|
Augen Zu Und Schlafen.JPG
Augen (from German "eyes") are large, lenticular eye-shaped mineral grains or mineral aggregates visible in some foliated metamorphic rocks. In cross section they have the shape of an eye. Feldspar, quartz, and garnet are common minerals which form augen. Augen form in rocks which have undergone metamorphism and shearing. The core of the augen is a porphyroblast or porphyroclast of a hard, resilient mineral such as garnet. The augen grows by crystallisation of a ''mantle'' of new mineral around the porphyroblast. The mantle is formed contiguous with the foliation which is imparted upon the rock, and forms a blanket which tapers off from either side of the porphyroblast within the strain shadows. During shearing, the porphyroblast may rotate, to form a characteristic augen texture of asymmetric shearing. In this case, the position of the tails is unequal across the foliation, with some augen showing clear drag folding of the mantle into the strain shadow. This derives a form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyroclast
350px, A mylonite showing a number of (rotated) porphyroclasts: a clear red garnet left in the picture while smaller white feldspar porphyroclasts can be found all over. ''Location'': the tectonics, tectonic contact between the wiktionary:autochthonous, autochthonous Western Gneiss Region and rocks of the allochthonous Blåhø nappe on Otrøy, Caledonides, Central Norway. A porphyroclast is a clast or mineral fragment in a metamorphic rock, surrounded by a groundmass of finer grained crystals. Porphyroclasts are fragments of the original rock before dynamic recrystallisation or cataclasis produced the groundmass. This means they are older than the groundmass. They were stronger pieces of the original rock, that could not as easily deform and were therefore not or hardly affected by recrystallisation. They may have been phenocrysts or porphyroblasts in the original rock. Porphyroclasts are often confused with porphyroblasts. The latter are also large crystals in a finer matrix, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Microstructure
Rock microstructure includes the texture and small-scale structures of a rock. The words ''texture'' and ''microstructure'' are interchangeable, with the latter preferred in modern geological literature. However, ''texture'' is still acceptable because it is a useful means of identifying the origin of rocks, how they formed, and their appearance. Textures are ''penetrative fabrics'' of rocks; they occur throughout the entirety of the rock mass on a microscopic, hand-specimen, and often outcrop scale. This is similar in many ways to foliations, except a texture does not necessarily carry structural information in terms of deformation events and orientation information. Structures occur on a hand-specimen scale and above. Microstructure analysis describes the textural features of the rock, and can provide information on the conditions of formation, petrogenesis, and subsequent deformation, folding, or alteration events. Sedimentary microstructures Description of sedimentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures and pressures than schist. Gneiss nearly always shows a banded texture characterized by alternating darker and lighter colored bands and without a distinct cleavage. Gneisses are common in the ancient crust of continental shields. Some of the oldest rocks on Earth are gneisses, such as the Acasta Gneiss. Description Orthogneiss from the Czech Republic In traditional English and North American usage, a gneiss is a coarse-grained metamorphic rock showing compositional banding ( gneissic banding) but poorly developed schistosity and indistinct cleavage. In other words, it is a metamorphic rock composed of mineral grains easily seen with the unaided eye, which form obvious compositional layers, but which has only a weak tendency to fract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foliation (geology)
Foliation in geology refers to repetitive layering in metamorphic rocks.Marshak, Stephen, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton 3rd Ed, 2009 Each layer can be as thin as a sheet of paper, or over a meter in thickness. The word comes from the Latin ''folium'', meaning "leaf", and refers to the sheet-like planar structure. It is caused by shearing forces (pressures pushing different sections of the rock in different directions), or differential pressure (higher pressure from one direction than in others). The layers form parallel to the direction of the shear, or perpendicular to the direction of higher pressure. Nonfoliated metamorphic rocks are typically formed in the absence of significant differential pressure or shear. Foliation is common in rocks affected by the regional metamorphic compression typical of areas of mountain belt formation (orogenic belts). More technically, foliation is any penetrative planar fabric present in metamorphic rocks. Rocks exhibiting foliat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
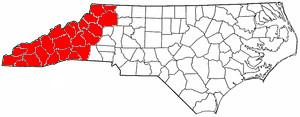
Western North Carolina
Western North Carolina (often abbreviated as WNC) is the region of North Carolina which includes the Appalachian Mountains; it is often known geographically as the state's Mountain Region. It contains the highest mountains in the Eastern United States, with 125 peaks rising to over 5,000 feet (1,500 meters) in elevation. Mount Mitchell at 6,684 feet (2,037 meters), is the highest peak of the Appalachian Mountains and mainland eastern North America. The population of the region, as measured by the 2010 U.S. Census, is 1,473,241, which is approximately 15% of North Carolina's total population. Located east of the Tennessee state line and west of the Piedmont, Western North Carolina contains few major urban centers. Asheville, located in the region's center, is the area's largest city and most prominent commercial hub. The Foothills region of the state is loosely defined as the area along Western North Carolina's eastern boundary; this region consists of a transitional terrain of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral And Lapidary Museum
The Mineral and Lapidary Museum of Henderson County is a non-profit, Volunteering, volunteer-run museum in Hendersonville, North Carolina founded in 1997 at 400 North Main Street in the middle of the city's Historic District. Located in Western North Carolina in the geologically rich Blue Ridge Mountains, the decade-old museum has been nicknamed The Geode-Cracking Museum. On a typical day, geodes are cracked in half by volunteer staff. ''The Ultimate Guide to Asheville & The Western North Carolina Mountains'' explains that "The purpose of the museum is to support the education of the children of Henderson County, NC, Henderson and neighboring counties in the Earth Science areas of Mineralogy, Geology, Paleontology and the associated Lapidary, Lapidary Arts. The museum has ongoing exhibits of regional minerals and gemstones of interest to the general public and a workshop where gem-cutting and polishing demonstrations are held." The guidebook further elaborates that "This museum is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augen Gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures and pressures than schist. Gneiss nearly always shows a banded texture characterized by alternating darker and lighter colored bands and without a distinct cleavage. Gneisses are common in the ancient crust of continental shields. Some of the oldest rocks on Earth are gneisses, such as the Acasta Gneiss. Description Orthogneiss from the Czech Republic In traditional English and North American usage, a gneiss is a coarse-grained metamorphic rock showing compositional banding (gneissic banding) but poorly developed schistosity and indistinct cleavage. In other words, it is a metamorphic rock composed of mineral grains easily seen with the unaided eye, which form obvious compositional layers, but which has only a weak tendency to fracture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyroblast
A porphyroblast is a large mineral crystal in a metamorphic rock which has grown within the finer grained matrix. Porphyroblasts are commonly euhedral crystals, but can also be partly to completely irregular in shape. The most common porphyroblasts in metapelites (metamorphosed mudstones and siltstones) are garnets and staurolites, which stand out in well- foliated metapelites (such as schists) against the platy mica matrix. A similar type of crystal is a '' phenocryst'', a large crystal in an igneous rock. Porphyroblasts are often confused with ''porphyroclasts'', which can also be large outstanding crystals, but which are ''older'' than the matrix of the rock. If a porphyroblastic mineral has small inclusions of minerals within it, the mineral is described as poikiloblast A poikiloblast is a porphyroblast mineral with small inclusions of the previous rock in it. From the texture (if any) shown in the inclusion, the deformation history of the rock can be interpreted, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or are organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral, or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear (geology)
Boudinaged quartz vein (with strain fringe) showing ''Fault (geology)">sinistral shear sense'', Starlight Pit, Fortnum Gold Mine, Western Australia In geology, shear is the response of a rock to deformation usually by compressive stress and forms particular textures. Shear can be homogeneous or non-homogeneous, and may be pure shear or simple shear. Study of geological shear is related to the study of structural geology, rock microstructure or rock texture and fault mechanics. The process of shearing occurs within brittle, brittle-ductile, and ductile rocks. Within purely brittle rocks, compressive stress results in fracturing and simple faulting. Rocks Rocks typical of shear zones include mylonite, cataclasite, S-tectonite and L-tectonite, pseudotachylite, certain breccias and highly foliated versions of the wall rocks. Shear zone A shear zone is a tabular to sheetlike, planar or curviplanar zone composed of rocks that are more highly strained than rocks adjace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives. All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different species are pyrope, almandine, spessartine, grossular (varieties of which are hessonite or cinnamon-stone and tsavorite), uvarovite and andradite. The garnets make up two solid solution series: pyrope-almandine-spessartine (pyralspite), with the composition range ; and uvarovite-grossular-andradite (ugrandite), with the composition range . Etymology The word ''garnet'' comes from the 14th-century Middle English word ''gernet'', meaning 'dark red'. It is borrowed from Old French ''grenate'' from Latin ''granatus,'' from ''granum'' ('grain, seed'). This is possibly a reference to ''mela granatum'' or even ''pomum granatum'' ('pomegranate', ''Punica granatum''), a plant whose fruits contain abundant and vivid red seed covers ( arils), whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |