|
Ateji PX
Ateji PX is an object-oriented programming language extension for Java. It is intended to facilliate parallel computing on multi-core processors, GPU, Grid and Cloud. Ateji PX can be integrated with the Eclipse IDE, requires minimal learning of the additional parallel constructs and does not alter the development process. Code examples Hello World public class HelloWorld Each , , symbol introduces a parallel branch. Running this program will print either Hello World or World Hello depending on how the parallel branches happen to be scheduled. Data parallelism , (int i : array.length) array +; The quantification (int i : N) creates one parallel branch for each value of i. The effect of this code is to increment all elements of array in parallel. This code is equivalent to , array , array , array rray.length-1+; More complex quantifications are possible. The following example quantifies over the upper left triangle of a square matrix: , (int i:N, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object-oriented Programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which can contain data and code. The data is in the form of fields (often known as attributes or ''properties''), and the code is in the form of procedures (often known as ''methods''). A common feature of objects is that procedures (or methods) are attached to them and can access and modify the object's data fields. In this brand of OOP, there is usually a special name such as or used to refer to the current object. In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another. OOP languages are diverse, but the most popular ones are class-based, meaning that objects are instances of classes, which also determine their types. Many of the most widely used programming languages (such as C++, Java, Python, etc.) are multi-paradigm and they support object-oriented programming to a greater or lesser degree, typically in combination with imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenMP
OpenMP (Open Multi-Processing) is an application programming interface (API) that supports multi-platform shared-memory multiprocessing programming in C, C++, and Fortran, on many platforms, instruction-set architectures and operating systems, including Solaris, AIX, FreeBSD, HP-UX, Linux, macOS, and Windows. It consists of a set of compiler directives, library routines, and environment variables that influence run-time behavior. OpenMP is managed by the nonprofit technology consortium ''OpenMP Architecture Review Board'' (or ''OpenMP ARB''), jointly defined by a broad swath of leading computer hardware and software vendors, including Arm, AMD, IBM, Intel, Cray, HP, Fujitsu, Nvidia, NEC, Red Hat, Texas Instruments, and Oracle Corporation. OpenMP uses a portable, scalable model that gives programmers a simple and flexible interface for developing parallel applications for platforms ranging from the standard desktop computer to the supercomputer. An application built wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Programming Language Family
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's most populous island, home to approximately 56% of the Indonesian population. Indonesia's capital city, Jakarta, is on Java's northwestern coast. Many of the best known events in Indonesian history took place on Java. It was the centre of powerful Hindu-Buddhist empires, the Islamic sultanates, and the core of the colonial Dutch East Indies. Java was also the center of the Indonesian struggle for independence during the 1930s and 1940s. Java dominates Indonesia politically, economically and culturally. Four of Indonesia's eight UNESCO world heritage sites are located in Java: Ujung Kulon National Park, Borobudur Temple, Prambanan Temple, and Sangiran Early Man Site. Formed by volcanic eruptions due to geologic subduction of the Australian P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrent Programming Languages
Concurrent computing is a form of computing in which several computations are executed '' concurrently''—during overlapping time periods—instead of ''sequentially—''with one completing before the next starts. This is a property of a system—whether a program, computer, or a network—where there is a separate execution point or "thread of control" for each process. A ''concurrent system'' is one where a computation can advance without waiting for all other computations to complete. Concurrent computing is a form of modular programming. In its paradigm an overall computation is factored into subcomputations that may be executed concurrently. Pioneers in the field of concurrent computing include Edsger Dijkstra, Per Brinch Hansen, and C.A.R. Hoare. Introduction The concept of concurrent computing is frequently confused with the related but distinct concept of parallel computing, Pike, Rob (2012-01-11). "Concurrency is not Parallelism". ''Waza conference'', 11 January ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object-oriented Programming Languages
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects", which can contain data and code. The data is in the form of fields (often known as attributes or ''properties''), and the code is in the form of procedures (often known as ''methods''). A common feature of objects is that procedures (or methods) are attached to them and can access and modify the object's data fields. In this brand of OOP, there is usually a special name such as or used to refer to the current object. In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another. OOP languages are diverse, but the most popular ones are class-based, meaning that objects are instances of classes, which also determine their types. Many of the most widely used programming languages (such as C++, Java, Python, etc.) are multi-paradigm and they support object-oriented programming to a greater or lesser degree, typically in combination with impera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dataflow
In computing, dataflow is a broad concept, which has various meanings depending on the application and context. In the context of software architecture, data flow relates to stream processing or reactive programming. Software architecture Dataflow computing is a software paradigm based on the idea of representing computations as a directed graph, where nodes are computations and data flow along the edges. Dataflow can also be called stream processing or reactive programming. There have been multiple data-flow/stream processing languages of various forms (see Stream processing). Data-flow hardware (see Dataflow architecture) is an alternative to the classic von Neumann architecture. The most obvious example of data-flow programming is the subset known as reactive programming with spreadsheets. As a user enters new values, they are instantly transmitted to the next logical "actor" or formula for calculation. Distributed data flows have also been proposed as a programming abstrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilk
Cilk, Cilk++, Cilk Plus and OpenCilk are general-purpose programming languages designed for multithreaded parallel computing. They are based on the C and C++ programming languages, which they extend with constructs to express parallel loops and the fork–join idiom. Originally developed in the 1990s at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the group of Charles E. Leiserson, Cilk was later commercialized as Cilk++ by a spinoff company, Cilk Arts. That company was subsequently acquired by Intel, which increased compatibility with existing C and C++ code, calling the result Cilk Plus. After Intel stopped supporting Cilk Plus in 2017, MIT is again developing Cilk in the form of OpenCilk. History MIT Cilk The Cilk programming language grew out of three separate projects at the MIT Laboratory for Computer Science: * Theoretical work on scheduling multi-threaded applications. * StarTech – a parallel chess program built to run on the Thinking Machines Corporation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Array
In computing, a group of parallel arrays (also known as structure of arrays or SoA) is a form of implicit data structure that uses multiple arrays to represent a singular array of records. It keeps a separate, homogeneous data array for each field of the record, each having the same number of elements. Then, objects located at the same index in each array are implicitly the fields of a single record. Pointers from one object to another are replaced by array indices. This contrasts with the normal approach of storing all fields of each record together in memory (also known as array of structures or AoS). For example, one might declare an array of 100 names, each a string, and 100 ages, each an integer, associating each name with the age that has the same index. Examples An example in C using parallel arrays: int ages[] = ; char *names[] = ; int parent[] = ; for (i = 1; i Joe', 'Bob', 'Frank', 'Hans' last_name => Smith','Seger','Sinatra','Schultze' he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
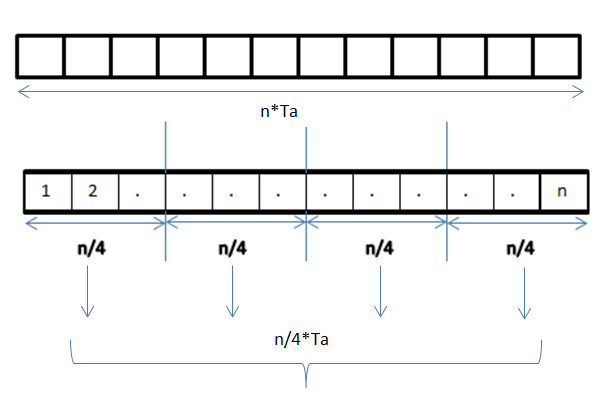
Data Parallelism
Data parallelism is parallelization across multiple processors in parallel computing environments. It focuses on distributing the data across different nodes, which operate on the data in parallel. It can be applied on regular data structures like arrays and matrices by working on each element in parallel. It contrasts to task parallelism as another form of parallelism. A data parallel job on an array of ''n'' elements can be divided equally among all the processors. Let us assume we want to sum all the elements of the given array and the time for a single addition operation is Ta time units. In the case of sequential execution, the time taken by the process will be ''n''×Ta time units as it sums up all the elements of an array. On the other hand, if we execute this job as a data parallel job on 4 processors the time taken would reduce to (''n''/4)×Ta + merging overhead time units. Parallel execution results in a speedup of 4 over sequential execution. One important thing to note ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pi Calculus
The number (; spelled out as "pi") is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. The number appears in many formulas across mathematics and physics. It is an irrational number, meaning that it cannot be expressed exactly as a ratio of two integers, although fractions such as \tfrac are commonly used to approximate it. Consequently, its decimal representation never ends, nor enters a permanently repeating pattern. It is a transcendental number, meaning that it cannot be a solution of an equation involving only sums, products, powers, and integers. The transcendence of implies that it is impossible to solve the ancient challenge of squaring the circle with a compass and straightedge. The decimal digits of appear to be randomly distributed, but no proof of this conjecture has been found. For thousands of years, mathematicians have attempted to extend their understanding of , sometimes by computing i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipse IDE
Eclipse is an integrated development environment (IDE) used in computer programming. It contains a base workspace and an extensible plug-in system for customizing the environment. It is the second-most-popular IDE for Java development, and, until 2016, was the most popular. Eclipse is written mostly in Java and its primary use is for developing Java applications, but it may also be used to develop applications in other programming languages via plug-ins, including Ada, ABAP, C, C++, C#, Clojure, COBOL, D, Erlang, Fortran, Groovy, Haskell, JavaScript, Julia, Lasso, Lua, NATURAL, Perl, PHP, Prolog, Python, R, Ruby (including Ruby on Rails framework), Rust, Scala, and Scheme. It can also be used to develop documents with LaTeX (via a TeXlipse plug-in) and packages for the software Mathematica. Development environments include the Eclipse Java development tools (JDT) for Java and Scala, Eclipse CDT for C/C++, and Eclipse PDT for PHP, among others. The initial codebase origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-core Processor
A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions (such as add, move data, and branch) but the single processor can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die (known as a chip multiprocessor or CMP) or onto multiple dies in a single chip package. The microprocessors currently used in almost all personal computers are multi-core. A multi-core processor implements multiprocessing in a single physical package. Designers may couple cores in a multi-core device tightly or loosely. For example, cores may or may not share caches, and they may implement message passing or shared-memory inter-core communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |