait in the Kuril Islands *''Boussole'' ( fr), novel by Mathias Énard 2015 Prix Goncourt *La Boussole ( fr), 1990s French rap group including Médine (rapper) Médine Zaouiche (; born 24 February 1983 in Le Havre), better known by his stage name Médine, is a French rapper of Algerian descent. He has been a part of the hip hop collective La Boussole since 1996. Médine is a practicing Muslim, and man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Adams (mutineer)
John Adams, known as Jack Adams (4 July 1767– 5 March 1829), was the last survivor of the mutineers who settled on Pitcairn Island in January 1790, the year after the mutiny. His real name was John Adams, but he used the name Alexander Smith until he was discovered in 1808 by Captain Mayhew Folger of the American whaling ship ''Topaz''. His children used the surname "Adams".Frederick Chamier ''Jack Adams, the Mutineer '' 1838 Pitcairn The mutineers of HMS ''Bounty'' and their Tahitian companions settled on the island and set fire to the ''Bounty''. Only the ballast stone remains of the wreck in Bounty Bay. Although the settlers were able to survive by farming and fishing, the initial period of settlement was marked by serious tensions among the settlers. Alcoholism, murder, disease and other ills had taken the lives of most of the mutineers and Tahitian men. John Adams, Ned Young, and Matthew Quintal were the last three mutineers surviving in 1799 when the thuggish Qui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
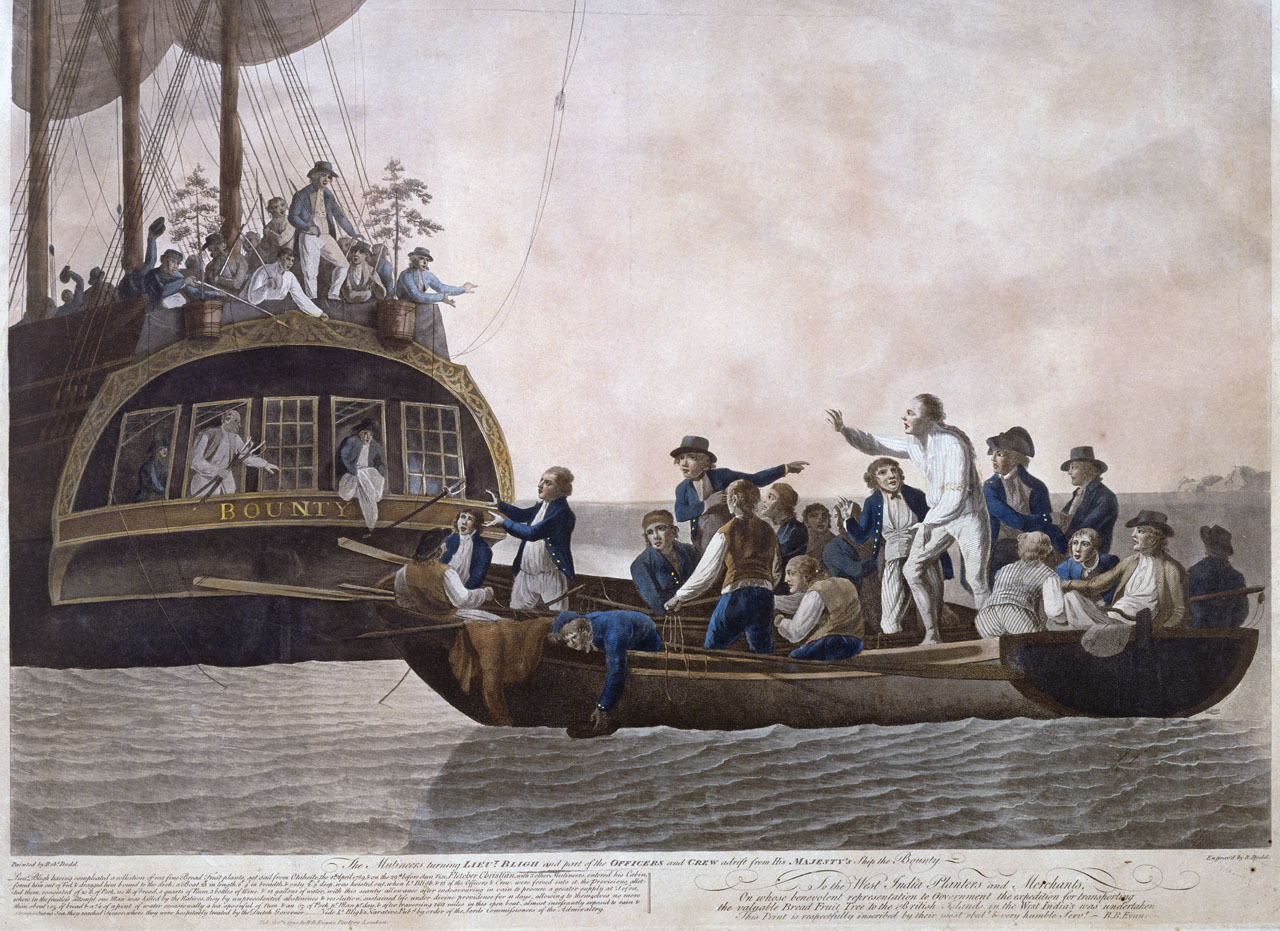
Mutiny On The Bounty
The mutiny on the Royal Navy vessel occurred in the South Pacific Ocean on 28 April 1789. Disaffected crewmen, led by acting-Lieutenant Fletcher Christian, seized control of the ship from their captain, Lieutenant William Bligh, and set him and eighteen loyalists adrift in the ship's open launch. The mutineers variously settled on Tahiti or on Pitcairn Island. Bligh navigated more than in the launch to reach safety, and began the process of bringing the mutineers to justice. ''Bounty'' had left England in 1787 on a mission to collect and transport breadfruit plants from Tahiti to the West Indies. A five-month layover in Tahiti, during which many of the men lived ashore and formed relationships with native Polynesians, led those men to be less amenable to military discipline. Relations between Bligh and his crew deteriorated after he allegedly began handing out increasingly harsh punishments, criticism, and abuse, Christian being a particular target. After three weeks ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
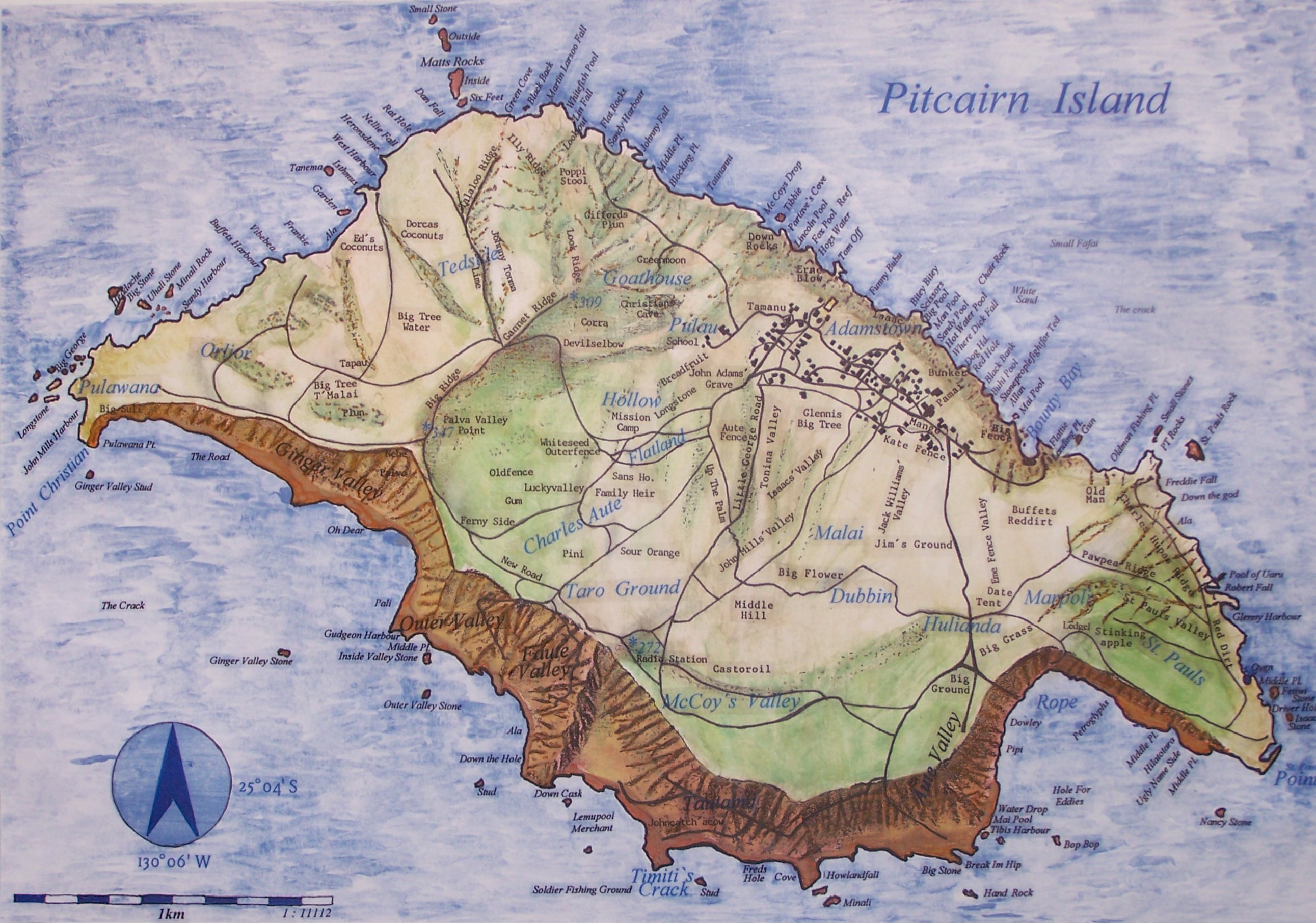
Pitcairn Island
Pitcairn Island is the only inhabited island of the Pitcairn Islands, of which many inhabitants are descendants of mutineers of HMS ''Bounty''. Geography The island is of volcanic origin, with a rugged cliff coastline. Unlike many other South Pacific islands, it is not surrounded by coral reefs that protect the coast. The only access to the island is via a small pier on Bounty Bay. Adamstown is the sole settlement. Pawala Valley Ridge is the island's highest point at 346 m above sea level. The volcanic soil and tropical climate with abundant rainfall make the soil productive. The average temperature ranges from 19 to 24°C. The annual rainfall is 1,800 mm. As there are no rivers or lakes, drinking water is collected from the rain with cisterns. Fauna Indigenous fauna consists of insects and lizards. Since their introduction, rats have become an invasive species. A large number of seabirds nest along the steep shorelines. Due to the absence of coral reefs, fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayhew Folger
Mayhew Folger (March 9, 1774 – September 1, 1828) was an American whaler who captained the sealing ship ''Topaz'' that rediscovered the Pitcairn Islands in 1808, while one of 's mutineers was still living. Early life and family Mayhew was born on March 12, 1774, in Nantucket, Massachusetts, the second child of William Folger and Ruth Coffin. Mayhew was a member of the Folger whaling family of Nantucket, who were prominent Quakers. He was the great-great-great grandson of Peter Foulger and Mary ''Morrill'' Foulger and, through them, is the first cousin, three times removed, of Benjamin Franklin. He married his second cousin, Mary Joy, on March 7, 1798, on Nantucket. Mayhew was the uncle of Lucretia Coffin Mott, daughter of his sister, Anna Folger, and Thomas Coffin. Folgers grandson, William Mayhew Folger (1844-1928), became a United States Navy rear admiral. Rediscovery of the Pitcairn Islands Mayhew Folger captained the ship ''Topaz'' that left Boston on April 5, 1807, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and to New Zealand and Australia in particular. He made detailed maps of Newfoundland prior to making three voyages to the Pacific, during which he achieved the first recorded European contact with the eastern coastline of Australia and the Hawaiian Islands, and the first recorded circumnavigation of New Zealand. Cook joined the British merchant navy as a teenager and joined the Royal Navy in 1755. He saw action in the Seven Years' War and subsequently surveyed and mapped much of the entrance to the St. Lawrence River during the siege of Quebec, which brought him to the attention of the Admiralty and the Royal Society. This acclaim came at a crucial moment for the direction of British overseas exploration, and it led to his commission in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Banks
Sir Joseph Banks, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1820) was an English naturalist, botanist, and patron of the natural sciences. Banks made his name on the 1766 natural-history expedition to Newfoundland and Labrador. He took part in Captain James Cook's first great voyage (1768–1771), visiting Brazil, Tahiti, and after 6 months in New Zealand, Australia, returning to immediate fame. He held the position of president of the Royal Society for over 41 years. He advised King George III on the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, and by sending botanists around the world to collect plants, he made Kew the world's leading botanical garden. He is credited for bringing 30,000 plant specimens home with him; amongst them, he was the first European to document 1,400. Banks advocated British settlement in New South Wales and the colonisation of Australia, as well as the establishment of Botany Bay as a place for the reception of convicts, and advised the British government on all Australian matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gowin Knight
Gowin Knight FRS (10 September 1713 – 8 June 1772) was a British physicist who, in 1745, discovered a process for producing strongly magnetised steel. He also served as the first principal librarian of the British Museum. Biography Born in Corringham, a small parish in Lincolnshire, Knight was educated at Leeds Grammar School and Magdalen Hall, Oxford. He was awarded a BA in October 1736, MA in June 1739 and MB in February 1742, after which he lived in London as a practising physician. In 1745, he discovered a process for forming strongly magnetised steel, which he used to develop a compass needle able to function with greater precision. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society the same year after presenting his findings to the Society. He was honoured in 1747 with the Copley Medal in recognition of his achievements and, by 1752, his technologically advanced compasses were adopted by the Royal Navy The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leadenhall Street
__NOTOC__ Leadenhall Street () is a street in the City of London. It is about and links Cornhill, London, Cornhill in the west to Aldgate in the east. It was formerly the start of the A11 road (England), A11 road from London to Norwich, but that route now starts further east at Aldgate. Leadenhall Street has always been a centre of commerce. It connected the medieval market of Leaden Hall with Aldgate, the eastern gate in the Roman city wall. The East India Company had its headquarters there, as later did the Peninsular and Oriental Steam Navigation Company (P&O). By the mid 20th century, grand stone-faced offices lined the street. Today it is closely associated with the insurance industry and particularly the Lloyd’s of London, Lloyd's insurance market, with its dramatic building in the adjacent Lime Street. It forms part of a cluster of tall buildings including the 48-storey 122 Leadenhall Street, “Cheesegrater” and the 38-storey The Scalpel, “Scalpel”. Other buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Gregory (instrument Maker)
Henry Gregory (1744–1782) was an English mathematical and optical instrument maker. Gregory was apprenticed to John Fowler in 1732 and was himself in business from c. 1750–1792 from premises in Francis Court, Clerkenwell, London and an establishment known as "The Azimuth Compass" in Leadenhall Street, London. His company later became known as Gregory and Son. Gregory manufactured navigational instruments, including quadrants of the type invented by John Hadley and compasses. One of his azimuth compasses traveled with the explorer James Cook on his second voyage to the southern Pacific Ocean in 1772–1775. An azimuth compass is a compass fitted with vertical sights, used to take the magnetic azimuth of a star or planet. Surviving examples of the azimuth compass exist in the collections of the National Maritime Museum The National Maritime Museum (NMM) is a maritime museum in Greenwich, London. It is part of Royal Museums Greenwich, a network of museums ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Ayres (instrument Maker)
Benjamin Ayres (died c. 1775) was an English instrument maker. Ayres may have been related to the scientist Thomas Ayres who was nominated to the Royal Society in 1707 and who was later involved in a joint-stock company to exploit the Newcomen steam engine. Ayres was an apprentice and brother-in-law of Jonathan Sisson of London. Ayres was active between 1731 and 1775, making mathematical instruments and compasses. He worked in Amsterdam from 1743 onward, and sold octants to the Dutch East India Company. His devices incorporate technical innovations introduced by Sisson, which were copied by others only after 1750. Some of them were included in the collection of instruments made by Gerard Arnout Hasselaer, a board member of the company. Hasselaer had connections with both Ayres and Sisson. In 1734 Caleb Smith invented a "sea quadrant" using an unsilvered glass mirror to reflect the image of the sun into the telescope. Ayres produced an instrument based on this design mounted o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_01.jpg)






.jpg)