|
Autoimmune Thyroiditis
Autoimmune thyroiditis, is a chronic disease in which the body interprets the thyroid glands and its hormone products T3, T4 and TSH as threats, therefore producing special antibodies that target the thyroid's cells, thereby destroying it. It may present with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism and with or without a goiter. Signs and symptoms The symptoms may vary depending on the thyroid function, i.e. hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Hyperthyroidism can cause sweating, rapid heart rate, anxiety, tremors, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, sudden weight loss, and protruding eyes. Hypothyroidism can cause weight gain, fatigue, dry skin, hair loss, intolerance to cold, and constipation. The effects of this disease may be permanent but can sometimes be transient. Symptoms may come and go depending on whether the person receives treatment, and whether the treatment takes effect. Causes Thyroid autoimmunity is familial. The disease is said to be inherited as a dominant trait since it h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
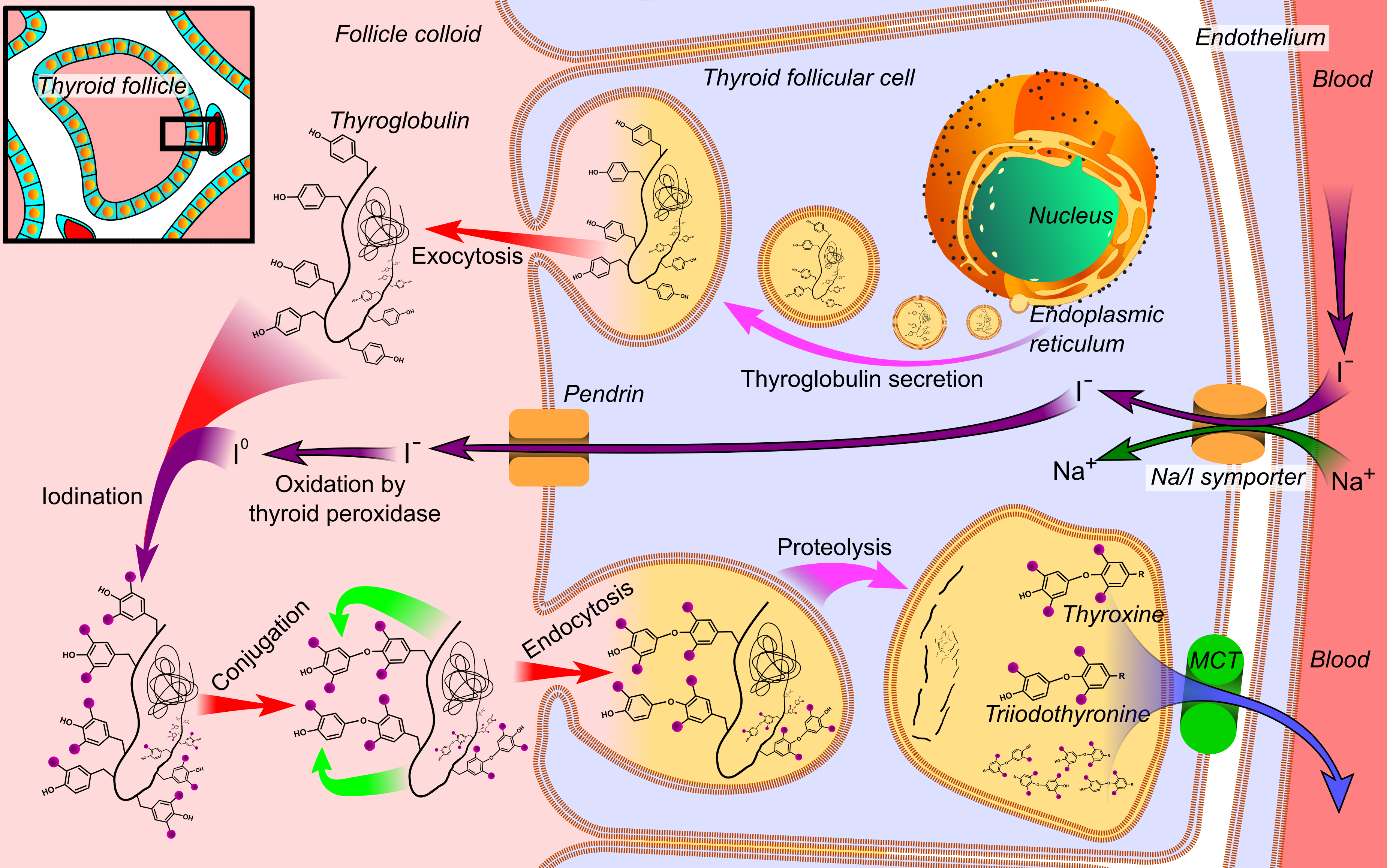
Thyroid Peroxidase
Thyroid peroxidase, also called thyroperoxidase (TPO) or iodide peroxidase, is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid. Thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms for addition onto tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin for the production of thyroxine (T4) or triiodothyronine (T3), the thyroid hormones. In humans, thyroperoxidase is encoded by the ''TPO'' gene. Catalyzed reaction + I− + H+ + H2O2 ⇒ + 2 H2O Iodide is oxidized to iodine radical which immediately reacts with tyrosine. + I− + H+ + H2O2 ⇒ + 2 H2O The second iodine atom is added in similar manner to the reaction intermediate 3-iodotyrosine. Function Inorganic iodine enters the body primarily as iodide, I−. After entering the thyroid follicle (or thyroid follicular cell) via a Na+/I− symporter (NIS) on the basolateral side, iodide is shuttled across the apical membrane into the colloid via pendrin, after which thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium (medication)
Certain lithium compounds, also known as lithium salts, are used as psychiatric medication, primarily for bipolar disorder and for major depressive disorder. In these disorders, it sometimes reduces the risk of suicide. Lithium is taken orally. Common side effects include increased urination, shakiness of the hands, and increased thirst. Serious side effects include hypothyroidism, diabetes insipidus, and lithium toxicity. Blood level monitoring is recommended to decrease the risk of potential toxicity. If levels become too high, diarrhea, vomiting, poor coordination, sleepiness, and ringing in the ears may occur. Lithium is teratogenic, especially during the first trimester of pregnancy and at higher dosages. The use of lithium while breastfeeding is controversial; however, many international health authorities advise against it, and the long-term outcomes of perinatal lithium exposure have not been studied. The American Academy of Pediatrics lists lithium as contraindicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Thyroiditis
Postpartum thyroiditis refers to thyroid dysfunction occurring in the first 12 months after pregnancy and may involve hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism or the two sequentially. According to the National Institute of Health, postpartum thyroiditis affects about 8% of pregnancies. There are, however, different rates reported globally. This is likely due to the differing amounts of average postpartum follow times around the world, and due to humans' own innate differences. For example, in Bangkok, Thailand the rate is 1.1%, but in Brazil it is 13.3%. The first phase is typically hyperthyroidism. Then, the thyroid either returns to normal or a woman develops hypothyroidism. Of those women who experience hypothyroidism associated with postpartum thyroiditis, one in five will develop permanent hypothyroidism requiring lifelong treatment. Postpartum thyroiditis is believed to result from the modifications to the immune system necessary in pregnancy, and histologically is a subacute lymphoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graves' Disease
Graves' disease (german: Morbus Basedow), also known as toxic diffuse goiter, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It also often results in an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea and unintentional weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye bulging, a condition caused by Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25 to 30% of people with the condition develop eye problems. The exact cause of the disease is unclear; however, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A person is more likely to be affected if they have a family member with the disease. If one twin is affected, a 30% chance exists that the other twin will also have the disease. The onset of disease may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Early on, symptoms may not be noticed. Over time, the thyroid may enlarge, forming a painless goiter. Some people eventually develop hypothyroidism with accompanying weight gain, fatigue, constipation, depression, hair loss, and general pains. After many years the thyroid typically shrinks in size. Potential complications include thyroid lymphoma. Furthermore, because it is common for untreated patients of Hashimoto's to develop hypothyroidism, further complications can include, but are not limited to, high cholesterol, heart disease, heart failure, high blood pressure, myxedema, and potential pregnancy problems. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is thought to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include a family history of the condition and having another autoimmune disease. Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor
The thyrotropin receptor (or TSH receptor) is a receptor (and associated protein) that responds to thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as "thyrotropin") and stimulates the production of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The TSH receptor is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily of integral membrane proteins and is coupled to the Gs protein. It is primarily found on the surface of the thyroid epithelial cells, but also found on adipose tissue and fibroblasts. The latter explains the reason of the myxedema finding during Graves disease. In addition, it has also been found to be expressed in the anterior pituitary gland, hypothalamus and kidneys. Its presence in the anterior pituitary gland may be involved in mediating the paracrine signaling feedback inhibition of thyrotropin along the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis. Function Upon binding circulating TSH, a G-protein signal cascade activates adenylyl cyclase and intracellular levels of cAMP rise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroglobulin
Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a 660 kDa, dimeric glycoprotein produced by the follicular cells of the thyroid and used entirely within the thyroid gland. Tg is secreted and accumulated at hundreds of grams per litre in the extracellular compartment of the thyroid follicles, accounting for approximately half of the protein content of the thyroid gland. Human TG (hTG) is a homodimer of subunits each containing 2768 amino acids as synthesized (a short signal peptide of 19 aminoacids may be removed from the N-terminus in the mature protein). Thyroglobulin is in all vertebrates the main precursor to thyroid hormones, which are produced when thyroglobulin's tyrosine residues are combined with iodine and the protein is subsequently cleaved. Each thyroglobulin molecule contains approximately 100–120 tyrosine residues, but only a small number (20) of these are subject to iodination by thyroperoxidase in the follicular colloid. Therefore, each Tg molecule forms approximately 10 thyroid hormo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immunity), and B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- or bursa-derived cells) are the major cellular components of the adaptive immune response. T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity, whereas B cells are primarily responsible for humoral immunity (relating to antibodies). The function of T cells and B cells is to recognize specif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological processes and behavioral activities such as diges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoantibodies
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies. Production Antibodies are produced by B cells in two ways: (i) randomly, and (ii) in response to a foreign protein or substance within the body. Initially, one B cell produces one specific kind of antibody. In either case, the B cell is allowed to proliferate or is killed off through a process called clonal deletion. Normally, the immune system is able to recognize and ignore the body's own healthy proteins, cells, and tissues, and to not overreact to non-threatening substances in the environment, such as foods. Sometimes, the immune system ceases to recognize one or more of the body's normal constituents as "self," leading to production of pathological autoantibodies. Autoantibodies may also play a nonpathological role; for instance they m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turner Syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hairline at the back of the neck, short stature, and swollen hands and feet are seen at birth. Typically, those affected do not develop menstrual periods, or breasts without hormone treatment and are unable to have children without reproductive technology. Heart defects, diabetes, and low thyroid hormone occur in the disorder more frequently than average. Most people with Turner syndrome have normal intelligence; however, many have problems with spatial visualization that may be needed in order to learn mathematics. Vision and hearing problems also occur more often than average. Turner syndrome is not usually inherited; rather, it occurs during formation of the reproductive cells in a parent or in early cell division during development. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)