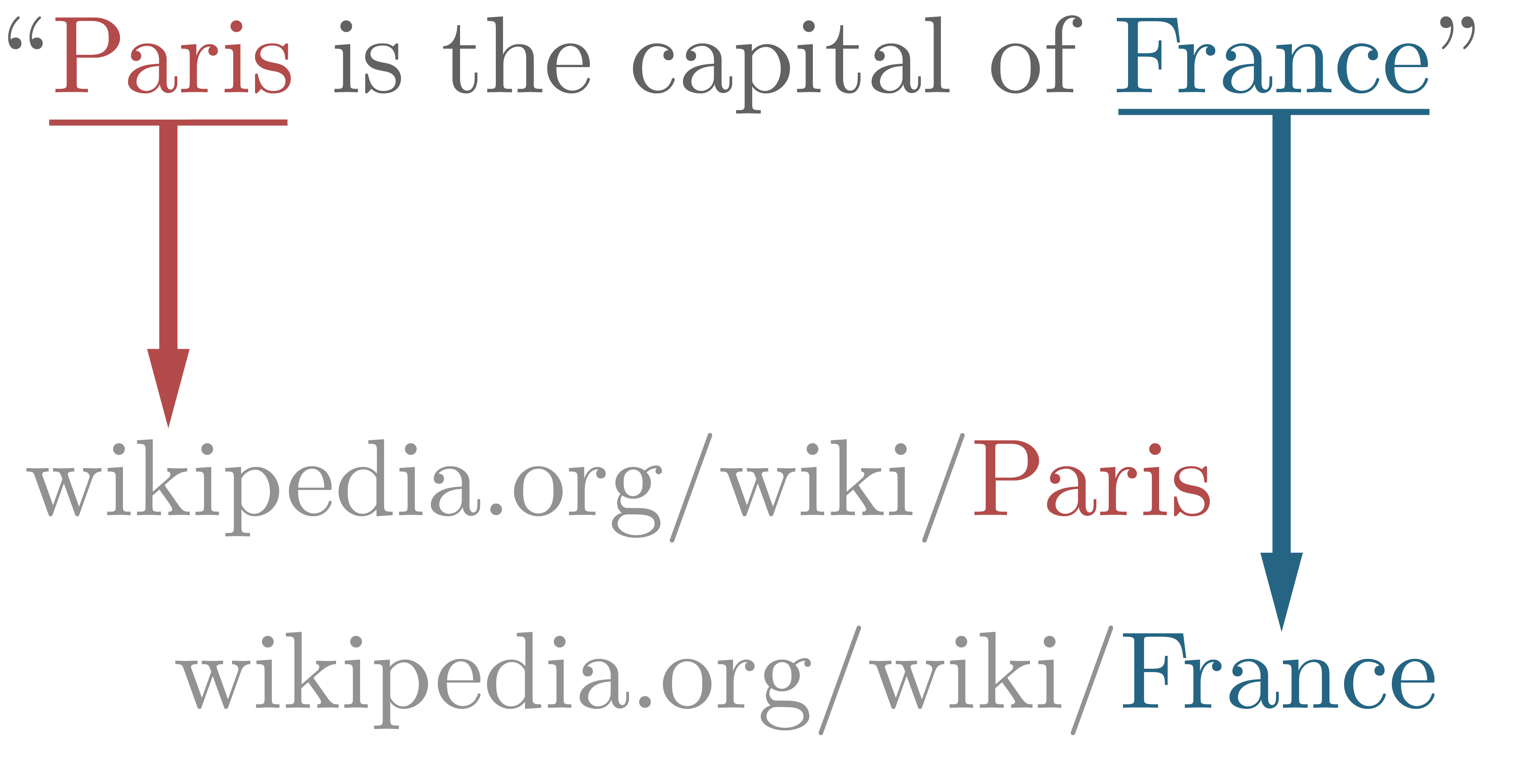|
Automatic Hyperlinking
An autolink is a hyperlink added automatically to a hypermedia document, after it has been authored or published. Automatic hyperlinking describes the process or the software feature that produces autolinks. Segments of the hypermedia are identified through a process of pattern matching. For example, in hypertext, the software could recognise textual patterns for street addresses, phone numbers, ISBNs, or Uniform Resource Locator, URLs. In a distributed hypermedia system, such as the World Wide Web, autolinking can be carried out by client or server software. For example, a web server could add links to a web page as it sends it to a web browser. A browser can also add links to a page after it has received it from the server. Examples Google Toolbar AutoLink is a feature of the Google Toolbar. Users can convert street addresses, ISBNs in a web page in their browser to links by clicking a button on Google Toolbar. The links direct the users to Google Maps for street addresses and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperlink
In computing, a hyperlink, or simply a link, is a digital reference to data that the user can follow or be guided by clicking or tapping. A hyperlink points to a whole document or to a specific element within a document. Hypertext is text with hyperlinks. The text that is linked from is known as anchor text. A software system that is used for viewing and creating hypertext is a ''hypertext system'', and to create a hyperlink is ''to hyperlink'' (or simply ''to link''). A user following hyperlinks is said to ''navigate'' or ''browse'' the hypertext. The document containing a hyperlink is known as its source document. For example, in an online reference work such as Wikipedia or Google, many words and terms in the text are hyperlinked to definitions of those terms. Hyperlinks are often used to implement reference mechanisms such as tables of contents, footnotes, bibliographies, indexes, letters, and glossaries. In some hypertext, hyperlinks can be bidirectional: they c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Issue Tracking System
An issue tracking system (also ITS, trouble ticket system, support ticket, request management or incident ticket system) is a computer software package that manages and maintains lists of issues. Issue tracking systems are generally used in collaborative settings, especially in large or distributed collaborations, but can also be employed by individuals as part of a time management or personal productivity regimen. These systems often encompass resource allocation, time accounting, priority management, and oversight workflow in addition to implementing a centralized issue registry. Background In the institutional setting, issue tracking systems are commonly used in an organization's customer support call center to create, update, and resolve reported customer issues, or even issues reported by that organization's other employees. A support ticket should include vital information for the account involved and the issue encountered. An issue tracking system often also contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Named Entity Recognition
Named-entity recognition (NER) (also known as (named) entity identification, entity chunking, and entity extraction) is a subtask of information extraction that seeks to locate and classify named entities mentioned in unstructured text into pre-defined categories such as person names, organizations, locations, medical codes, time expressions, quantities, monetary values, percentages, etc. Most research on NER/NEE systems has been structured as taking an unannotated block of text, such as this one: And producing an annotated block of text that highlights the names of entities: In this example, a person name consisting of one token, a two-token company name and a temporal expression have been detected and classified. State-of-the-art NER systems for English produce near-human performance. For example, the best system entering MUC-7 scored 93.39% of F-measure while human annotators scored 97.60% and 96.95%. Named-entity recognition platforms Notable NER platforms include: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entity Linking
In natural language processing, entity linking, also referred to as named-entity linking (NEL), named-entity disambiguation (NED), named-entity recognition and disambiguation (NERD) or named-entity normalization (NEN) is the task of assigning a unique identity to entities (such as famous individuals, locations, or companies) mentioned in text. For example, given the sentence ''"Paris is the capital of France"'', the idea is to determine that ''"Paris"'' refers to the city of Paris and not to Paris Hilton or any other entity that could be referred to as ''"Paris"''. Entity linking is different from named-entity recognition (NER) in that NER identifies the occurrence of a named entity in text but it does not identify which specific entity it is (see Differences from other techniques). Introduction In entity linking, words of interest (names of persons, locations and companies) are mapped from an input text to corresponding unique entities in a target knowledge base. Words of inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary
A glossary (from grc, γλῶσσα, ''glossa''; language, speech, wording) also known as a vocabulary or clavis, is an alphabetical list of terms in a particular domain of knowledge with the definitions for those terms. Traditionally, a glossary appears at the end of a book and includes terms within that book that are either newly introduced, uncommon, or specialized. While glossaries are most commonly associated with non-fiction books, in some cases, fiction novels may come with a glossary for unfamiliar terms. A bilingual glossary is a list of terms in one language defined in a second language or glossed by synonyms (or at least near-synonyms) in another language. In a general sense, a glossary contains explanations of concepts relevant to a certain field of study or action. In this sense, the term is related to the notion of ontology In metaphysics, ontology is the philosophical study of being, as well as related concepts such as existence, becoming, and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moodle
Moodle is a free and open-source learning management system written in PHP and distributed under the GNU General Public License. Moodle is used for blended learning, distance education, flipped classroom and other online learning projects in schools, universities, workplaces and other sectors. Moodle is used to create custom websites with online courses and allows for community-sourced plugins. Overview Moodle was originally developed by Martin Dougiamas with the goal of helping educators create online courses and a focus on interaction and collaborative construction of content. The first version of Moodle was released on , and it continues to be actively developed. The Moodle Project is led and coordinated by Moodle HQ, an Australian company, that is financially supported by a network of eighty-four Moodle Partner service companies worldwide. Development is also assisted by the open-source community. Moodle is a learning platform used to augment and move existing learning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Email Address
An email address identifies an email box to which messages are delivered. While early messaging systems used a variety of formats for addressing, today, email addresses follow a set of specific rules originally standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in the 1980s, and updated by . The term email address in this article refers to just the ''addr-spec'' in Section 3.4 of RFC 5322. The RFC defines ''address'' more broadly as either a ''mailbox'' or ''group''. A ''mailbox'' value can be either a ''name-addr'', which contains a ''display-name'' and ''addr-spec'', or the more common ''addr-spec'' alone. An email address, such as ''john.smith@example.com'', is made up from a local-part, the symbol @, and a '' domain'', which may be a domain name or an IP address enclosed in brackets. Although the standard requires the local part to be case-sensitive, it also urges that receiving hosts deliver messages in a case-independent manner, e.g., that the mail system in the dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Wiki
A personal wiki is wiki software that allows individual users to organize information on their desktop or mobile computing devices in a manner similar to community wikis, but without collaborative software or multiple users. Personal wiki software can be broadly divided into two categories: * Multi-user applications with personal editions (such as MoinMoin or TWiki), installed for standalone use and inaccessible to outside users, which may require additional software such as a web server, database management system and/or WAMP/ LAMP bundle * Applications designed for single users, not dependent on a database engine or web server Some personal wikis are public, but password-protected, and run on dedicated web servers or are hosted by third parties. Multi-user wiki software Multi-user wiki applications with personal editions include: * MoinMoin desktop edition (written in Python) * TWiki for Windows Personal and Certified TWiki (both written in Perl) * MediaWiki (powers Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomboy Notes
Tomboy is a free and open-source desktop notetaking app written for Windows, macOS, Linux, and BSD operating systems. Tomboy is part of the GNOME desktop environment. As Ubuntu changed over time and its cloud synchronization software Ubuntu One came and went, Tomboy inspired various forks and clones. Its interface is a word processor with a wiki-like linking system to connect notes together. Words in the note body that match existing note titles become hyperlinks automatically, making it simple to construct a personal wiki. For example, repeated references to favorite artists would be automatically highlighted in notes containing their names. As of version 1.6 (2010), it supports text entries and hyperlinks to the World Wide Web, but not graphic image linking or embedding. Development of the original Tomboy software ceased in 2017. Starting in 2017 the development team rewrote the software from scratch, for ease of maintenance and installation, renaming it tomboy-ng. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Forum
An Internet forum, or message board, is an online discussion site where people can hold conversations in the form of posted messages. They differ from chat rooms in that messages are often longer than one line of text, and are at least temporarily archived. Also, depending on the access level of a user or the forum set-up, a posted message might need to be approved by a moderator before it becomes publicly visible. Forums have a specific set of jargon associated with them; example: a single conversation is called a "thread", or ''topic''. A discussion forum is hierarchical or tree-like in structure: a forum can contain a number of subforums, each of which may have several topics. Within a forum's topic, each new discussion started is called a thread and can be replied to by as many people as so wish. Depending on the forum's settings, users can be anonymous or have to register with the forum and then subsequently log in to post messages. On most forums, users do not have to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Term
In information retrieval, an index term (also known as subject term, subject heading, descriptor, or keyword) is a term that captures the essence of the topic of a document. Index terms make up a controlled vocabulary for use in bibliographic records. They are an integral part of bibliographic control, which is the function by which libraries collect, organize and disseminate documents. They are used as keywords to retrieve documents in an information system, for instance, a catalog or a search engine. A popular form of keywords on the web are tags, which are directly visible and can be assigned by non-experts. Index terms can consist of a word, phrase, or alphanumerical term. They are created by analyzing the document either manually with subject indexing or automatically with automatic indexing or more sophisticated methods of keyword extraction. Index terms can either come from a controlled vocabulary or be freely assigned. Keywords are stored in a search index. Common wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |