|
Avalanche (phishing Group)
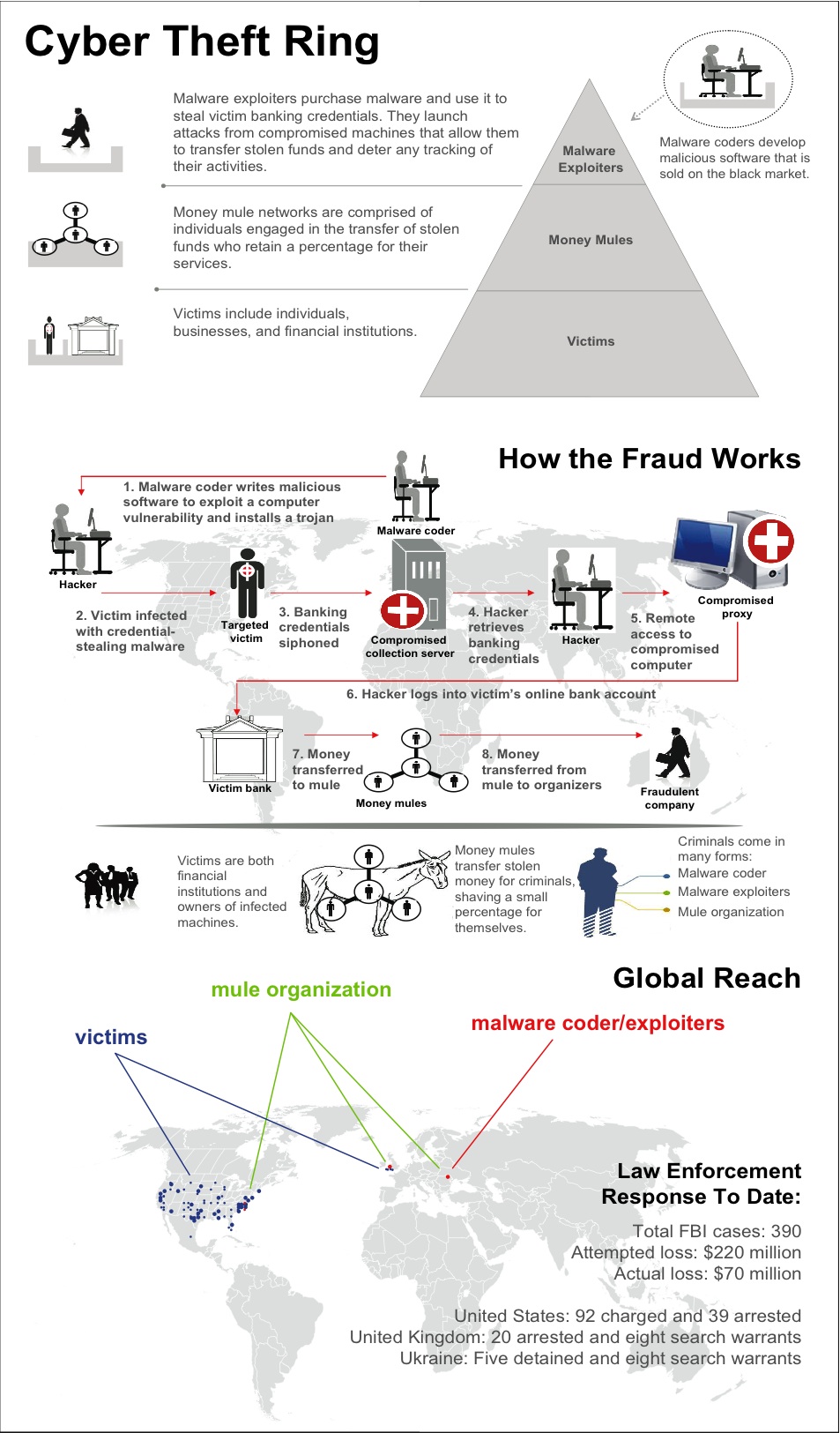
Avalanche was a criminal syndicate involved in phishing attacks, online bank fraud, and ransomware. The name also refers to the network of owned, rented, and compromised systems used to carry out that activity. Avalanche only infected computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system. In November 2016, the Avalanche botnet was destroyed after a four-year project by an international consortium of law enforcement, commercial, academic, and private organizations. History Avalanche was discovered in December 2008, and may have been a replacement for a phishing group known as Rock Phish which stopped operating in 2008. It was run from Eastern Europe and was given its name by security researchers because of the high volume of its attacks. Avalanche launched 24% of phishing attacks in the first half of 2009; in the second half of 2009, the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) recorded 84,250 attacks by Avalanche, constituting 66% of all phishing attacks. The number of total phishin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criminal
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definitions of", in Cane and Conoghan (editors), ''The New Oxford Companion to Law'', Oxford University Press, 2008 (), p. 263Google Books). though statutory definitions have been provided for certain purposes. The most popular view is that crime is a category created by law; in other words, something is a crime if declared as such by the relevant and applicable law. One proposed definition is that a crime or offence (or criminal offence) is an act harmful not only to some individual but also to a community, society, or the state ("a public wrong"). Such acts are forbidden and punishable by law. The notion that acts such as murder, rape, and theft are to be prohibited exists worldwide. What precisely is a criminal offence is defined by the criminal law of each r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man-in-the-middle Attack
In cryptography and computer security, a man-in-the-middle, monster-in-the-middle, machine-in-the-middle, monkey-in-the-middle, meddler-in-the-middle, manipulator-in-the-middle (MITM), person-in-the-middle (PITM) or adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) attack is a cyberattack where the attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communications between two parties who believe that they are directly communicating with each other, as the attacker has inserted themselves between the two parties. One example of a MITM attack is active eavesdropping, in which the attacker makes independent connections with the victims and relays messages between them to make them believe they are talking directly to each other over a private connection, when in fact the entire conversation is controlled by the attacker. The attacker must be able to intercept all relevant messages passing between the two victims and inject new ones. This is straightforward in many circumstances; for example, an attacker wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICANN
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN ) is an American multistakeholder group and nonprofit organization responsible for coordinating the maintenance and procedures of several databases related to the namespaces and numerical spaces of the Internet, ensuring the network's stable and secure operation. ICANN performs the actual technical maintenance work of the Central Internet Address pools and DNS root zone registries pursuant to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) function contract. The contract regarding the IANA stewardship functions between ICANN and the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) of the United States Department of Commerce ended on October 1, 2016, formally transitioning the functions to the global multistakeholder community. Much of its work has concerned the Internet's global Domain Name System (DNS), including policy development for internationalization of the DNS, introduction of new ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Name
A domain name is a string that identifies a realm of administrative autonomy, authority or control within the Internet. Domain names are often used to identify services provided through the Internet, such as websites, email services and more. As of 2017, 330.6 million domain names had been registered. Domain names are used in various networking contexts and for application-specific naming and addressing purposes. In general, a domain name identifies a network domain or an Internet Protocol (IP) resource, such as a personal computer used to access the Internet, or a server computer. Domain names are formed by the rules and procedures of the Domain Name System (DNS). Any name registered in the DNS is a domain name. Domain names are organized in subordinate levels (subdomains) of the DNS root domain, which is nameless. The first-level set of domain names are the top-level domains (TLDs), including the generic top-level domains (gTLDs), such as the prominent domains com, info, net ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uptime
Uptime is a measure of system reliability, expressed as the percentage of time a machine, typically a computer, has been working and available. Uptime is the opposite of downtime. It is often used as a measure of computer operating system reliability or stability, in that this time represents the time a computer can be left unattended without crashing, or needing to be rebooted for administrative or maintenance purposes. Conversely, long uptime may indicate negligence, because some critical updates can require reboots on some platforms. Records In 2005, Novell reported a server with a 6-year uptime. Although that might sound unusual, that is actually common when servers are maintained under an industrial context and host critical applications such as banking systems. Netcraft maintains the uptime records for many thousands of web hosting computers. A server running Novell NetWare has been reported to have been shut down after 16 years of uptime due to a failing hard disk. A Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaspersky Lab
Kaspersky Lab (; Russian: Лаборатория Касперского, tr. ''Laboratoriya Kasperskogo'') is a Russian multinational cybersecurity and anti-virus provider headquartered in Moscow, Russia, and operated by a holding company in the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1997 by Eugene Kaspersky, Natalya Kaspersky, and Alexey De-Monderik; Eugene Kaspersky is currently the CEO. Kaspersky Lab develops and sells antivirus, internet security, password management, endpoint security, and other cybersecurity products and services. Kaspersky expanded abroad from 2005 to 2010 and grew to $704 million in annual revenues by 2020, up 8% from 2016, though annual revenues were down 8% in North America due to U.S. government security concerns. As of 2016, the software has about 400 million users and has the largest market-share of cybersecurity software vendors in Europe. Kaspersky Lab ranks fourth in the global ranking of antivirus vendors by revenue. It was the first Russian company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Name Registrar
A domain name registrar is a company that manages the reservation of Internet domain names. A domain name registrar must be accredited by a generic top-level domain (gTLD) registry or a country code top-level domain (ccTLD) registry. A registrar operates in accordance with the guidelines of the designated domain name registries. History Until 1999, Network Solutions Inc. (NSI) operated the registries for the ''com'', ''net'', and ''org'' top-level domains (TLDs). In addition to the function of domain name registry operator, it was also the sole registrar for these domains. However, several companies had developed independent registrar services. In 1996 one such company, Ivan Pope's company, NetNames, developed the concept of a standalone commercial domain name registration service which would sell domain registration and other associated services to the public, effectively establishing the retail arm of an industry with the registries being the wholesalers. NSI assimilated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trojan Horse (computing)
In computing, a Trojan horse is any malware that misleads users of its true intent. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek story of the deceptive Trojan Horse that led to the fall of the city of Troy. Trojans generally spread by some form of social engineering; for example, where a user is duped into executing an email attachment disguised to appear innocuous (e.g., a routine form to be filled in), or by clicking on some fake advertisement on social media or anywhere else. Although their payload can be anything, many modern forms act as a backdoor, contacting a controller who can then have unauthorized access to the affected computer. Ransomware attacks are often carried out using a Trojan. Unlike computer viruses and worms, Trojans generally do not attempt to inject themselves into other files or otherwise propagate themselves. Use of the term It's not clear where or when the concept, and this term for it, was first used, but by 1971 the first Unix manual assumed its r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeus (malware)
Zeus, ZeuS, or Zbot is a Trojan horse malware package that runs on versions of Microsoft Windows. While it can be used to carry out many malicious and criminal tasks, it is often used to steal banking information by man-in-the-browser keystroke logging and form grabbing. It is also used to install the CryptoLocker ransomware. Zeus is spread mainly through drive-by downloads and phishing schemes. First identified in July 2007 when it was used to steal information from the United States Department of Transportation, it became more widespread in March 2009. In June 2009 security company Prevx discovered that Zeus had compromised over 74,000 FTP accounts on websites of such companies as the Bank of America, NASA, Monster.com, ABC, Oracle, Play.com, Cisco, Amazon, and ''BusinessWeek''. Similarly to Koobface, Zeus has also been used to trick victims of technical support scams into giving the scam artists money through pop-up messages that claim the user has a virus, when in realit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Name System
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical and distributed naming system for computers, services, and other resources in the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the associated entities. Most prominently, it translates readily memorized domain names to the numerical IP addresses needed for locating and identifying computer services and devices with the underlying network protocols. The Domain Name System has been an essential component of the functionality of the Internet since 1985. The Domain Name System delegates the responsibility of assigning domain names and mapping those names to Internet resources by designating authoritative name servers for each domain. Network administrators may delegate authority over sub-domains of their allocated name space to other name servers. This mechanism provides distributed and fault tolerance, fault-tolerant service and was designed to avoid a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast-flux
Fast flux is a domain name system (DNS) based evasion technique used by cyber criminals to hide phishing and malware delivery websites behind an ever-changing network of compromised hosts acting as reverse proxies to the backend botnet master—a bulletproof autonomous systems. It can also refer to the combination of peer-to-peer networking, distributed command and control, web-based load balancing and proxy redirection used to make malware networks more resistant to discovery and counter-measures. The fundamental idea behind fast-flux is to have numerous IP addresses associated with a single fully qualified domain name, where the IP addresses are swapped in and out with extremely high frequency, through changing DNS resource records, thus the authoritative name servers of the said fast-fluxing domain name is—in most cases—hosted by the criminal actor. Depending on the configuration and complexity of the infrastructure, fast-fluxing is generally classified into sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |