|
Augeron
Augeron is the Norman dialect of the Pays d'Auge. It is highly endangered. This dialect includes both coastal and inland areas. Phonology Augeron can be characterised by means of its position within the isoglosses that traverse the Norman-speaking territory. Situated near the division between Lower and Upper Normandy, it can be described as transitional, displaying as it does features typical of western and eastern dialects. Augeron lies north of the Joret line and therefore shares unpalatalised (example: = cat) and palatalised (example: = five) with the northern dialects from the insular varieties and Cotentinais in the west to Cauchois in the east. It lies west of the isogloss - (example: = conceal). It is at the easternmost boundary of the Norman dialects displaying this feature. By contrast, it lies east of the isogloss - (example: = place). It is near the westernmost boundary of the Norman dialects displaying this feature. Along with other northern dialects it di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
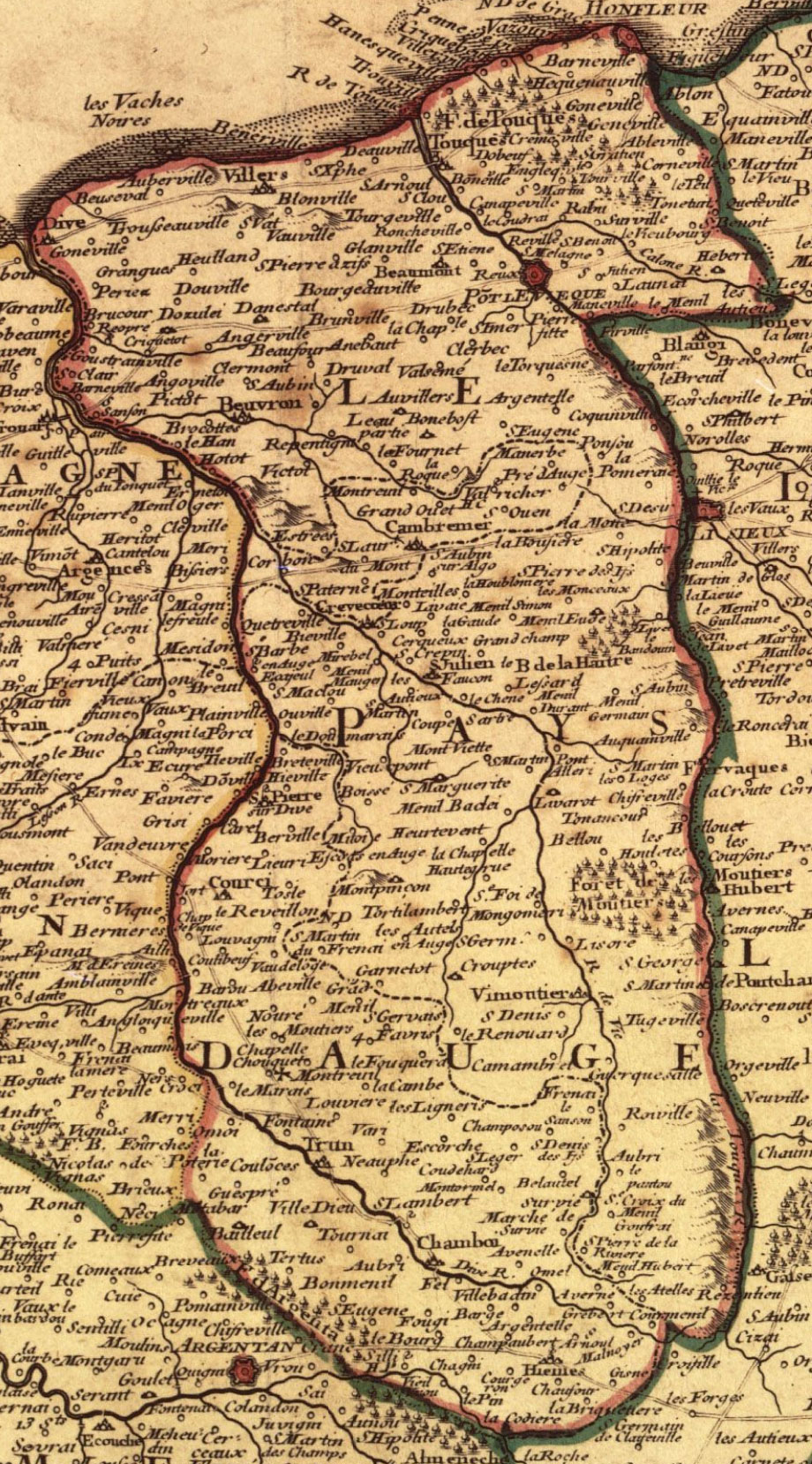
Pays D'Auge
The Pays d'Auge (, literally ''Land of Auge'') is an area in Normandy, straddling the ''départements'' of Calvados and Orne (plus a small part of the territory of Eure). The chief town is Lisieux. Geography Generally it consists of the basin of the Touques River. The Pays d'Auge is divided into the following cantons: Canton of Cabourg, Canton of Dozulé, Canton of Trouville Deauville, Canton of Honfleur, Canton of Troarn, Canton of Cambremer, Canton of Pont-l'Evêque, Canton of Blangy-le-Château, Canton of Mézidon-Canon, Canton of Lisieux, Canton of Saint-Pierre-sur-Dives, Canton of Livarot, Canton of Orbec, Canton of Trun, Canton of Vimoutiers, Canton of Exmes and Canton of Gacé. Economy The landscape of this area is considered typical of Normandy—agricultural and producing dairy produce and apples. It is noted for its cheeses, especially Camembert (named for a place in Pays d'Auge), Livarot and Pont-l'Évêque, also names of villages. The Pays d'Auge has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvados (department)
Calvados (, , ) is a department in the Normandy region in northwestern France. It takes its name from a cluster of rocks off the English Channel coast. In 2019, it had a population of 694,905.Populations légales 2019: 14 Calvados INSEE History Calvados is one of the original 83 departments created during the on 4 March 1790, in application of the law of 22 December 1789. It had been part of the former province of |
Orne
Orne (; nrf, Ôrne or ) is a département in the northwest of France, named after the river Orne. It had a population of 279,942 in 2019.Populations légales 2019: 61 Orne INSEE History Orne is one of the original 83 départements created during the , on 4 March 1790. It was created from parts of the of and[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Language
Norman or Norman French (, french: Normand, Guernésiais: , Jèrriais: ) is a Romance language which can be classified as one of the Oïl languages along with French, Picard and Walloon. The name "Norman French" is sometimes used to describe not only the Norman language, but also the administrative languages of ''Anglo-Norman'' and ''Law French'' used in England. For the most part, the written forms of Norman and modern French are mutually intelligible. This intelligibility was largely caused by the Norman language's planned adaptation to French orthography (writing). History When Norse Vikings from modern day Scandinavia arrived in Neustria, in the western part of the then Kingdom of the Franks, and settled the land that became known as Normandy, these North-Germanic–speaking people came to live among a local Gallo-Romance–speaking population. In time, the communities converged, so that ''Normandy'' continued to form the name of the region while the original Norse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isogloss
An isogloss, also called a heterogloss (see Etymology below), is the geographic boundary of a certain linguistic feature, such as the pronunciation of a vowel, the meaning of a word, or the use of some morphological or syntactic feature. Major dialects are typically demarcated by ''bundles'' of isoglosses, such as the Benrath line that distinguishes High German from the other West Germanic languages and the La Spezia–Rimini Line that divides the Northern Italian languages and Romance languages west of Italy from Central Italian dialects and Romance languages east of Italy. However, an ''individual'' isogloss may or may not have any coterminus with a language border. For example, the front-rounding of /y/ cuts across France and Germany, while the /y/ is absent from Italian and Spanish words that are cognates with the /y/-containing French words. One of the best-known isoglosses is the centum-satem isogloss. Similar to an isogloss, an isograph is a distinguishing feature of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joret Line
The Joret line (french: ligne Joret; Norman: ''lène Joret'') is an isogloss used in the linguistics of the . Dialects north and west of the line have preserved Vulgar Latin and before ; dialects south and east of the line have palatalized and before . This palatalization gave Old French and , then modern French and . The line was first identified by Charles Joret and published in 1883. To the north and west of the line are found Picard and some dialects of Norman. To the south and the east lie other Oïl dialects including southern Norman, Walloon and French. The area north and west of the is sometimes called the ''Normano-Picard'' domain. Geography The Joret line extends from the Channel Islands (including Jèrriais, Guernésiais and Sercquiais) and across the continent from Granville, Manche to the linguistic border with Dutch in the North of France and Belgium. It runs approximately west to east through Normandy north of Granville and Villedieu-les-Poêles and divid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotentinais
Cotentinais is the dialect of the Norman language spoken in the Cotentin Peninsula of France. It is one of the strongest dialects of the language on the mainland. Dialects Due to the relative lack of standardisation of Norman, there are five main subdialects of Cotentinais: # ''Haguais'' - La Hague, in the north west of the Cotentin Peninsula # Val de Saire, in the north east # ''Coutançais du nord'', to the north of the Coutances-Saint-Lô line # ''Coutançais du sud'', to the north of the Joret line # ''Baupteis'', from Bauptois, between Carentan and La Haye-du-Puits History At the end of the 18th century and beginning of the 19th century a new movement arose in the Channel Islands, led by writers such as George Métivier (Guernsey, 1790–1881—dubbed the ''Guernsey Burns'') and writers from Jersey. The independent governments, lack of censorship and diverse social and political milieu of the Islands enabled a growth in the publication of vernacular literature—often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauchois Dialect
Cauchois (Norman: ) is one of the eastern dialects of the Norman language that is spoken in and takes its name from the Pays de Caux region of the Seine-Maritime départment. Status The Pays de Caux is one of the remaining strongholds of the Norman language outside the Cotentin. Statistics give a wide range of interpretations as to numbers of speakers: between 0.3% and 19.1% of residents of Seine-Maritime identify themselves as speakers of Cauchois. Phonology These are some distinguishing features of Cauchois from other Norman dialects: *the absence of /h/ *the loss of /r/ between vowels *a greater tendency to metathesis (linguistics), metathesis than in western dialects: instead of (English ''I''), instead of (''of''), instead of (''that''), instead of (''the'') Literature The ''Purin'' literature of the 17th and 18th centuries, published in Rouen, is the earliest Norman literature displaying Cauchois features.''La Normandie dialectale'', René Lepelley, Caen 1999, H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pont-Audemer
Pont-Audemer () is a commune in the Eure department in the Normandy region in northern France.Commune de Pont-Audemer (27467) INSEE On 1 January 2018, the former commune of Saint-Germain-Village was merged into Pont-Audemer. 6 December 2017 Geography The commune is situated on the river , 13 km upstream from its outflow into the |
Honfleur
Honfleur () is a commune in the Calvados department in northwestern France. It is located on the southern bank of the estuary of the Seine across from le Havre and very close to the exit of the Pont de Normandie. The people that inhabit Honfleur are called ''Honfleurais.'' It is especially known for its old port, characterized by its houses with slate-covered frontages, painted frequently by artists. There have been many notable artists, including, Gustave Courbet, Eugène Boudin, Claude Monet and Johan Jongkind, forming the ''école de Honfleur'' (Honfleur school) which contributed to the appearance of the Impressionist movement. The Sainte-Catherine church, which has a bell tower separate from the principal building, is the largest wooden church in France. History The first written record of Honfleur is a reference by Richard III, Duke of Normandy, in 1027. By the middle of the 12th century, the city represented a significant transit point for goods from Rouen to Engla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |