|
Austrian Goods
The Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) 403 (or 'Austrian Goods') Class was a class of 2-6-0 (mogul) steam locomotive designed by Peter Drummond, of which 11 were built in 1915 by the North British Locomotive Company at its Queens Park works. Originally built as the 403 class, as a result of renumbering they became known as the 33 Class in 1916 and then 51 Class in 1919, before passing to the London Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) on its formation in 1923, where they were given power classification 4F. These freight-traffic locomotives were given the nickname ''Austrian Goods''. The nickname was acquired because when the locomotives were delivered it was rumoured that they had been built from materials that NBL had gathered for a contract for Austria which was cancelled when World War I broke out. However, this rumour was unfounded as the design was entirely Drummond's and there is no evidence of any Austrian contract. History The class was a development of Drummond's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Drummond (engineer)
Peter Drummond (1850–1918) was a Scottish Locomotive Superintendent with the Highland Railway from 1896 to 1911 and with the Glasgow and South Western Railway from 1912 to 1918. He was the younger brother of the engineer Dugald Drummond. Locomotives Locomotives designed by Peter Drummond include: *Highland Railway Drummond 0-6-0 Class goods engine *Highland Railway Drummond 0-6-4T Class The Highland Railway Drummond 0-6-4T or X class were large tank engines originally intended for banking duty. They were designed by Peter Drummond. Construction The first four were built by the North British Locomotive Company and delivered ... banking engine * Highland Railway L Class 4-4-0 passenger engine * Highland Railway Ben Class 4-4-0 passenger engine * G&SWR 'Austrian Goods' 2-6-0 References 1850 births 1918 deaths British mechanical engineers Locomotive builders and designers Glasgow and South Western Railway people {{UK-engineer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into superheated steam or dry steam. Superheated steam is used in steam turbines for electricity generation, steam engines, and in processes such as steam reforming. There are three types of superheaters: radiant, convection, and separately fired. A superheater can vary in size from a few tens of feet to several hundred feet (a few metres to some hundred metres). Types * A radiant superheater is placed directly in radiant zone of the combustion chamber near the water wall so as to absorb heat by radiation. * A convection superheater is located in the convective zone of the furnace usually ahead of economizer (in the path of the hot flue gases). These are also called primary superheaters. * A separately fired superheater is a superheater that is placed outside the main boiler, which has its own separate combustion system. This superheater design incorporates additional burners in the area of superheater pipes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1915
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NBL Locomotives
NBL may refer to: Business * Namibia Breweries Limited * National Bank Limited, the first private sector bank fully owned by Bangladeshi entrepreneurs * Nepal Bank Limited * Noble Energy, a former oil and natural gas exploration and production company with the NYSE ticker symbol NBL, now part of Chevron Corporation * North British Locomotive Company Science * n-Butyllithium, an organic compound * Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory, an astronaut training facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center * New Brunswick Laboratory Sports * National Badminton League (United Kingdom) * National Basketball League (other) * National Bicycle League (United States) * National Bowling League (United States) – defunct * North Bay League, now part of the North Coast Section (NCS) of the California Interscholastic Federation (CIF) Other uses * North Berwick Law, a volcanic plug in East Lothian, Scotland, United Kingdom * Northumberland, county in England, Chapman code * ''Nuestra Belleza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow And South Western Railway Locomotives
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between historic Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and is governed by Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's West Central Lowlands. Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK. Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the Burrell Collection, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland, the Royal Scottish National Orchestra, Scottish Ballet and Scottish Opera – enjoy international reputations. The city was the European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its architecture, culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMS Hughes Crab
The London Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) Hughes Crab or Horwich Mogul is a class of mixed-traffic 2-6-0 steam locomotive built between 1926 and 1932. They are noted for their appearance with large steeply-angled cylinders to accommodate a restricted loading gauge A loading gauge is a diagram or physical structure that defines the maximum height and width dimensions in railway vehicles and their loads. Their purpose is to ensure that rail vehicles can pass safely through tunnels and under bridges, and ke .... Overview Designed by George Hughes (engineer), George Hughes, Chief Mechanical Engineer of the LMS, and built at the ex-Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway, L&YR works at Horwich railway works, Horwich and the ex-London and North Western Railway, LNWR works at Crewe. The inspiration came from a Caledonian Railway design at the grouping, however the cylinders were too large for the LMS's English section's loading gauge, resulting in Hughes having to adapt the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
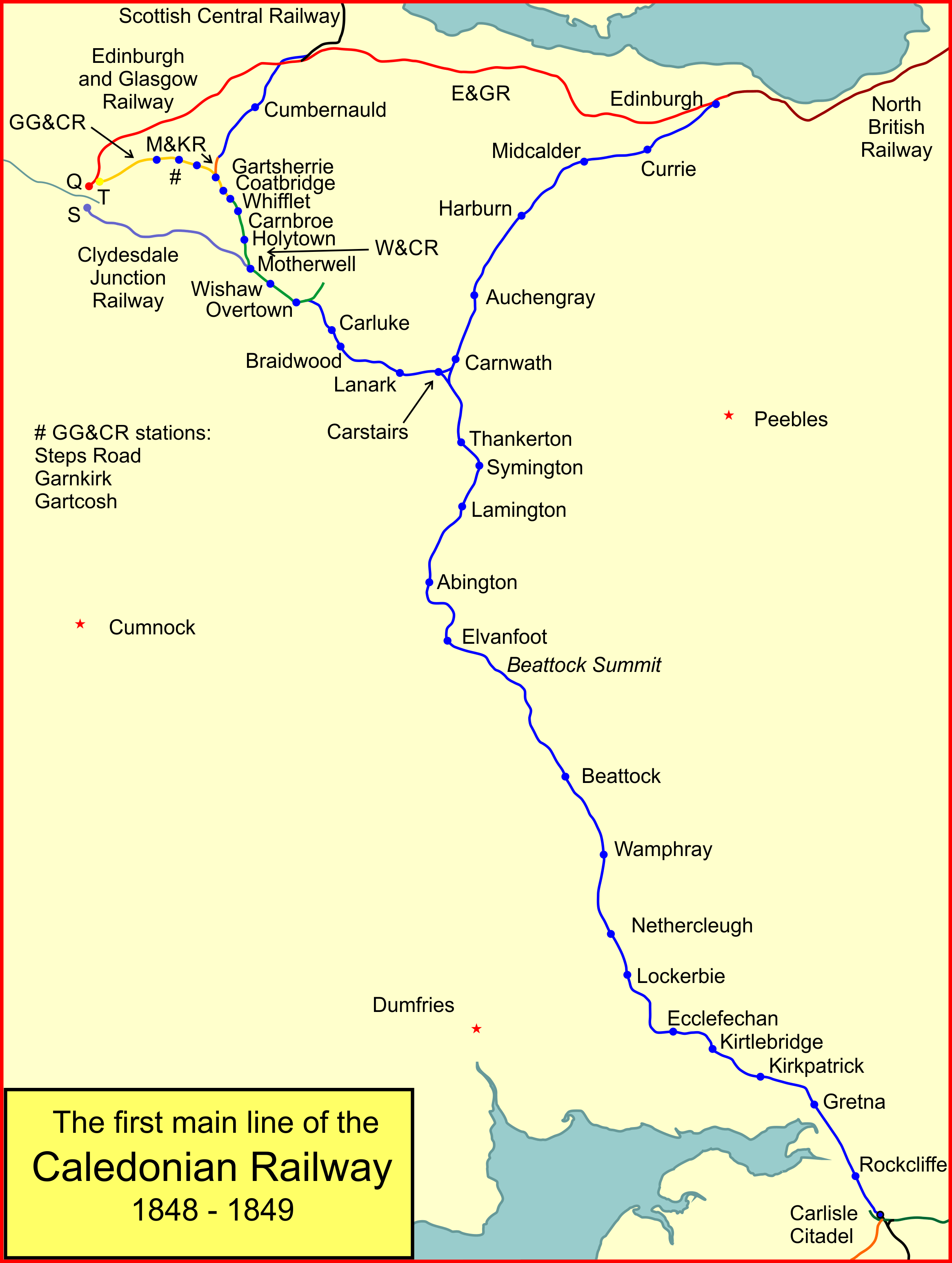
Caledonian Main Line
The Caledonian Railway main line in Scotland connected Glasgow and Edinburgh with Carlisle, via Carstairs and Beattock. It was opened in 1847 by the Caledonian Railway. The approach to Glasgow used railways already built, primarily for mineral traffic; these were later by-passed by a more direct route. Today, the route forms the northern section of the West Coast Main Line, and was electrified in the early 1970s. Opening From 1830 onwards considerable attention was given to the means by which Glasgow and Edinburgh might be connected to London, and as English railways began to develop into a network, the urgency of making a railway accelerated. The difficult terrain of the Southern Uplands and Cumberland made the selection of a route controversial. After much difficulty, the Caledonian Railway was authorised to build a line via Beattock; this was known as the ''Annandale Route''. On 10 September 1847 the line was opened between Carlisle and Beattock. The station at Carlisle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankpin
A crankpin or crank pin, also known as a rod bearing journal, is a mechanical device in an engine which connects the crankshaft to the connecting rod for each cylinder. It has a cylindrical surface, to allow the crankpin to rotate relative to the "big end" of the connecting rod. The most common configuration is for a crankpin to serve one cylinder. However, many V engines have each crankpin shared by each pair of cylinders. Design The crankpin connects to the larger end of the connecting rod for each cylinder. This end of the connecting rod is called the "big end", as opposed to the "small end" or "little end" (which connects to the wrist/gudgeon pin in the piston). The bearing which allows the crankpin to rotate around its shaft is called the "rod bearing". In automotive engines, the most common type of rod bearing is the plain bearing, however Bushing (bearing), bushings or roller bearings are also used in some engines. Configurations In a single-cylinder engine, strai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pony Truck
A Bissell or Bissel truck (also Bissel bogie or Pony truck) is a single-axle bogie which pivots towards the centre of a steam locomotive to enable it to negotiate curves more easily. Invented in 1857 by and usually then known as a ''pony truck'', it is a very simple and common means of designing a carrying wheel. Name variants A pony truck in railway terminology, is a leading truck with only two wheels. Its invention is generally credited to Bissell, who devised one in 1857 and patented it the following year. Hence the term ''Bissel bogie'', ''Bissel truck'', or ''Bissel axle'' is used in continental Europe. In the UK, the term is Bissell truck.''Spellings" Conservative locomotive builders in Bissell's native |
G&SWR 279 Class
The Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) 279 class was a class of 0-6-0 steam locomotive designed by Peter Drummond, of which 15 were built in 1913 by the North British Locomotive Company at its Queen's Park works. Originally built as the 279 class, as a result of renumbering they became known as the 71 class in 1919, before passing to the London Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) on its formation in 1923, where they were given power classification 4F. History Until the retirement of James Manson from the post of locomotive superintendent at the end of 1911, the development of Glasgow and South Western Railway locomotives had been a matter of gradual evolution. Successive locomotive superintendents had learned their trade at the company's Kilmarnock Locomotive Works before reaching the top job. Most of the locomotives were efficient and reliable machines, but by 1911 many were elderly and even the newer locomotives were somewhat small by contemporary standards. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |