|
Auf Dem Wasser Zu Singen
"" (To sing on the water), D. 774, is a Lied composed by Franz Schubert in 1823, based on the poem of the same name by Friedrich Leopold zu Stolberg-Stolberg. The text describes a scene on the water from the perspective of the narrator who is in a boat, and delves into the narrator's reflections on the passing of time. The song's piano accompaniment recreates the texture of the shimmering waves (') mentioned in the third line of the poem and its rhythmic style in the 6/8 meter is reminiscent of a barcarole. Harmonically, the song as a whole and within each stanza traces a movement from the minor mode to the major mode: the song begins in A-flat minor and ends in A-flat major. Franz Liszt transcribed the piece for solo piano, S. 558. Text Mitten im Schimmer der spiegelnden Wellen Gleitet, wie Schwäne, der wankende Kahn; Ach, auf der Freude sanftschimmernden Wellen Gleitet die Seele dahin wie der Kahn; Denn von dem Himmel herab auf die Wellen Tanzet das Abendrot rund um den K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Schubert C1827
{{disambiguation ...
Franz may refer to: People * Franz (given name) * Franz (surname) Places * Franz (crater), a lunar crater * Franz, Ontario, a railway junction and unorganized town in Canada * Franz Lake, in the state of Washington, United States – see Franz Lake National Wildlife Refuge Businesses * Franz Deuticke, a scientific publishing company based in Vienna, Austria * Franz Family Bakeries, a food processing company in Portland, Oregon * Franz-porcelains, a Taiwanese brand of pottery based in San Francisco Other uses * ''Franz'' (film), a 1971 Belgian film * Franz Lisp, a dialect of the Lisp programming language See also * Frantz (other) * Franzen (other) * Frantzen (other) Frantzen or Frantzén is a surname. It may refer to: * Allen Frantzen (born 1947/48), American medievalist * Björn Frantzén (born 1977), Swedish chef and owner of the Frantzén restaurant * Jean-Pierre Frantzen (1890–1957), Luxembourgian gym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-flat Minor
A-flat minor is a minor scale based on A♭ (musical note), A, consisting of the pitches A, B♭ (musical note), B, C♭ (musical note), C, D♭ (musical note), D, E♭ (musical note), E, F♭ (musical note), F, and G♭ (musical note), G. Its key signature has seven flats. Its Relative key, relative major is C-flat major (or enharmonically B major), its parallel key, parallel major is A-flat major, and its enharmonic equivalent is G-sharp minor. The A-flat natural minor scale is: : Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The A-flat Harmonic minor scale, harmonic minor and Melodic minor scale, melodic minor scales are: : : Music in A-flat minor Although A-flat minor occurs in modulation in works in other keys, it is only rarely used as the principal key of a piece of music. Some well-known uses of the key in classical and romantic piano music include: * The Funeral March in Ludwig van Beethoven's P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieder Composed By Franz Schubert
In Western classical music tradition, (, plural ; , plural , ) is a term for setting poetry to classical music to create a piece of polyphonic music. The term is used for any kind of song in contemporary German, but among English and French speakers, is often used interchangeably with "art song" to encompass works that the tradition has inspired in other languages as well. The poems that have been made into lieder often center on pastoral themes or themes of romantic love. The earliest lied date from the late fourteenth or early fifteenth centuries, and can even refer to from as early as the 12th and 13th centuries. It later came especially to refer to settings of Romantic poetry during the late eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, and into the early twentieth century. Examples include settings by Joseph Haydn, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Ludwig van Beethoven, Franz Schubert, Robert Schumann, Johannes Brahms, Hugo Wolf, Gustav Mahler or Richard Strauss. History For German sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Parsons (pianist)
Geoffrey Penwill Parsons AO OBE (15 June 192926 January 1995) was an Australian pianist, most particularly notable as an accompanist to singers and instrumentalists. After the retirement of Gerald Moore, he was generally considered the world's finest and most sympathetic accompanist of lieder singers, "elevating the role of the accompanist to new heights with his musicality, authority and quiet strength of playing". Biography Geoffrey Parsons was born in the Sydney suburb of Ashfield, to a working-class family. He had two older brothers and a large extended family. He originally intended to study architecture, but his love of music prevailed. From 1941 to 1948 he studied with Winifred Burston (a student of Ferruccio Busoni) at the NSW State Conservatorium of Music (where a family friend, George Vern Barnett, was on the piano staff) and under the general tutelage of Eugene Goossens. He won the ABC's Instrumental and Vocal Competition in 1947 with a performance of Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Bonney
Barbara Bonney (born April 14, 1956) is an American soprano. She is associated with lyric soprano roles in operas by Mozart and Richard Strauss as well as lieder performances. Early life Bonney was born in Montclair, New Jersey. As a child she practised piano and cello. When Bonney was 13 her family moved to Maine, where she became part of the Portland Symphony Youth Orchestra as a cellist. She spent two years at the University of New Hampshire (UNH) studying German and music including voice with Patricia Stedry, and spent her junior year at the University of Salzburg, where she switched from cello to voice. While there, she studied at Mozarteum University Salzburg. Years later she received an honorary doctorate from UNH. Career In 1979, Bonney joined the Staatstheater Darmstadt, where she made her debut as Anna in ''The Merry Wives of Windsor''. In the subsequent five years she made appearances in Germany and throughout Europe, notably at the Royal Opera House at Covent Garden i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Compositions By Franz Liszt
Hungarian Romantic composer Franz Liszt (1811–1886) was especially prolific, composing more than 700 works. A virtuoso pianist himself, much of his output is dedicated to solo works for the instrument and is particularly technically demanding. The primary cataloguing system for his compositions was developed by Humphrey Searle; it has been thoroughly revamped by Michael Short and Leslie Howard. Legend The table below gives the following information for works by Franz Liszt (where applicable): # S. — numbering as given in Humphrey Searle, ''The Music of Liszt'', 1966 (with additions by Sharon Winklhofer and Leslie Howard). A number sign (#) signifies that a number is no longer in use. # LW. — numbering by R. Charnin Mueller and M. Eckhardt referenced in ''Grove Music Online'' (2010) # Title — normally following the New Liszt Edition' and Library of Congress', as well as other authoritative sources # Forces — the instrumentation used (seAbbreviations for Instruments # K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piano Solo
The piano is often used to provide harmonic accompaniment to a voice or other instrument. However, solo parts for the piano are common in many musical styles. These can take the form of a section in which the piano is heard more prominently than other instruments, or in which the piano may be played entirely unaccompanied. The term ''piano solo'' is also often used to mean a musical composition written solely for piano. Compositions for solo piano Composition or Compositions may refer to: Arts and literature *Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography * Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include ... Piano Music performance Solo music {{Music-theory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Liszt
Franz Liszt, in modern usage ''Liszt Ferenc'' . Liszt's Hungarian passport spelled his given name as "Ferencz". An orthographic reform of the Hungarian language in 1922 (which was 36 years after Liszt's death) changed the letter "cz" to simply "c" in all words except surnames; this has led to Liszt's given name being rendered in modern Hungarian usage as "Ferenc". From 1859 to 1867 he was officially Franz Ritter von Liszt; he was created a ''Ritter'' (knight) by Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria, Francis Joseph I in 1859, but never used this title of nobility in public. The title was necessary to marry the Princess Carolyne zu Sayn-Wittgenstein without her losing her privileges, but after the marriage fell through, Liszt transferred the title to his uncle Eduard in 1867. Eduard's son was Franz von Liszt., group=n (22 October 1811 – 31 July 1886) was a Hungarian composer, pianist and teacher of the Romantic music, Romantic period. With a diverse List of compositions by Franz L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-flat Major
A-flat major (or the key of A-flat) is a major scale based on A, with the pitches A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. Its key signature has four flats. The A-flat major scale is: : Its relative minor is F minor. Its parallel minor, A-flat minor, is usually written instead as the enharmonic key of G-sharp minor, since A-flat minor contains seven flats and G-sharp minor only contains five sharps, making A-flat minor rarely usable. Its enharmonic, G-sharp major, with eight sharps, including the F, has a similar problem, and so A-flat major is often used as the parallel major for G-sharp minor. (The same enharmonic situation also occurs with the keys of D-flat major and C-sharp minor.) Compositions in A-flat major Beethoven chose A-flat major as the key of the slow movement for most of his C minor works, a practice which Anton Bruckner imitated in his first two C minor symphonies and also Antonín Dvořák in his only C minor symphony. The second movement of Haydn's 43rd sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
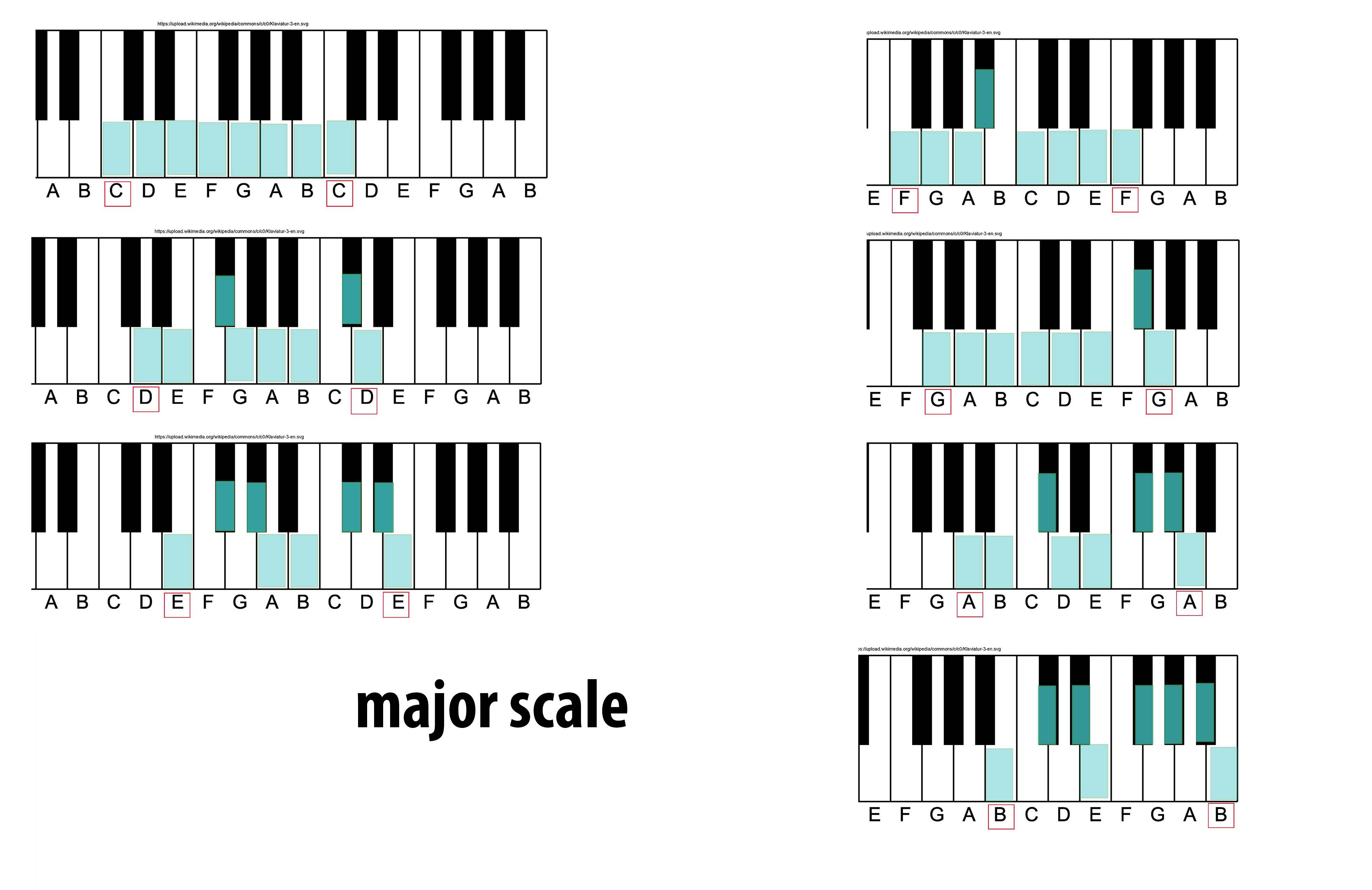
Major Mode
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale had a central importance in Western music, particularly in the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled line in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsch Catalogue
''Schubert: Thematic Catalogue of all his Works in Chronological Order'', also known as the Deutsch catalogue, is a numbered list of all compositions by Franz Schubert compiled by Otto Erich Deutsch. Since its first publication in 1951, Deutsch (abbreviated as D or D.) numbers are used for the unique identification of Schubert's compositions. 1951 edition The Deutsch catalogue was first published in London in 1951 by J. M. Dent & Sons, as ''Schubert: Thematic Catalogue of all his Works in Chronological Order, compiled by O. E. Deutsch, in collaboration with Donald R. Wakeling.'' 1978 edition: NSE VIII/4 In 1978, as part VIII Supplement / Volume 4 of the New Schubert Edition (NSE), an updated version of the catalogue was published in German. A few compositions that had been undated in the first edition received a new number (usually followed by a letter), e.g. was renumbered to . Later versions The original 1951 edition (in English) was re-issued several times, for instance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Mode
In music theory, the minor scale is three scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending) – rather than just two as with the major scale, which also has a harmonic form but lacks a melodic form. In each of these scales, the first, third, and fifth scale degrees form a minor triad (rather than a major triad, as in a major scale). In some contexts, ''minor scale'' is used to refer to any heptatonic scale with this property (see Related modes below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth degree of its relative major scale. For instance, the A natural minor scale can be built by starting on the 6th degree of the C major scale: : Because of this, the key of A minor is called the ''relative minor'' of C major. Every major key has a relative minor, which starts on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |