|
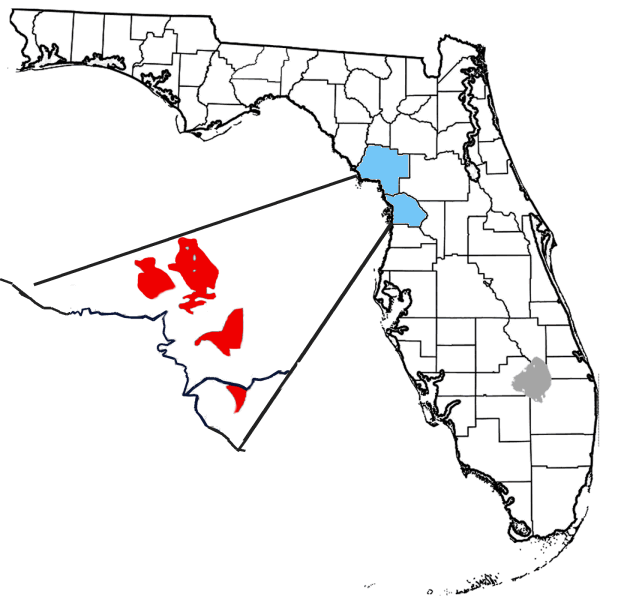
Avon Park Formation
The Avon Park Formation is a Middle Eocene geologic formation and is the oldest exposed sediments in Florida, United States. Age Period: Paleogene Epoch: Middle Eocene~55.8 to 33.9 mya, calculates to a period of Faunal stage: Clarkforkian through early Chadronian Location The Avon Park formation is located on the crest of the Ocala Platform in Levy County with three distinct outcroppings. Citrus County has one outcropping near the county line with Levy County. Composition The Avon Park Formation consists of cream to light-brown or tan, poorly hardened to very hard, grainstone, packstone and wackestone, with rare mudstone. Fossils found throughout but not densely. These limestones are interbedded with vuggy dolomites which are soft to very hard and tan to brown, very fine to medium crystalline structure. The Avon Park Formation, as with many formations, is part of the Floridan Aquifer system. Parts of the Avon Park Formation comprise important, subregional confining units wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Florida Barge Canal
The Marjorie Harris Carr Cross Florida Greenway is a protected green belt corridor, more than one and a half miles (1.6 km) wide in places, that was the former route of the proposed Cross Florida Barge Canal. It is named for the leader of opposition to the Cross Florida Barge Canal, Marjorie Harris Carr, and was originally a U.S. Army Corps of Engineers canal project to connect the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean across Florida for barge traffic. Two sections were built, but the project was ultimately cancelled because of local opposition related to environmental concerns, including protecting the state's water supply and conservation of the Ocklawaha River Valley ecosystem, as well as national opposition for the costs being perceived as "government waste" with "limited national value." The greenway is part of the system of Florida State Parks, including the Santos Trail System, and is managed by the Florida Department of Environmental Protection. History The idea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomite (rock)
Dolomite (also known as dolomite rock, dolostone or dolomitic rock) is a sedimentary carbonate rock that contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, CaMg(CO3)2. It occurs widely, often in association with limestone and evaporites, though it is less abundant than limestone and rare in Cenozoic rock beds (beds less than about 66 million years in age). The first geologist to distinguish dolomite rock from limestone was Belsazar Hacquet in 1778. Most dolomite was formed as a magnesium replacement of limestone or of lime mud before lithification. The geological process of conversion of calcite to dolomite is known as dolomitization and any intermediate product is known as dolomitic limestone. The "dolomite problem" refers to the vast worldwide depositions of dolomite in the past geologic record in contrast to the limited amounts of dolomite formed in modern times. Recent research has revealed sulfate-reducing bacteria living in anoxic conditions precipitate dolomite which ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from '' shale'' by its lack of fissility (parallel layering).Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, W. H. Freeman, 2nd ed, 529 pp. The term ''mudstone'' is also used to describe carbonate rocks (limestone or dolomite) that are composed predominantly of carbonate mud. However, in most contexts, the term refers to siliciclastic mudstone, composed mostly of silicate minerals. The NASA Curiosity rover has found deposits of mudstone on Mars that contain organic substances such as propane, benzene and toluene. Definition There is not a single definition of mudstone that has gained general acceptance,Boggs 2006, p.143 though there is wide agreement that mudstones are fine-grained sedimentary rocks, composed mostly of silicate grains with a grain size less than . Individual grains this size are too small to be disting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grainstone
Under the Dunham classification (Dunham, 1962) system of limestones, a grainstone is defined as a grain-supported carbonate rock that contains less than 1% mud-grade material. This definition has recently been clarified as ''a carbonate-dominated rock that does not contain any carbonate mud and where less than 10% of the components are larger than 2 mm.'' The spaces between grains may be empty (pores) or filled by cement. The identification of grainstone The presence of any primary carbonate mud precludes a classification of grainstone. A study of the use of carbonate classification systems by Lokier and Al Junaibi (2016) highlighted that the most common source of confusion in the classification of grainstone was to misidentify fine-grained internal micrite, generated by in-situ processes, as clay–silt grade sediment - thus resulting in the misidentification of grainstone as packstone Under the Dunham classification (Dunham, 1962Dunham, R.J. (1962) Classification of carbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocala Platform
The Ocala Platform or Ocala Uplift is a geologic feature, a structural high, and a northwest-trending uplift paralleling the Peninsular Arch along the west coast of Florida. Age Period: Neogene Epoch: Early Late Oligocene through Pliocene Faunal stage: Chattian through early Blancan ~23.03 to ~2.588 mya, calculates to a period of Origin The Ocala Platform was originally named by Hopkins in 1920. Due to the uncertainty of its creation, T. M. Scott used the term "platform" in place of "uplift" or "arch". This geologic feature was described as a gentle flexure developed in Tertiary sediments with a northwest-southeast trending crest by Vernon in 1951. The Ocala Platform was created during two episodes. The first occurred during the Late Oligocene through Early Miocene and the second episode occurred in Early Pliocene and into Late Pleistocene according to Williams et al. This movement created the feature referred to as the Ocala Uplift. It has been suggested that the uplift was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chadronian
The Chadronian age within the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology is the North American faunal stage typically set from 38,000,000 to 33,900,000 years BP, a period of . It is usually considered to fall within the Eocene epoch. The Chadronian is preceded by the Duchesnean and followed by the Orellan NALMA stages. The Chadronian can be further divided into the substages of: *Late/Upper Chadronian (shares upper boundary). Lower boundary source of the base of the Priabonian (approximate) *Middle Chadronian. Lower boundary source and base of the Priabonian (approximate). Upper boundary source of the base of the Orellan (approximate). *Early/Lower Chadronian (shares lower boundary). Upper boundary source: base of Orellan (approximate). Geological time The Chadronian maintains a period of time within the Priabonian through Rupelian of the Late Eocene through Early Oligocene in the geologic time scale The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a represent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clarkforkian
The Clarkforkian North American Stage, on the geologic timescale, is the North American faunal stage according to the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology (NALMA), typically set from 56,800,000 to 55,400,000 years BP lasting . Considered to be within the Paleocene, more specifically the Late Paleocene, the Clarkforkian shares its upper boundary with the Thanetian. The Clarkforkian is preceded by the Tiffanian and followed by the Wasatchian NALMA stages. Substages It is considered to contain the following substages: *Cf3: (shares the upper boundary) and lower boundary source of the base of Clarkforkian (approximate) and upper boundary source of the base of the Ypresian (approximate). *Cf2: Is the lower boundary source of the base of the Clarkforkian (approximate) *Cf1: Upper boundary source of the base of the Ypresian (approximate) Fauna Notable mammals Multituberculata - non-therian mammals * '' Ectypodus'', neoplagiaulacid multituberculate Metatheria - marsupi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faunal Stage
In chronostratigraphy, a stage is a succession of rock strata laid down in a single age on the geologic timescale, which usually represents millions of years of deposition. A given stage of rock and the corresponding age of time will by convention have the same name, and the same boundaries. Rock series are divided into stages, just as geological epochs are divided into ages. Stages can be divided into smaller stratigraphic units called chronozones. (See chart at right for full terminology hierarchy.) Stages may also be divided into substages or indeed grouped as superstages. The term faunal stage is sometimes used, referring to the fact that the same fauna (animals) are found throughout the layer (by definition). Definition Stages are primarily defined by a consistent set of fossils (biostratigraphy) or a consistent magnetic polarity (see paleomagnetism) in the rock. Usually one or more index fossils that are common, found worldwide, easily recognized, and limited to a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |