|
Atatürk Dam
The Atatürk Dam ( tr, Atatürk Barajı), originally the Karababa Dam, is the third largest dam in the world and it is a zoned rock-fill dam with a central core on the Euphrates River on the border of Adıyaman Province and Şanlıurfa Province in the Southeastern Anatolia Region of Turkey. Built both to generate electricity and to irrigate the plains in the region, it was renamed in honour of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk (1881–1938), the founder of the Turkish Republic. The construction began in 1983 and was completed in 1990. The dam and the hydroelectric power plant, which went into service after the upfilling of the reservoir was completed in 1992, are operated by the State Hydraulic Works (DSİ). The reservoir created behind the dam, called Atatürk Reservoir ( tr, Atatürk Baraj Gölü), is the third largest in Turkey. The dam is situated northwest of Bozova, Şanlıurfa Province, on state road D-875 from Bozova to Adıyaman. Centerpiece of the 22 dams on the Euphrates and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeastern Anatolia Project
The Southeastern Anatolia Project ( tr, Güneydoğu Anadolu Projesi, GAP) is a multi-sector integrated regional development project based on the concept of sustainable development for the 9 million people (2005) living in the Southeastern Anatolia region of Turkey. GAP's basic aim is to eliminate regional development disparities by raising incomes and living standards and to contribute to the national development targets of social stability and economic growth by enhancing the productive and employment generating capacity of the rural sector. The total cost of the project is over 100 billion Turkish lira (TL) (2017 adjusted price), of which 30.6 billion TL of this investment was realized at the end of 2010. The real investment (corrected value) was 72.6% for the end of 2010. (in Turkish) The project area covers nine provinces ( Adıyaman, Batman, Diyarbakır, Gaziantep, Kilis, Siirt, Şanlıurfa, Mardin, and Şırnak) which are located in the basins of the Euphrates and Tigris a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keban Dam
The Keban Dam ( tr, Keban Barajı) is a hydroelectric dam on the Euphrates, located in the Elazığ Province of Turkey. The dam is the first and uppermost of several large-scale dams to be built on the Euphrates by Turkey. Although the Keban Dam was not originally constructed as a part of the Southeastern Anatolia Project (GAP), it is now a fully integrated component of the project, which aims to stimulate economic development in Southeastern Turkey. Construction of the dam commenced in 1966 and was completed in 1974. Keban Dam Lake ( tr, Keban Baraj Gölü), the reservoir created by Keban Dam, has a surface area of and is reputedly the fourth-largest lake in Turkey after Lake Van, Lake Tuz, and the reservoir created by the Atatürk Dam. Project history Construction of the Keban Dam was first proposed in 1936 by the newly established Electric Affairs Survey Administration, but not started before 1966. Construction was carried out by the French-Italian consortium SCI-Impreglio an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
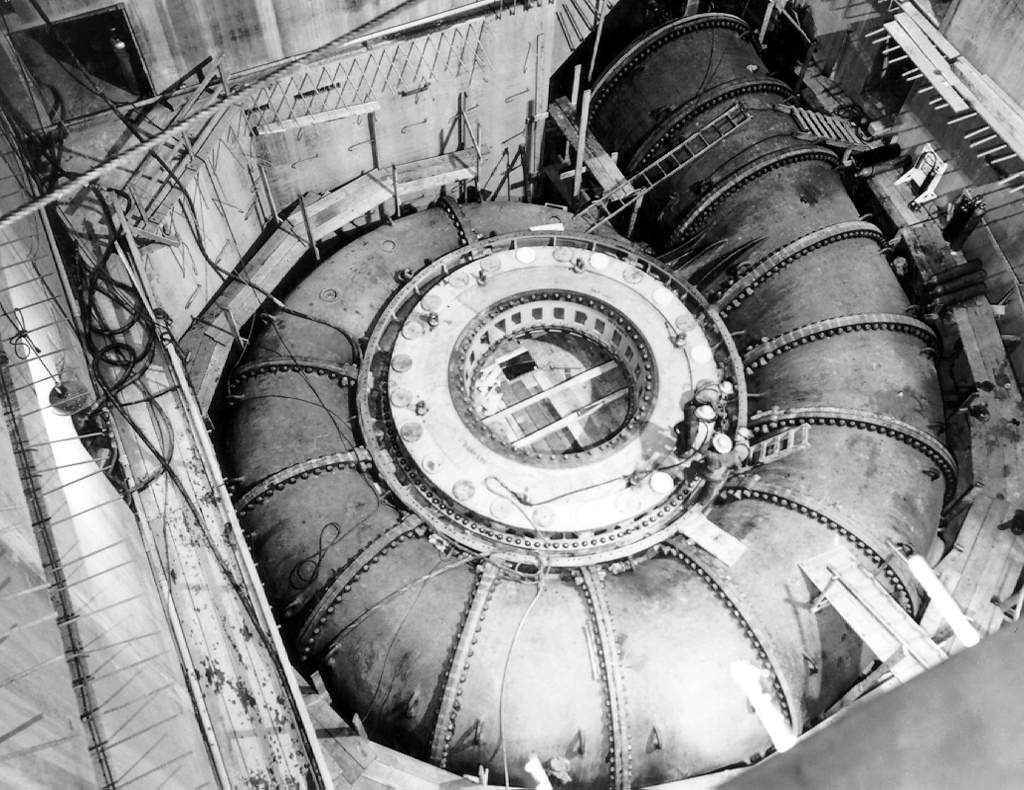
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permeation
In physics and engineering, permeation (also called imbuing) is the penetration of a permeate (a fluid such as a liquid, gas, or vapor) through a solid. It is directly related to the concentration gradient of the permeate, a material's intrinsic permeability, and the materials' mass diffusivity. Permeation is modeled by equations such as Fick's laws of diffusion, and can be measured using tools such as a minipermeameter. Description The process of permeation involves the diffusion of molecules, called the permeant, through a membrane or interface. Permeation works through diffusion; the permeant will move from high concentration to low concentration across the interface. A material can be semipermeable, with the presence of a semipermeable membrane. Only molecules or ions with certain properties will be able to diffuse across such a membrane. This is a very important mechanism in biology where fluids inside a blood vessel need to be regulated and controlled. Permeation can o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofferdam
A cofferdam is an enclosure built within a body of water to allow the enclosed area to be pumped out. This pumping creates a dry working environment so that the work can be carried out safely. Cofferdams are commonly used for construction or repair of permanent dams, oil platforms, bridge piers, etc., built within water. These cofferdams are usually welded steel structures, with components consisting of sheet piles, wales, and cross braces. Such structures are usually dismantled after the construction work is completed. The origin of the word comes from ''coffer'' (originally from Latin ''cophinus'' meaning "basket") and ''dam'' from Proto-German ''*dammaz'' meaning "barrier across a stream of water to obstruct its flow and raise its level"). Uses For dam construction, two cofferdams are usually built, one upstream and one downstream of the proposed dam, after an alternative diversion tunnel or channel has been provided for the river flow to bypass the foundation area o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Lira
The lira ( tr, Türk lirası; sign: ₺; ISO 4217 code: TRY; abbreviation: TL) is the official currency of Turkey and Northern Cyprus. One lira is divided into one hundred ''kuruş''. History Ottoman lira (1844–1923) The lira, along with the related currencies of Europe and the Middle East, has its roots in the ancient Roman unit of weight known as the libra which referred to the Troy pound of silver. The Roman libra adoption of the currency spread it throughout Europe and the Near East, where it continued to be used into medieval times. The Turkish lira, the French livre (until 1794), the Italian lira (until 2002), Syrian pound, Lebanese pound and the pound unit of account in sterling (a translation of the Latin ''libra''; the word "pound" as a unit of weight is still abbreviated as "lb.") are the modern descendants of the ancient currency. The lira was introduced as the main unit of account in 1844, with the former currency, kuruş, remaining as a subdivision. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obverse And Reverse
Obverse and its opposite, reverse, refer to the two flat faces of coins and some other two-sided objects, including paper money, flags, seals, medals, drawings, old master prints and other works of art, and printed fabrics. In this usage, ''obverse'' means the front face of the object and ''reverse'' means the back face. The obverse of a coin is commonly called ''heads'', because it often depicts the head of a prominent person, and the reverse ''tails''. In numismatics, the abbreviation ''obv.'' is used for ''obverse'',David Sear. ''Greek Imperial Coins and Their Values.'' Spink Books, 1982. p. xxxv. while ℞, )(Jonathan Edwards. ''Catalogue of the Greek and Roman Coins in the Numismatic Collection of Yale College, Volume 2.'' Tuttle, Morehouse & Taylor, 1880. p. 228. and rev.Allen G. Berman. ''Warman's Coins And Paper Money: Identification and Price Guide.'' Penguin, 2008. are used for reverse. In fields of scholarship outside numismatics, the term ''front'' is more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilowatt Hour
A kilowatt-hour ( unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common billing unit for electrical energy delivered to consumers by electric utilities. Definition The kilowatt-hour is a composite unit of energy equal to one kilowatt (kW) sustained for (multiplied by) one hour. Expressed in the standard unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI), the joule (symbol J), it is equal to 3,600 kilojoules or 3.6 MJ."Half-high dots or spaces are used to express a derived unit formed from two or more other units by multiplication.", Barry N. Taylor. (2001 ed.''The International System of Units.'' (Special publication 330). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. 20. Unit representations A widely used representation of the kilowatt-hour is "kWh", derived from its co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical circu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |