|
Atlas Autocode
Atlas Autocode (AA)Original scans)) is a programming language developed around 1963 at the University of Manchester. A variant of the language ALGOL, it was developed by Tony Brooker and Derrick Morris for the Atlas computer. The initial AA and AB compilers were written by Jeff Rohl and Tony Brooker using the Brooker-Morris Compiler-compiler, with a later hand-coded non-CC implementation (ABC) by Jeff Rohl. The word '' Autocode'' was basically an early term for ''programming language''. Different autocodes could vary greatly. Features AA was a block structured language that featured explicitly typed variables, subroutines, and functions. It omitted some ALGOL features such as '' passing parameters by name'', which in ALGOL 60 means passing the memory address of a short subroutine (a ''thunk'') to recalculate a parameter each time it is mentioned. The AA compiler could generate range-checking for array accesses, and allowed an array to have dimensions that were determined at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Procedural Programming
Procedural programming is a programming paradigm, classified as imperative programming, that involves implementing the behavior of a computer program as Function (computer programming), procedures (a.k.a. functions, subroutines) that call each other. The resulting program is a series of steps that forms a hierarchy of calls to its constituent procedures. The first major procedural programming languages appeared –1964, including Fortran, ALGOL, COBOL, PL/I and BASIC. Pascal (programming language), Pascal and C (programming language), C were published –1972. Computer processors provide hardware support for procedural programming through a stack register and instructions for Subroutine#Jump to subroutine, calling procedures and returning from them. Hardware support for other types of programming is possible, like Lisp machines or Java processors, but no attempt was commercially successful. Development practices Certain software development practices are often employed with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Variable (computer Science)
In computer programming, a variable is an abstract storage location paired with an associated symbolic name, which contains some known or unknown quantity of data or object referred to as a '' value''; or in simpler terms, a variable is a named container for a particular set of bits or type of data (like integer, float, string, etc...). A variable can eventually be associated with or identified by a memory address. The variable name is the usual way to reference the stored value, in addition to referring to the variable itself, depending on the context. This separation of name and content allows the name to be used independently of the exact information it represents. The identifier in computer source code can be bound to a value during run time, and the value of the variable may thus change during the course of program execution. Variables in programming may not directly correspond to the concept of variables in mathematics. The latter is abstract, having no reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Imaginary Unit
The imaginary unit or unit imaginary number () is a mathematical constant that is a solution to the quadratic equation Although there is no real number with this property, can be used to extend the real numbers to what are called complex numbers, using addition and multiplication. A simple example of the use of in a complex number is Imaginary numbers are an important mathematical concept; they extend the real number system \mathbb to the complex number system \mathbb, in which at least one Root of a function, root for every nonconstant polynomial exists (see Algebraic closure and Fundamental theorem of algebra). Here, the term ''imaginary'' is used because there is no real number having a negative square (algebra), square. There are two complex square roots of and , just as there are two complex square roots of every real number other than zero (which has one multiple root, double square root). In contexts in which use of the letter is ambiguous or problematic, the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alternating Current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, Fan (machine), fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', respectively, as when they modify ''Electric current, current'' or ''voltage''. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa (the full period is called a ''wave cycle, cycle''). "Alternating current" most commonly refers to power distribution, but a wide range of other appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, Electromagnetism, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Complex Number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with real or complex coefficie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inner Loop
In computer programs, an important form of control flow is the Loop (computing), loop which causes a block of code to be executed more than once. A common idiom is to have a loop Nested loop, nested inside another loop, with the contained loop being commonly referred to as the inner loop. Program optimization Because the entire inner loop is performed for each iteration of the outer loop, loop optimization, optimizations of the inner loop will have much greater effect than optimizations of the outer loop. In many languages there are at least two types of loops – for loop, for loops and while loop, while loops – and they can be nested within each other. Tosin P. Adewumi has shown that performance of a while loop with an inner for loop is better than of a while loop without the inner for loop. It was observed that more computations are performed per unit time when an inner for loop is involved than otherwise. This implies, given the same number of computations to perform, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Machine Code
In computer programming, machine code is computer code consisting of machine language instructions, which are used to control a computer's central processing unit (CPU). For conventional binary computers, machine code is the binaryOn nonbinary machines it is, e.g., a decimal representation. representation of a computer program that is actually read and interpreted by the computer. A program in machine code consists of a sequence of machine instructions (possibly interspersed with data). Each machine code instruction causes the CPU to perform a specific task. Examples of such tasks include: # Load a word from memory to a CPU register # Execute an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) operation on one or more registers or memory locations # Jump or skip to an instruction that is not the next one In general, each architecture family (e.g., x86, ARM) has its own instruction set architecture (ISA), and hence its own specific machine code language. There are exceptions, such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
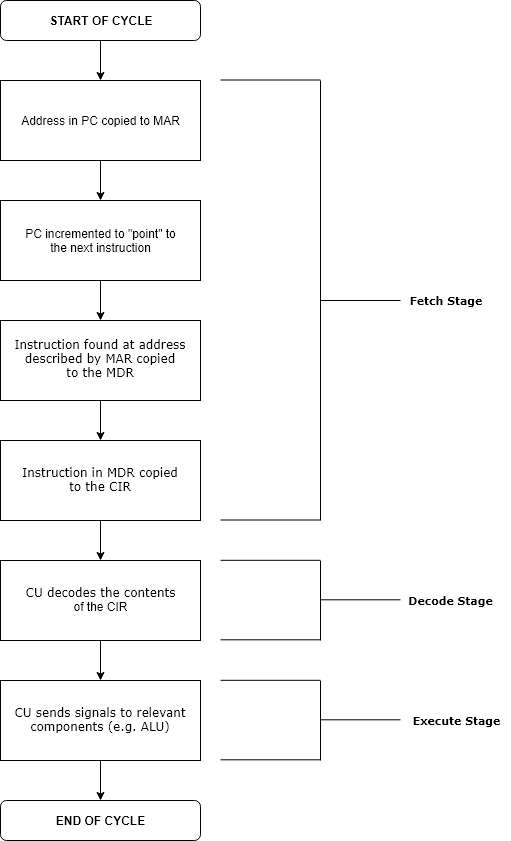
Runtime (program Lifecycle Phase)
Execution in computer engineering, computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a "Instruction cycle, fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the Formal semantics of programming languages, semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a Batch processing, batch process without human interaction or a User (computing), user may type Command (computing), commands in an Session (computer science), interactive session of an Interpreter (computing), interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose executio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Array Data Structure
In computer science, an array is a data structure consisting of a collection of ''elements'' (value (computer science), values or variable (programming), variables), of same memory size, each identified by at least one ''array index'' or ''key'', a collection of which may be a tuple, known as an index tuple. An array is stored such that the position (memory address) of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula. The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called a one-dimensional array. For example, an array of ten 32-bit (4-byte) integer variables, with indices 0 through 9, may be stored as ten Word (data type), words at memory addresses 2000, 2004, 2008, ..., 2036, (in hexadecimal: 0x7D0, 0x7D4, 0x7D8, ..., 0x7F4) so that the element with index ''i'' has the address 2000 + (''i'' × 4). The memory address of the first element of an array is called first address, foundation address, or base address. Because the mathematical conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a lower level language, low-level programming language (e.g. assembly language, object code, or machine code) to create an executable program.Compilers: Principles, Techniques, and Tools by Alfred V. Aho, Ravi Sethi, Jeffrey D. Ullman - Second Edition, 2007 There are many different types of compilers which produce output in different useful forms. A ''cross-compiler'' produces code for a different Central processing unit, CPU or operating system than the one on which the cross-compiler itself runs. A ''bootstrap compiler'' is often a temporary compiler, used for compiling a more permanent or better optimised compiler for a language. Related software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thunk
In computer programming Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of proc ..., a thunk is a subroutine used to inject a calculation into another subroutine. Thunks are primarily used to delay a calculation until its result is needed, or to insert operations at the beginning or end of the other subroutine. They have many other applications in Code generation (compiler), compiler code generation and modular programming. The term originated as a whimsical English irregular verbs, irregular form of the verb ''think''. It refers to the original use of thunks in ALGOL 60 compilers, which required special analysis (thought) to determine what type of routine to generate. Background The early years of compiler research saw broad experimentation with different evaluation strategy, evaluation s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |