|
Aughton, East Riding Of Yorkshire
Aughton is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Ellerton, in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It is situated approximately north-west of the market town of Howden and south-west of the market town of Pocklington. In 1931 the parish had a population of 100. It lies west of the B1228 road and east of the River Derwent. All Saints Church All Saints Church, Aughton is located at the far end of the village and overlooks vast expanses of the floodplains of the River Derwent. Tucked away in the village, it can only be accessed on foot through a small gate and field adjacent to Aughton Hall. An historic church, famous for its association with Robert Aske, leader of the insurgents in the Pilgrimage of Grace, October 1536. Aske was executed for treason on 12 July 1537. The church displays a mixture of architectural designs as it has been altered throughout the years, but is noted especially for its Norman arch between the chancel and nave. On the chanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellerton, East Riding Of Yorkshire
Ellerton is a village and civil parish in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It is situated approximately north-west of the market town of Howden and 8 miles south-west of the market town of Pocklington. It lies west of the B1228 road and east of the River Derwent. According to the 2011 UK census, the parish had a population of 388, an increase on the 2001 UK census figure of 355. and covers an area of . Civil parish The parish includes Aughton. In 1935 the civil parishes of Ellerton Priory and Aughton were abolished and merged into Ellerton. Although the civil parish is called "Ellerton" its parish council is called "Ellerton & Aughton Parish Council". History A priory of canons of the Gilbertine Order existed at Ellerton, which was known as Ellerton Priory. The priory was founded before 1212, and relinquished on 11 December 1536 under the Suppression of the Monasteries. The site of the priory is now a scheduled ancient monument. In 1823 Ellerton, was in the Wapent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Architecture
The term Norman architecture is used to categorise styles of Romanesque architecture developed by the Normans in the various lands under their dominion or influence in the 11th and 12th centuries. In particular the term is traditionally used for English Romanesque architecture. The Normans introduced large numbers of castles and fortifications including Norman keeps, and at the same time monasteries, abbeys, churches and cathedrals, in a style characterised by the usual Romanesque rounded arches (particularly over windows and doorways) and especially massive proportions compared to other regional variations of the style. Origins These Romanesque styles originated in Normandy and became widespread in northwestern Europe, particularly in England, which contributed considerable development and where the largest number of examples survived. At about the same time, a Norman dynasty that ruled in Sicily produced a distinctive variation–incorporating Byzantine and Saracen influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Monument
In British law, an ancient monument is an early historical structure or monument (e.g. an archaeological site) worthy of preservation and study due to archaeological or heritage interest. The '' Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979'' classified ancient monuments as "scheduled monuments" or monuments that are considered by the Secretary of State of archaeological, historical or artistic importance. In addition, the term "ancient monument" can also refer to any early or historical manmade structure and/or architecture. Certain ancient monuments are of cultural importance for nations and become symbols of international recognition, including the ruins of Baalbek on Lebanese currency, the Angkor Wat on Cambodian currency and the Great Wall of China on the Chinese currency. There are some countries that display ancient buildings as symbols on their coats of arms as a way to affirm national identity. In this way, ancient monuments in the modern world are used as icons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Monuments And Archaeological Areas Act 1979
The Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979 or AMAAA was a law passed by the UK government, the latest in a series of Ancient Monument Acts legislating to protect the archaeological heritage of England & Wales and Scotland. Northern Ireland has its own legislation. Section 61(12) defines sites that warrant protection due to their being of national importance as 'ancient monuments'. These can be either scheduled monuments or "any other monument which in the opinion of the Secretary of State is of public interest by reason of the historic, architectural, traditional, artistic or archaeological interest attaching to it". If an ancient monument is scheduled then it gains additional legal protection. A monument is defined as: Damage to a scheduled monument is a criminal offence and any works taking place within one require scheduled monument consent from the Secretary of State. The Act also provides for taking ancient monuments into the care of the Secretary of Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motte-and-bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy to build with unskilled labour, but still militarily formidable, these castles were built across northern Europe from the 10th century onwards, spreading from Normandy and Anjou in France, into the Holy Roman Empire in the 11th century. The Normans introduced the design into England and Wales. Motte-and-bailey castles were adopted in Scotland, Ireland, the Low Countries and Denmark in the 12th and 13th centuries. Windsor Castle, in England, is an example of a motte-and-bailey castle. By the end of the 13th century, the design was largely superseded by alternative forms of fortification, but the earthworks remain a prominent feature in many countries. Architecture Structures A motte-and-bailey castle was made up of two structures: a motte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic England
Historic England (officially the Historic Buildings and Monuments Commission for England) is an executive non-departmental public body of the British Government sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. It is tasked with protecting the historic environment of England by preserving and listing historic buildings, scheduling ancient monuments, registering historic Parks and Gardens and by advising central and local government. The body was officially created by the National Heritage Act 1983, and operated from April 1984 to April 2015 under the name of English Heritage. In 2015, following the changes to English Heritage's structure that moved the protection of the National Heritage Collection into the voluntary sector in the English Heritage Trust, the body that remained was rebranded as Historic England. The body also inherited the Historic England Archive from the old English Heritage, and projects linked to the archive such as Britain from Above, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Heritage List For England
The National Heritage List for England (NHLE) is England's official database of protected heritage assets. It includes details of all English listed buildings, scheduled monuments, register of historic parks and gardens, protected shipwrecks, and registered battlefields. It is maintained by Historic England, a government body, and brings together these different designations as a single resource even though they vary in the type of legal protection afforded to them. Although not designated by Historic England, World Heritage Sites also appear on the NHLE; conservation areas do not appear since they are designated by the relevant local planning authority. The passage of the Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1882 established the first part of what the list is today, by granting protection to 50 prehistoric monuments. Amendments to this act increased the levels of protection and added more monuments to the list. Beginning in 1948, the Town and Country Planning Acts created the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
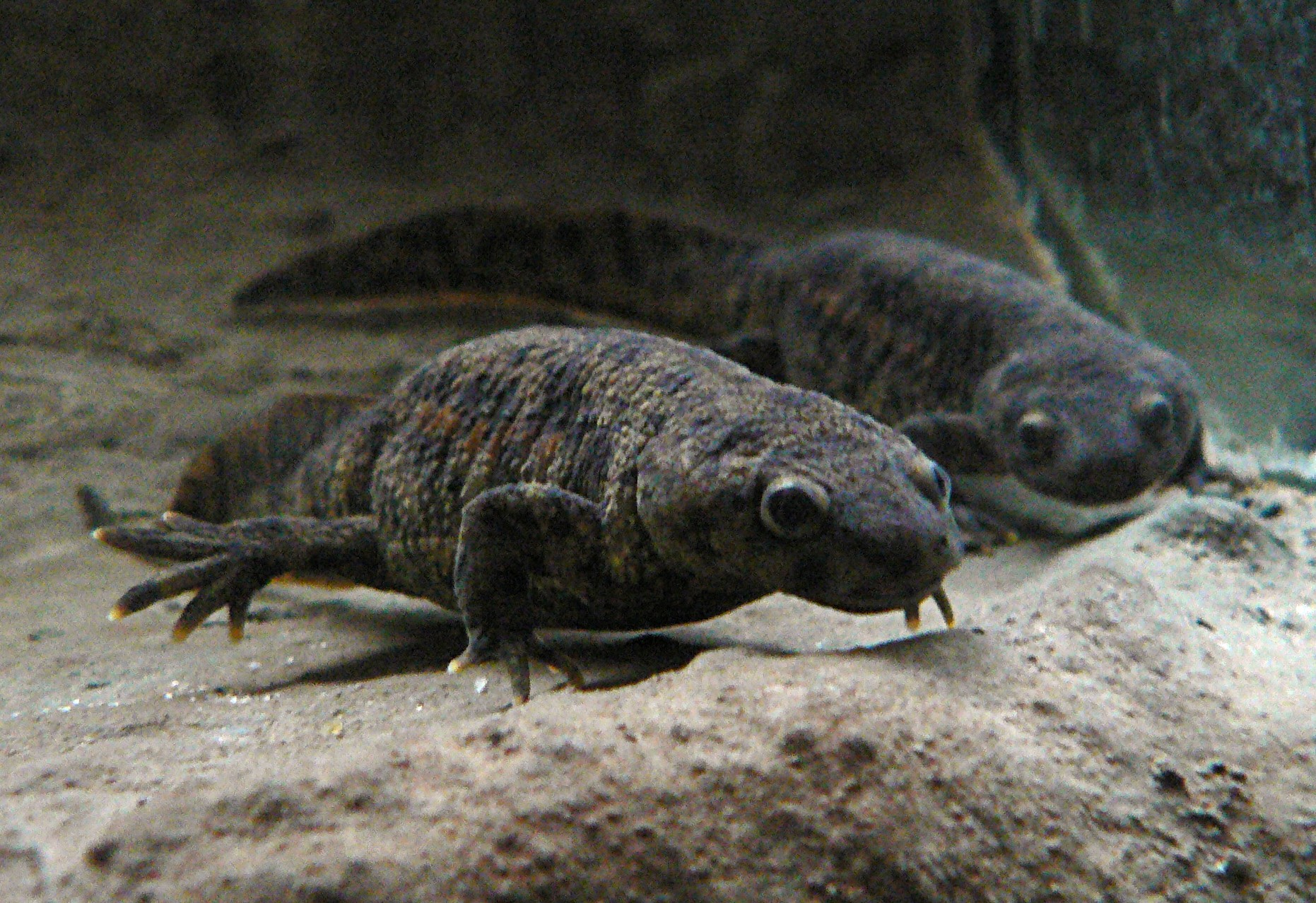
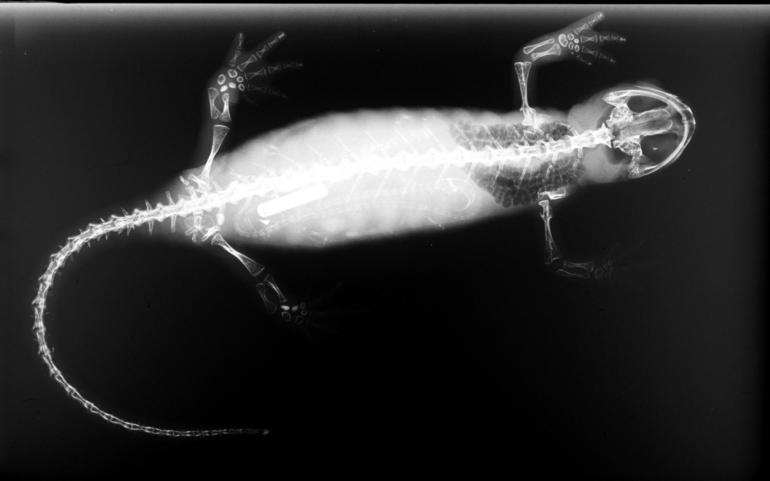
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults. This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newt
A newt is a salamander in the subfamily Pleurodelinae. The terrestrial juvenile phase is called an eft. Unlike other members of the family Salamandridae, newts are semiaquatic, alternating between aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Not all aquatic salamanders are considered newts, however. More than 100 known species of newts are found in North America, Europe, North Africa and Asia. Newts metamorphose through three distinct developmental life stages: aquatic larva, terrestrial juvenile (eft), and adult. Adult newts have lizard-like bodies and return to the water every year to breed, otherwise living in humid, cover-rich land habitats. Newts are threatened by habitat loss, fragmentation and pollution. Several species are endangered, and at least one species, the Yunnan lake newt, has become extinct recently. Etymology The Old English name of the animal was , (of unknown origin), resulting in Middle English ; this word was transformed irregularly into , , or . The initial "n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Armour
Plate armour is a historical type of personal body armour made from bronze, iron, or steel plates, culminating in the iconic suit of armour entirely encasing the wearer. Full plate steel armour developed in Europe during the Late Middle Ages, especially in the context of the Hundred Years' War, from the coat of plates worn over mail suits during the 14th century. In Europe, plate armour reached its peak in the late 15th and early 16th centuries. The full suit of armour, also referred to as a panoply, is thus a feature of the very end of the Middle Ages and the Renaissance period. Its popular association with the " medieval knight” is due to the specialised jousting armour which developed in the 16th century. Full suits of Gothic plate armour were worn on the battlefields of the Burgundian and Italian Wars. The most heavily armoured troops of the period were heavy cavalry, such as the gendarmes and early cuirassiers, but the infantry troops of the Swiss mercenaries and the La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |