|
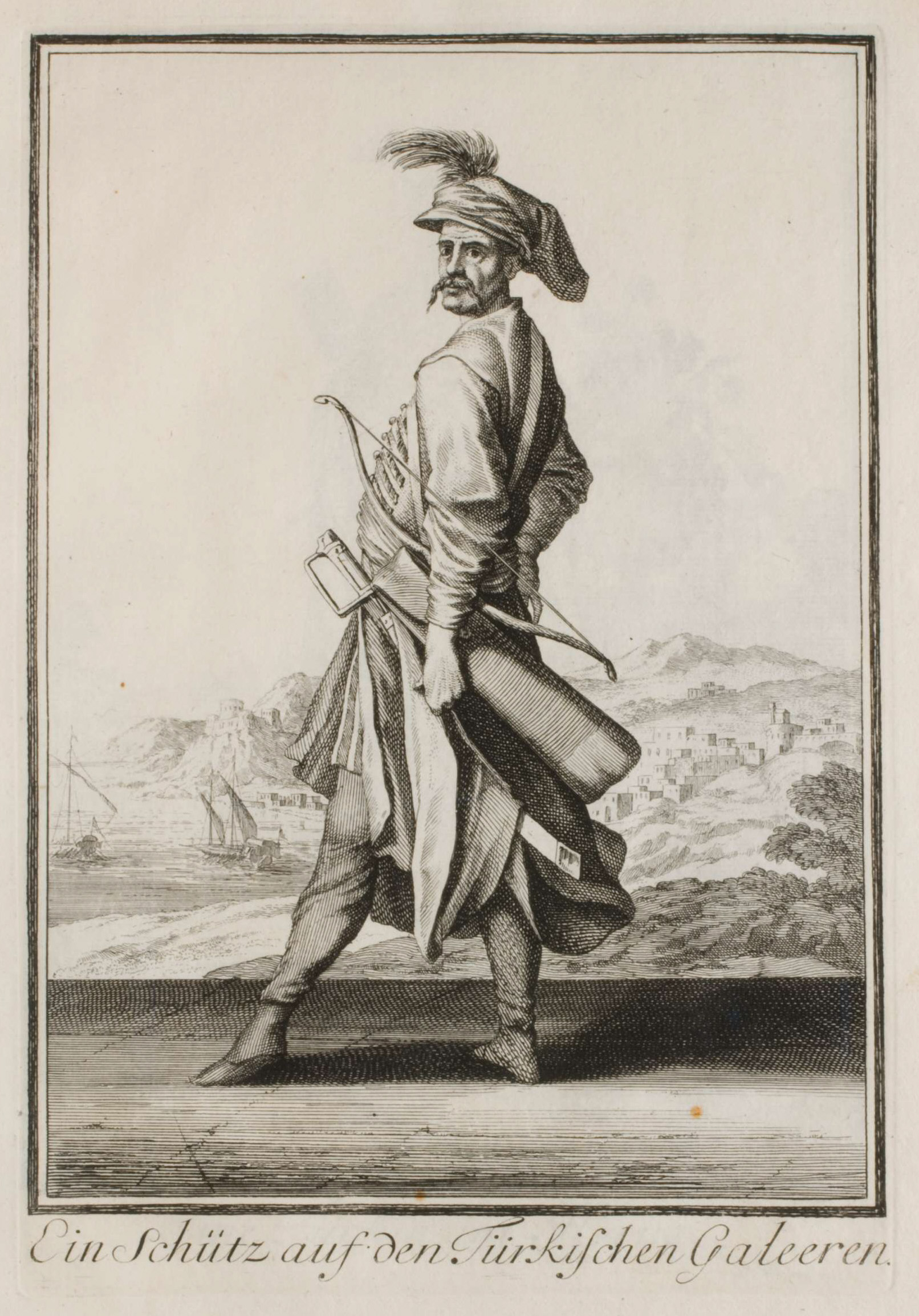
Azeb
Azebs, azabs or azaps ( ota, عزب, from Arabic, literally ''unmarried'', meaning ''bachelor''), also known as Asappes or Asappi, were irregular soldiers, originally made up of unmarried youths. They were conscripted among Rayah, reayas and served in various roles in the early Ottoman army. The word azeb either often indicates a light infantry soldier which was called ''yaya'' azeb or a Marines, marine soldier which was called ''bahriye'' (navy) and ''deniz'' (sea) azeb. The term was used in the sense of "pirate" or "buccaneer" in Greek language, Byzantine, Latin, and Italian language, Italian sources from 14th to 16th century. History Azebs were originally an auxiliary infantry unit harkening back to Anatolian beyliks that became independent from the Sultanate of Rum, Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate. In the maritime beyliks they also served as naval units. For instance, in the 13th century sources address existence of troops called azebs in the Aydınids, Beylik of Aydın. Accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azap
Azebs, azabs or azaps ( ota, عزب, from Arabic, literally ''unmarried'', meaning ''bachelor''), also known as Asappes or Asappi, were irregular soldiers, originally made up of unmarried youths. They were conscripted among reayas and served in various roles in the early Ottoman army. The word azeb either often indicates a light infantry soldier which was called ''yaya'' azeb or a marine soldier which was called ''bahriye'' (navy) and ''deniz'' (sea) azeb. The term was used in the sense of "pirate" or "buccaneer" in Byzantine, Latin, and Italian sources from 14th to 16th century. History Azebs were originally an auxiliary infantry unit harkening back to Anatolian beyliks that became independent from the Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate. In the maritime beyliks they also served as naval units. For instance, in the 13th century sources address existence of troops called azebs in the Beylik of Aydın. According to Stein (2007), by the 14th century azebs garnisoned in strongholds were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mace (bludgeon)
A mace is a blunt weapon, a type of club or virge that uses a heavy head on the end of a handle to deliver powerful strikes. A mace typically consists of a strong, heavy, wooden or metal shaft, often reinforced with metal, featuring a head made of stone, bone, copper, bronze, iron, or steel. The head of a military mace can be shaped with flanges or knobs to allow greater penetration of plate armour. The length of maces can vary considerably. The maces of foot soldiers were usually quite short (two or three feet, or sixty to ninety centimetres). The maces of cavalrymen were longer and thus better suited for blows delivered from horseback. Two-handed maces could be even larger. Maces are rarely used today for actual combat, but many government bodies (for instance, the British House of Commons and the U.S. Congress), universities and other institutions have ceremonial maces and continue to display them as symbols of authority. They are often paraded in academic, parliamentary or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge) is a two-handed pole weapon that came to prominent use during the 13th, 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. The word ''halberd'' is cognate with the German word ''Hellebarde'', deriving from Middle High German ''halm'' (handle) and ''barte'' (battleaxe) joined to form ''helmbarte''. Troops that used the weapon were called halberdiers. The halberd consists of an axe blade topped with a spike mounted on a long shaft. It always has a hook or thorn on the back side of the axe blade for grappling mounted combatants. It is very similar to certain forms of the voulge in design and usage. The halberd was usually 1.5 to 1.8 metres (5 to 6 feet) long. The word has also been used to describe a weapon of the Early Bronze Age in Western Europe. This consisted of a blade mounted on a pole at a right angle. History The halberd was inexpensive to produce and very versatile in battle. As the halberd was eventually refined, its point was mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Scythe
A war scythe or military scythe is a form of pole weapon with a curving single-edged blade with the cutting edge on the concave side of the blade. Its blade bears a superficial resemblance to that of an agricultural scythe from which it is likely to have evolved, but the war scythe is otherwise unrelated to agricultural tools and is a purpose-built infantry melee weapon. The blade of a war scythe has regularly proportioned flats, a thickness comparable to that of a spear or sword blade, and slightly curves along its edge as it tapers to its point. This is very different from farming scythes, which have very thin and irregularly curved blades, specialised for mowing grass and wheat only, unsuitable as blades for improvised spears or polearms. Compared to a fauchard (which is believed to have evolved from the war scythe), the blade of the war scythe has the cutting edge on the concave side like the agricultural tool whereas the fauchard has the edge along the convex side. As an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
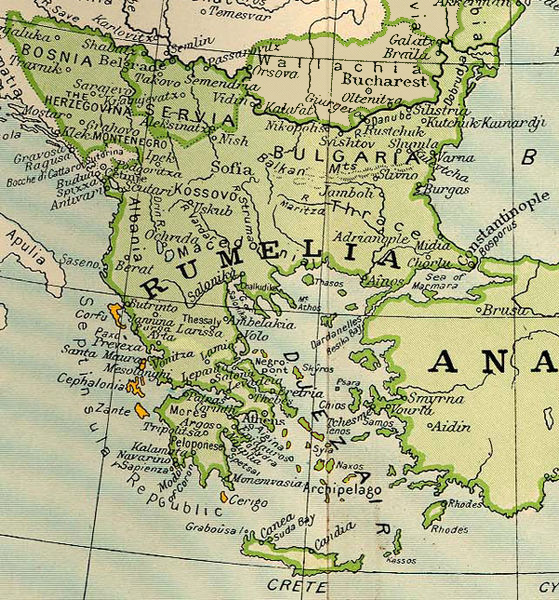
Rumelia
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Names of the Greeks#Romans (Ῥωμαῖοι), Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine Rite, Byzantine rite, was the name of a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and Vassal state, vassals in Europe that would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans". During the period of its existence, it was more often known in English as Ottoman Empire, Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means "Greek", or a Christian Greek speaker and ''ėli'' means "land" and ''Rumelia'' ( ota, روم ايلى, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish language, Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Ottoman Turkish language, Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Asian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kadi (Ottoman Empire)
A ''kadi'' ( ar, قاضي '; tr, kadı) was an official in the Ottoman Empire. The term ''kadi'' refers to judges who preside over matters in accordance with Islamic law, but in the Ottoman Empire, the ''kadi'' also became a crucial part of the central authority's administrative hierarchy. After Mehmed II codified his '' qanun'', ''kadis'' relied on this dynastic secular law, local customs, and the ''sharia''- Islamic divine law- to guide their rulings. Along with adjudicating over criminal and civil matters, the ''kadi'' oversaw the administration of religious endowments and was the legal guardian of orphans and others without a guardian. Although Muslims, in particular Muslim men, possessed a higher status in the ''kadi’s'' court, non-Muslims and foreigners also had access to the judicial system. Within the Ottoman's provincial administrative system, known as the timar system, the ''kadi'' served as an important check on the power of the military class. Despite the unquestione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suleiman The Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳānūnī Sulṭān Süleymān) in his realm, was the tenth and longest-reigning Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1520 until his death in 1566. Under his administration, the Ottoman Empire ruled over at least 25 million people. Suleiman succeeded his father, Selim I, as sultan on 30 September 1520 and began his reign with campaigns against the Christian powers in central Europe and the Mediterranean. Belgrade fell to him in 1521 and the island of Rhodes in 1522–23. At Mohács, in August 1526, Suleiman broke the military strength of Hungary. Suleiman became a prominent monarch of 16th-century Europe, presiding over the apex of the Ottoman Empire's economic, military and political power. Suleiman personally led Ottoman armies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Law
The Ottoman Empire was governed by different sets of laws during its existence. The '' Qanun'', sultanic law, co-existed with religious law (mainly the Hanafi school of Islamic jurisprudence). Legal administration in the Ottoman Empire was part of a larger scheme of balancing central and local authority. Ottoman power revolved crucially around the administration of the rights to land, which gave a space for the local authority develop the needs of the local millet. The jurisdictional complexity of the Ottoman Empire was aimed to permit the integration of culturally and religiously different groups. Legal system The Ottoman system had three court systems: one for Muslims, one for non-Muslims, involving appointed Jews and Christians ruling over their respective religious communities, and the "trade court". The codified administrative law was known as ''kanun'' and the ''ulema'' were permitted to invalidate secular provisions that contradicted the religious laws. In practice, howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janissary
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan (1324–1362), during the Viziership of Alaeddin. Janissaries began as elite corps made up through the devşirme system of child levy, by which Christian Albanians, Romanians, Armenians, Bulgarians, Croats, Greeks and Serbs were taken, levied, subjected to circumcision and conversion to Islam, and incorporated into the Ottoman army. They became famed for internal cohesion cemented by strict discipline and order. Unlike typical slaves, they were paid regular salaries. Forbidden to marry before the age of 40 or engage in trade, their complete loyalty to the Sultan was expected. By the seventeenth century, due to a dramatic increase in the size of the Ottoman standing army, the corps' initially strict recruitment policy was relaxed. Civili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)