|
Ayanin
Ayanin is an ''O''-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is the 3,7,4'-tri-''O''-methylated derivative of quercetin. It can be found in ''Croton schiedeanus''. It can also be synthetized. Biosynthesis The enzyme 3,7-dimethylquercetin 4'-O-methyltransferase uses ''S''-adenosyl methionine and rhamnazin Rhamnazin is an ''O''-methylated flavonol, a type of chemical compound. It can be found in ''Rhamnus petiolaris'', a buckthorn plant endemic to Sri Lanka. Metabolism The enzyme 3-methylquercetin 7-''O''-methyltransferase uses ''S''-adenosyl m ... to produce ''S''-adenosylhomocysteine and ayanin. References O-methylated flavonols {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-methylated Flavonoid
The O-methylated flavonoids or methoxyflavonoids are flavonoids with methylations on hydroxyl groups ( methoxy bonds). O-methylation has an effect on the solubility of flavonoids. Enzymes O-methylated flavonoids formation implies the presence of specific O-methyltransferase (OMT) enzymes which accept a variety of substrates. Those enzymes mediate the O-methylation on a specific hydroxyl group, like on 4' (example in '' Catharanthus roseus'') or 3' (example in rice) positions. Those positions can be ortho, meta, para and there can be a special 3-O-methyltransferase for the 3-OH position. Calamondin orange ('' Citrus mitis'') exhibits all of those activities. Plant enzymes * Apigenin 4'-O-methyltransferase * 8-hydroxyquercetin 8-O-methyltransferase * Isoflavone 4'-O-methyltransferase * Isoflavone 7-O-methyltransferase * Isoliquiritigenin 2'-O-methyltransferase * Isoorientin 3'-O-methyltransferase * Kaempferol 4'-O-methyltransferase * Luteolin O-methyltransferase * Methylquercetag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative (chemistry)
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction. In the past, derivative also meant a compound that ''can be imagined to'' arise from another compound, if one atom or group of atoms is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern chemical language now uses the term structural analog for this meaning, thus eliminating ambiguity. The term "structural analogue" is common in organic chemistry. In biochemistry, the word is used for compounds that at least theoretically can be formed from the precursor compound. Chemical derivatives may be used to facilitate analysis. For example, melting point (MP) analysis can assist in identification of many organic compounds. A crystalline derivative may be prepared, such as a semicarbazone or 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (derived from aldehydes or ketones), as a simple way of verifying the identity of the original compound, assuming that a table of derivative MP values is avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercetin
Quercetin is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, seeds, and grains; capers, red onions, and kale are common foods containing appreciable amounts of it. It has a bitter flavor and is used as an ingredient in dietary supplements, beverages, and foods. Occurrence Quercetin is a flavonoid widely distributed in nature. The name has been used since 1857, and is derived from ''quercetum'' (oak forest), after the oak genus ''Quercus''. It is a naturally occurring polar auxin transport inhibitor. Quercetin is one of the most abundant dietary flavonoids, with an average daily consumption of 25–50 milligrams. In red onions, higher concentrations of quercetin occur in the outermost rings and in the part closest to the root, the latter being the part of the plant with the highest concentration. One study found that organically grown tomatoes had 79% more quercetin than non-organically grown fruit. Quercetin is pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croton Schiedeanus
''Croton schiedeanus'' is a plant species native from Mexico to tropical South America. ''C schiedeanus'' is known to contain the flavonol ayanin and cis- clerodane diterpenoids. See also * List of Croton species This is the alphabetical list of 1149 species In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest gro ... References schiedeanus Flora of Mexico Flora of Central America Flora of South America {{euphorb-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3,7-dimethylquercetin 4'-O-methyltransferase
In enzymology, a 3,7-dimethylquercetin 4'-O-methyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :S-adenosyl-L-methionine + 5,3',4'-trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone \rightleftharpoons S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + 5,3'-dihydroxy-3,7,4'-trimethoxyflavone Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are S-adenosyl methionine and 5,3',4'-trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone (rhamnazin), whereas its two products are S-adenosylhomocysteine and 5,3'-dihydroxy-3,7,4'-trimethoxyflavone (ayanin). This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring one-carbon group methyltransferases. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivial ... of this enzyme class is S-adenosyl-L-methionine:5,3',4'-trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone 4'-O-met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
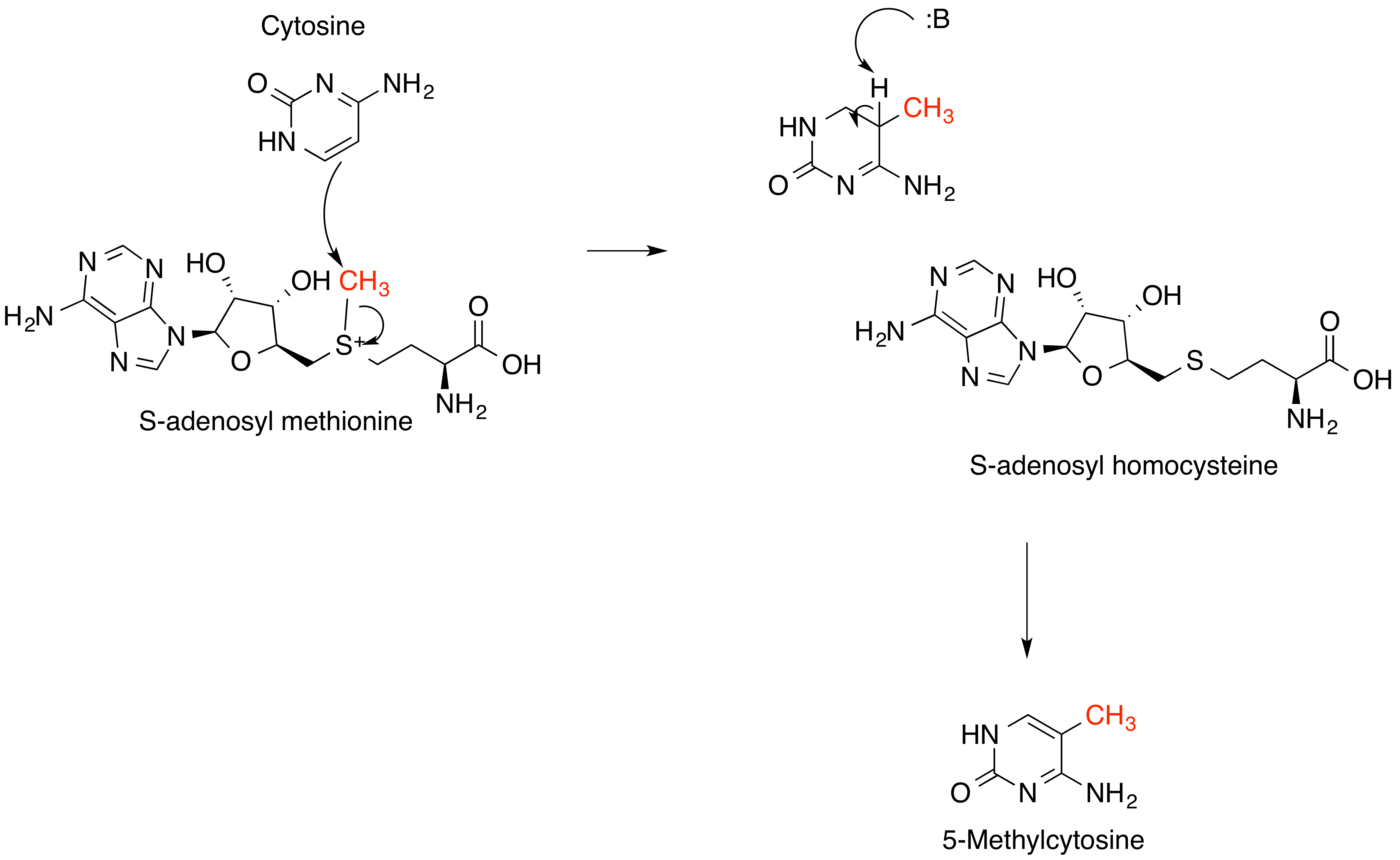
S-Adenosyl Methionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952. In bacteria, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates genes involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis. In eukaryotic cells, SAM serves as a regulator of a variety of processes including DNA, tRNA, and rRNA methylation; immune response; amino acid metabolism; transsulfuration; and more. In plants, SAM is crucial to the biosynthesis of ethylene, an important plant hormone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhamnazin
Rhamnazin is an ''O''-methylated flavonol, a type of chemical compound. It can be found in ''Rhamnus petiolaris'', a buckthorn plant endemic to Sri Lanka. Metabolism The enzyme 3-methylquercetin 7-''O''-methyltransferase uses ''S''-adenosyl methionine and isorhamnetin to produce ''S''-adenosyl homocysteine and rhamnazin. The enzyme 3,7-dimethylquercetin 4'-''O''-methyltransferase uses ''S''-adenosyl methionine and rhamnazin to produce ''S''-adenosyl homocysteine and ayanin Ayanin is an ''O''-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is the 3,7,4'-tri-''O''-methylated derivative of quercetin. It can be found in '' Croton schiedeanus''. It can also be synthetized. Biosynthesis The enzyme 3,7-dimethylquercetin .... References External links Rhamnazin on the Extrasynthese catalogue O-methylated flavonols {{Aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |