|
Aux Pékans River
The Aux Pékans River (french: Rivière aux Pékans) is a river in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada. It is a tributary of the Moisie River. Hydro-Québec caused controversy in the early 1990s by proposing to divert the river to supply the reservoir of the SM-3 power plant on the Sainte-Marguerite River. Location The Aux Pékans River is in the unorganized territory of Rivière-Mouchalagane in the Caniapiscau Regional County Municipality. The name was made official on 5 December 1968. The Commission de toponymie du Québec has no information on its origins. The river rises in Lac de la Bouteille, south of Lake Germaine and west of Fermont. It flows to the west of the Mont Wright mines. Quebec Route 389 crosses the Pékans River south of Fermont. In August 2015 a limit of 10 tonnes was placed on vehicles crossing the bridge. The Ministry of Transport was working on a replacement structure, due to be commissioned in summer 2016. The river flows in a generally SSE dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caniapiscau Regional County Municipality
Caniapiscau is a regional county municipality in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada. The seat is Fermont. The census groups Caniapiscau RCM with neighbouring Sept-Rivières into the single census division of Sept-Rivières—Caniapiscau. In the Canada 2011 Census, the combined population was 39,500. The population of Caniapiscau RCM itself was 4260, about two-thirds of whom live in its largest city of Fermont. Subdivisions There are 6 subdivisions and 3 native reserves within the RCM: ;Cities & Towns (2) * Fermont * Schefferville ;Unorganized territories (4) *Caniapiscau * Lac-Juillet * Lac-Vacher * Rivière-Mouchalagane ;Native Reserves (2) * Lac-John * Matimekosh ;Naskapi Reserve (1) * Kawawachikamach Demographics * Land area: 70,389.37 km² * Population: 4,260 Transportation Access routes Highways and numbered routes that run through the municipality, including external routes that start or finish at the county border: * Autoroutes ** None * Principa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipissis River
The Nipissis River (French: Rivière Nipissis) is a river in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada, a tributary of the Moisie River. It is a recognized salmon river. The river is known for its steep cliffs, which provide a challenging ice-climbing environment. Location The Nipissis River is in the unorganized territory of Rivière-Nipissis in the Sept-Rivières Regional County Municipality. Tributaries include the Wacouno and Nipisso rivers, both of which enter from the left. The Nipissis drains a region of , making it the most important tributary of the Moise River. It is followed by the Aux Pékans River, which drains an area of . The proposed Moisie River Aquatic Reserve would include the Nipissis River and a narrow strip along its shores. The Nipissis River is a little over long. It originates in the Siamois lakes, and empties into the Moisie River about from its mouth. According to the 1969 ''Répertoire géographique du Québec'' the river that runs for a little more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are found in the northern Atlantic Ocean and in rivers that flow into it. Most populations are anadromous, hatching in streams and rivers but moving out to sea as they grow where they mature, after which the adults seasonally move upstream again to spawn. When the mature fish re-enter rivers to spawn, they change in colour and appearance. Some populations of this fish only migrate to large lakes, and are "landlocked", spending their entire lives in freshwater. Such populations are found throughout the range of the species. Unlike Pacific species of salmon, ''S. salar'' is iteroparous, which means it can survive spawning and return to sea to repeat the process again in another year. Such individuals can grow to extremely large sizes, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sept-Îles, Quebec
Sept-Îles (Quebec French pronunciation : , French for "Seven Islands") is a city in the Côte-Nord region of eastern Quebec. It is among the northernmost locales with a paved connection to the rest of Quebec's road network. The population was 25,686 as of the 2011 Canadian census. The town is called Uashat, meaning "bay" in Innu-aimun. The city is well known for having major iron companies like Iron Ore Company of Canada and the Cleveland-Cliffs mining company. The city relies heavily on the iron industry. Sept-Îles has among the highest average wages and the highest average wage increases. The only settlements on the paved road network that are farther north are Fermont, Radisson and Chisasibi, the latter two of which are in the extreme western part of the province at the north end of the James Bay Road. The only other settlements at higher latitudes in the province are mostly isolated Cree, Innu, or Inuit villages, with access limited to seasonal gravel roads. Sept-Îl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uashat
Uashat is an Indian reserve in Quebec, located adjacent to the city of Sept-Îles. Together with Maliotenam some distance away, it forms the Innu community of Uashat-Maliotenam Innu Takuaikan Uashat Mak Mani-Utenam is an Innu First Nations band government in Quebec, Canada. It is based in Sept-Îles in the Côte-Nord region on the North shore of the Saint Lawrence River. It owns two reserves: Maliotenam 27A and Uasha .... Prior to December 24, 1993, it was known as the Indian reserve of "Sept-Îles", sharing the name with the adjacent city. References Innu communities in Quebec Communities in Côte-Nord Sept-Rivières Regional County Municipality {{Quebec-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylmercury
Methylmercury (sometimes methyl mercury) is an organometallic cation with the formula . It is the simplest organomercury compound. Methylmercury is extremely toxic, and its derivatives are the major source of organic mercury for humans. It is a bioaccumulative environmental toxicant. Structure and chemistry "Methylmercury" is a shorthand for the hypothetical "methylmercury cation", sometimes written "''methylmercury(1+) cation''" or "''methylmercury(II) cation''". This functional group is composed of a methyl group bonded to an atom of mercury. Its chemical formula is (sometimes written as ).The Methylmercury compound has an overall charge of +1, with Hg in the +2 oxidation state.Methylmercury exists as a substituent in many complexes of the type (L = Lewis base) and MeHgX (X = anion). As a positively charged ion it readily combines with anions such as chloride (), hydroxide () and nitrate (). It has particular affinity for sulfur-containing anions, particularly thiols (). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maliotenam
Maliotenam (Mani-Utenam in Innu-aimun) is a First Nations reserve in Quebec, located adjacent to the city of Sept-Îles, Quebec, Sept-Îles. Together with Uashat some distance away, it forms the Innu community of Uashat-Maliotenam. The community is a part of the Manicouagan district which is represented by Bloc Québécois MP Marilène Gill. The community has a population of approximately 1,600 people. The community share its administration with the nearby community of Uashat as the Innu Takuaikan Uashat Mak Mani-Utenam. The chief and council consists of the chief, deputy chief and five councillors. The chief and council are all elected by the members of the community Innu Takuaikan Uashat Mak Mani-Utenam. The current chief is Mike Pelash McKenzie, alongside Antoine (Maniteu) Grégoire as deputy chief. The current councillors are Jonathan St-Onge, Normand Ambroise, Dave Vollant, Kenny Régis, and Zachary Vollant. Maliotenam is enclaved within the city of Sept-Îles and is there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
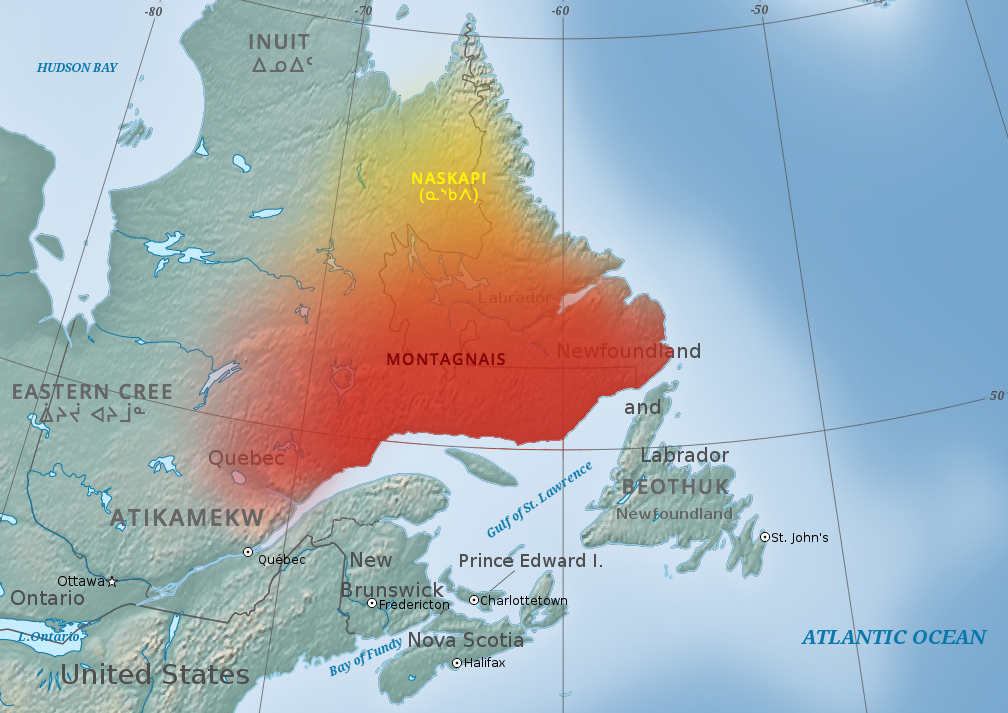
Innu
The Innu / Ilnu ("man", "person") or Innut / Innuat / Ilnuatsh ("people"), formerly called Montagnais from the French colonial period ( French for "mountain people", English pronunciation: ), are the Indigenous inhabitants of territory in the northeastern portion of the present-day province of Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to their traditional homeland as ''Nitassinan'' ("Our Land", ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) or ''Innu-assi'' ("Innu Land"). The Innu are divided into several bands, with the Montagnais being the southernmost group and the Naskapi being the northernmost. Their ancestors were known to have lived on these lands as hunter-gatherers for several thousand years. To support their seasonal hunting migrations, they created portable tents made of animal skins. Their subsistence activities were historically centred on hunting and trapping caribou, moose, deer, and small game. Their language, Ilnu-Aimun or Innu-Aimun (popularly known since the French colonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Regions Of Quebec
The Ecological regions of Quebec are regions with specific types of vegetation and climates as defined by the Quebec Ministry of Forests, Wildlife and Parks. Given the size of this huge province, there is wide variation from the temperate deciduous forests of the southwest to the arctic tundra of the extreme north. Vegetation zones Quebec covers more than of land between 45° and 62° north, with vegetation that varies greatly from south to north. Most of the natural vegetation is forest, with various species of trees and other plants, and these forests are the habitat for diverse fauna. Energy, precipitation and soil are all important factors in determining what can grow. The climate influences the natural disturbances that affect forests: western Quebec has a drier climate than the east, and experiences more fires. For most species these disturbances are not disasters, and some need them to regenerate. The climate in Quebec supports rich deciduous forest in the southern region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carheil Lake
Carheil Lake (french: Lac Carheil) is a lake in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada. It is just south of Fermont, and is the source of the Carheil River, which runs south to the Aux Pékans River. The lake has been polluted with phosphorus from wastewater effluent from Fermont, causing algal bloom. This is cause for concern since the lake is among the headwaters for the wild and unspoiled Moisie River. Location Carheil Lake is south of Fermont and of Quebec Route 389. It is in the Caniapiscau Regional County Municipality near the western boundary of Labrador. The lake is in the Grenville Province in the southeast of the Canadian Shield plateau, composed of Precambrian rocks, on average above sea level. Carheil Lake's elongated shape and orientation indicate a glacial origin. The lake has a maximum depth of in its center and average depth of . Name The lake's name was made official on 5 December 1968. The Commission de toponymie du Québec does not have informatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moisie River Aquatic Reserve
The Moisie River Aquatic Reserve (french: Réserve aquatique projetée de la rivière Moisie) is a proposed protected area in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada. It would protect the waters and surrounding lands of the Moisie River. The Moisie is one of the largest rivers in the region, flows through dramatic unspoiled scenery and is an important Atlantic salmon river. Although the plan to create the reserve was announced in 2003, as of 2018 the local Innu communities had yet to give their consent. Background The plan for the Moisie river aquatic reserve was officially announced by the Government of Quebec in February 2003. It would be the first aquatic reserve in Quebec, and the Moisie would become the first watercourse to the fully protected against any form of industrial exploitation. Measured by watershed, the Moisie would be the second largest protected river in southern Canada, after the Fraser River. The reserve includes the Aux Pékans and Carheil rivers, tribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |