|
Australian Charbray
The Australian Charbray (Bos taurus x Bos indicus) is an Australian breed of cattle derived from a cross between the French Charolais cattle and American Brahman cattle. The charbray breed was first conceived in the United States of America in the 1930s and later introduced into Australia in 1969. In Australia, Australian charbray breeders are concentrated in the tropical Northern regions of Queensland. As of 1977, the official breeder society of Charbray cattle in Australia and New Zealand is thCharbray Society of Australia Limited responsible for recording Charbray cattle in herd books, fostering improvement, enhancement and sales of Charbray cattle. History The Australian Charbray was first developed in the U.S. in the 1930s and later independently bred and introduced into Australia in the late 1960s. Within an agricultural context, innovation through new technology and practices are upheld by government agencies, breed societies, and agricultural firms. The Australian gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Charbray Bull
Australian(s) may refer to: Australia * Australia, a country * Australians, citizens of the Commonwealth of Australia ** European Australians ** Anglo-Celtic Australians, Australians descended principally from British colonists ** Aboriginal Australians, indigenous peoples of Australia as identified and defined within Australian law * Australia (continent) ** Indigenous Australians * Australian English, the dialect of the English language spoken in Australia * Australian Aboriginal languages * ''The Australian ''The Australian'', with its Saturday edition, ''The Weekend Australian'', is a broadsheet newspaper published by News Corp Australia since 14 July 1964.Bruns, Axel. "3.1. The active audience: Transforming journalism from gatekeeping to gatew ...'', a newspaper * Australiana, things of Australian origins Other uses * Australian (horse), a racehorse * Australian, British Columbia, an unincorporated community in Canada See also * The Australian (disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. Definition The concept of biotechnology encompasses a wide range of procedures for modifying living organisms according to human purposes, going back to domestication of animals, cultivation of the plants, and "improvements" to these through breeding programs that employ artificial selection and hybridization. Modern usage also includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. The American Chemical Society defines biotechnology as the application of biological organisms, systems, or processes by various industries to learning about the science of life and the improvement of the value of materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrous Cycle
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous phases, otherwise known as "rest" phases, or by pregnancies. Typically, estrous cycles repeat until death. These cycles are widely variable in duration and frequency depending on the species.Bronson, F. H., 1989. Mammalian Reproductive Biology. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL, USA. Some animals may display bloody vaginal discharge, often mistaken for menstruation. Many mammals used in commercial agriculture, such as cattle and sheep, may have their estrous cycles artificially controlled with hormonal medications for optimum productivity. The male equivalent, seen primarily in ruminants, is called rut. Differences from the menstrual cycle Mammals share the same reproductive system, including the regulatory hypothalamic system t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semen Cryopreservation
Semen cryopreservation (commonly called sperm banking or sperm freezing) is a procedure to preserve sperm cells. Semen can be used successfully indefinitely after cryopreservation. It can be used for sperm donation where the recipient wants the treatment in a different time or place, or as a means of preserving fertility for men undergoing vasectomy or treatments that may compromise their fertility, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy or surgery. It is also often used by transgender women prior to medically transitioning in ways that affect fertility, such as feminizing hormone therapy and orchiectomies. Freezing The most common cryoprotectant used for semen is glycerol (10% in culture medium). Often sucrose or other di-, trisaccharides are added to glycerol solution. Cryoprotectant media may be supplemented with either egg yolk or soy lecithin, with the two having no statistically significant differences compared to each other regarding motility, morphology, ability to bind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogenic Disease
This is a list of infectious diseases arranged by name, along with the infectious agents that cause them and the vaccines that can prevent or cure them when they exist. List See also * * List of oncogenic bacteria * − including specific infectious diseases and classes thereof * * References * Chin J. B., ed. Control of Communicable Diseases Manual The ''Control of Communicable Diseases Manual'' (CCDM) is one of the most widely recognized reference volumes on the topic of infectious diseases. It is useful for physicians, epidemiologists, global travelers, emergency volunteers and all who hav .... 17th ed. APHA merican Public Health AssociationPress; 2000. * Red Book: 2009 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 2009. American Academy of Pediatrics. 28th ed. * Centers for Disease Control and PreventionCDC Works 24/7 Retrieved on August 4, 2009. {{Pediculosis, acariasis and other infestations + * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stressor
A stressor is a chemical or biological agent, environmental condition, external stimulus or an event seen as causing stress to an organism. Psychologically speaking, a stressor can be events or environments that individuals might consider demanding, challenging, and/or threatening individual safety.Deckers, Lambert (2018). Motivation Biological, Psychological, and Environmental. New York, NY: Routledge. pp. 208-212. . Events or objects that may trigger a stress response may include: * environmental stressors ( hypo or hyper-thermic temperatures, elevated sound levels, over-illumination, overcrowding) * daily "stress" events (e.g., traffic, lost keys, money, quality and quantity of physical activity) * life changes (e.g., divorce, bereavement) * workplace stressors (e.g., high job demand vs. low job control, repeated or sustained exertions, forceful exertions, extreme postures, office clutter) * chemical stressors (e.g., tobacco, alcohol, drugs) * social stressor (e.g., socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or "knock out", genes. The new DNA can be inserted randomly, or targeted to a specific part of the genome. An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be genetically modified (GM) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterosis
Heterosis, hybrid vigor, or outbreeding enhancement is the improved or increased function of any biological quality in a hybrid offspring. An offspring is heterotic if its traits are enhanced as a result of mixing the genetic contributions of its parents. These effects can be due to Mendelian or non-Mendelian inheritance. Definitions In proposing the term heterosis to replace the older term heterozygosis, G.H. Shull aimed to avoid limiting the term to the effects that can be explained by heterozygosity in Mendelian inheritance. Heterosis is often discussed as the opposite of inbreeding depression, although differences in these two concepts can be seen in evolutionary considerations such as the role of genetic variation or the effects of genetic drift in small populations on these concepts. Inbreeding depression occurs when related parents have children with traits that negatively influence their fitness largely due to homozygosity. In such instances, outcrossing shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterosis
Heterosis, hybrid vigor, or outbreeding enhancement is the improved or increased function of any biological quality in a hybrid offspring. An offspring is heterotic if its traits are enhanced as a result of mixing the genetic contributions of its parents. These effects can be due to Mendelian or non-Mendelian inheritance. Definitions In proposing the term heterosis to replace the older term heterozygosis, G.H. Shull aimed to avoid limiting the term to the effects that can be explained by heterozygosity in Mendelian inheritance. Heterosis is often discussed as the opposite of inbreeding depression, although differences in these two concepts can be seen in evolutionary considerations such as the role of genetic variation or the effects of genetic drift in small populations on these concepts. Inbreeding depression occurs when related parents have children with traits that negatively influence their fitness largely due to homozygosity. In such instances, outcrossing shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
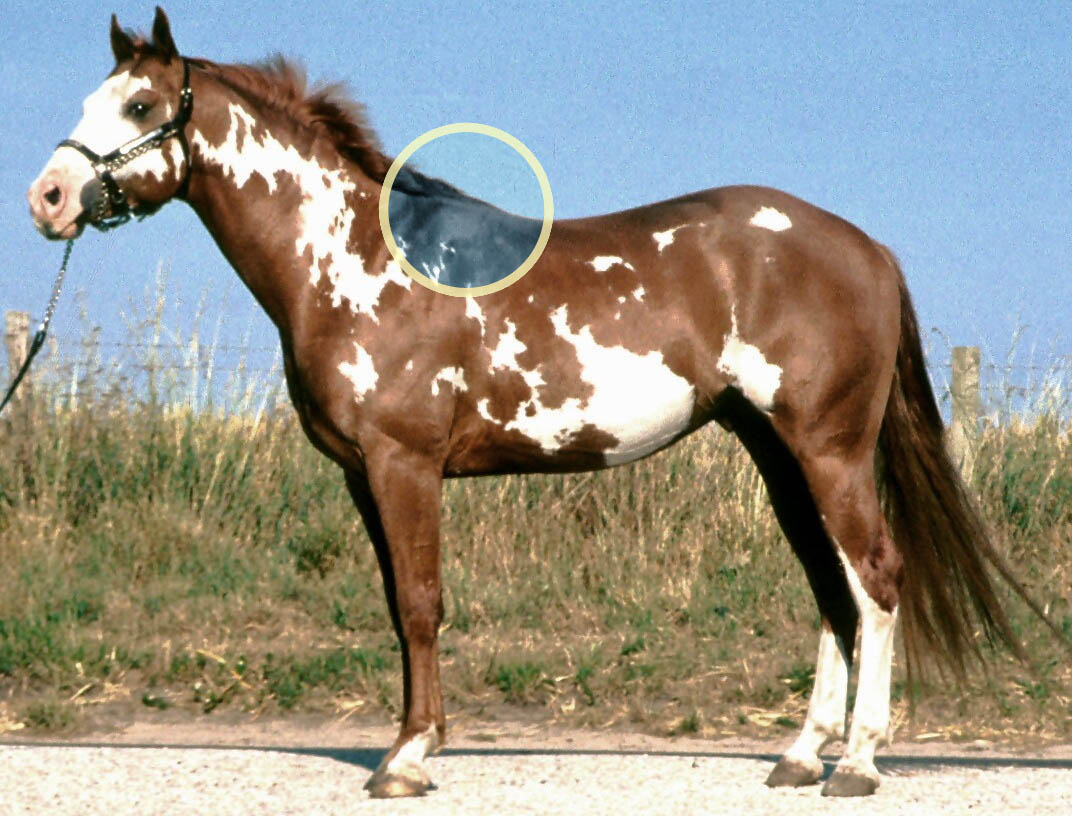
Withers
The withers is the ridge between the shoulder blades of an animal, typically a quadruped. In many species, it is the tallest point of the body. In horses and dogs, it is the standard place to measure the animal's height. In contrast, cattle are often measured to the top of the hips. The term (pronounced ) derives from Old English ''wither'' (“against”), because it is the part of a draft animal that pushes against a load. Horses The withers in horses are formed by the dorsal spinal processes of roughly the 3rd through 11th thoracic vertebrae, which are unusually long in this area. Most horses have 18 thoracic vertebrae. The processes at the withers can be more than long. Since they do not move relative to the ground as the horse's head does, the withers are used as the measuring point for the height of a horse. Horses are sometimes measured in hands – one hand is . Horse heights are extremely variable, from small pony breeds to large draft breeds. The height at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |