|
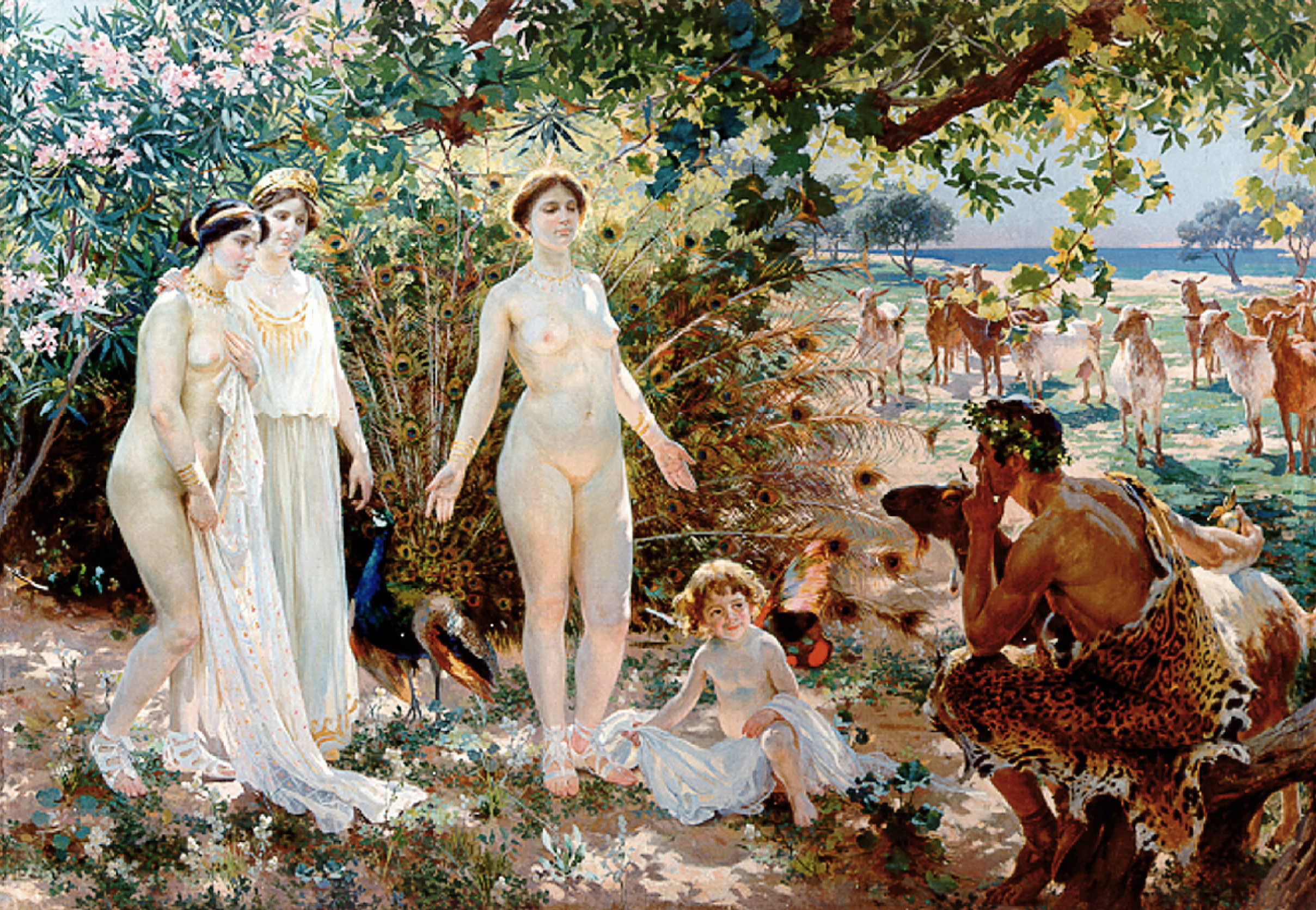
Atalanta
Atalanta (; grc-gre, Ἀταλάντη, Atalantē) meaning "equal in weight", is a heroine in Greek mythology. There are two versions of the huntress Atalanta: one from Arcadia (region), Arcadia, whose parents were Iasus and Clymene (mythology), Clymene and who is primarily known from the tales of the Calydonian boar hunt and the Argonauts; and the other from Boeotia, who is the daughter of King Schoeneus and is primarily noted for her skill in the footrace. In both versions, Atalanta was a local figure allied to the goddess Artemis; in such oral traditions, minor characters were often assigned different names, resulting in minor regional variations. Mythology Early life At birth, Atalanta was taken to Mount Parthenion to be Infant exposure, exposed because her father had desired a son. A she-bear—one of the symbols of Artemis—whose cubs had been recently killed by hunters came upon Atalanta and nursed her until those same hunters discovered her and raised her themselves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atalanta Peleus Staatliche Antikensammlungen 596
Atalanta (; grc-gre, Ἀταλάντη, Atalantē) meaning "equal in weight", is a heroine in Greek mythology. There are two versions of the huntress Atalanta: one from Arcadia (region), Arcadia, whose parents were Iasus and Clymene (mythology), Clymene and who is primarily known from the tales of the Calydonian boar hunt and the Argonauts; and the other from Boeotia, who is the daughter of King Schoeneus and is primarily noted for her skill in the footrace. In both versions, Atalanta was a local figure allied to the goddess Artemis; in such oral traditions, minor characters were often assigned different names, resulting in minor regional variations. Mythology Early life At birth, Atalanta was taken to Mount Parthenion to be Infant exposure, exposed because her father had desired a son. A she-bear—one of the symbols of Artemis—whose cubs had been recently killed by hunters came upon Atalanta and nursed her until those same hunters discovered her and raised her themselves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
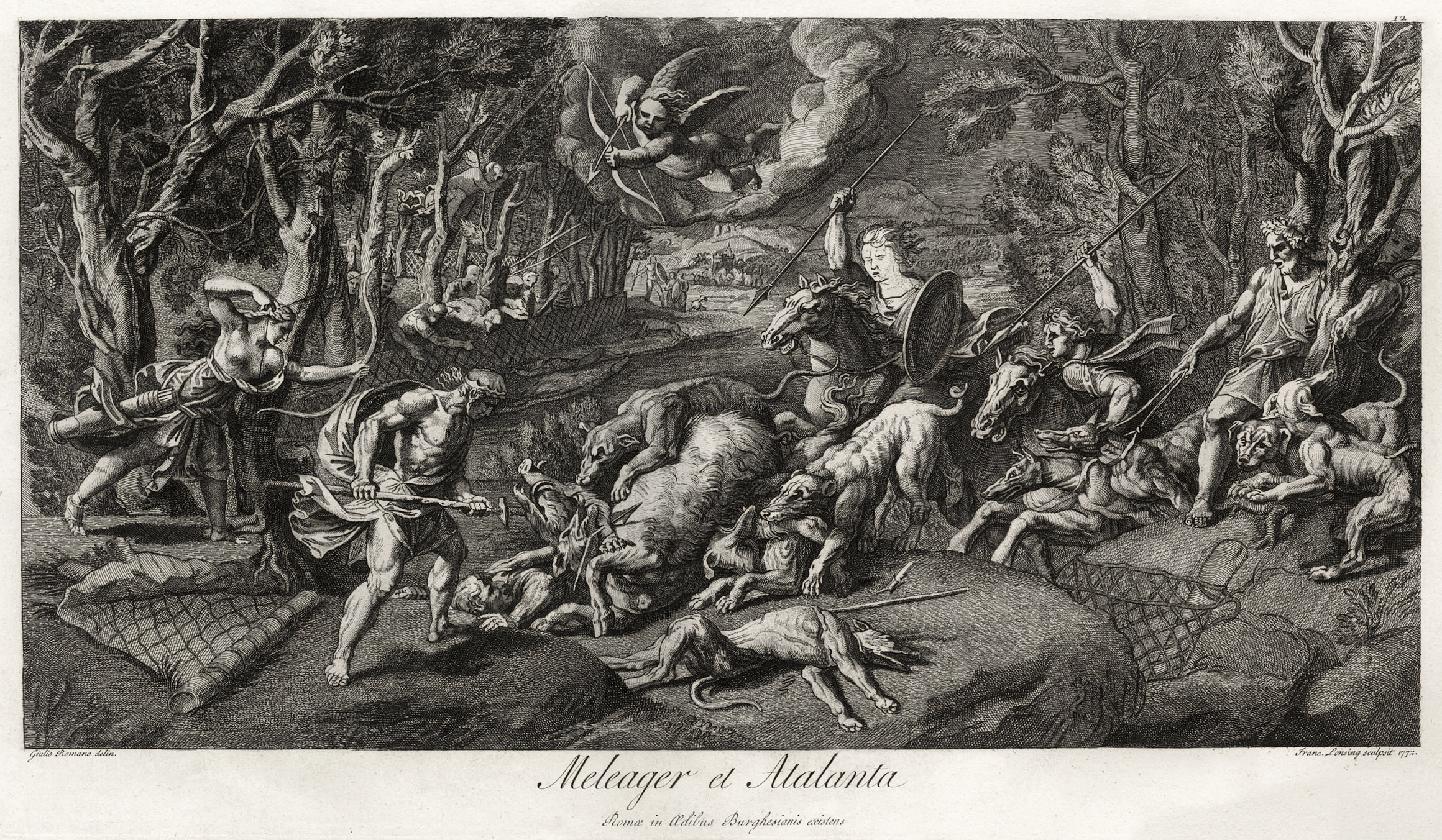
Meleager
In Greek mythology A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of ..., Meleager (, grc-gre, Μελέαγρος, Meléagros) was a Greek hero, hero venerated in his ''temenos'' at Calydon in Aetolia. He was already famed as the host of the Calydonian Boar, Calydonian boar hunt in the epic tradition that was reworked by Homer. Meleager is also mentioned as one of the Argonauts. Biography Meleager was a Calydonian prince as the son of Althaea (Greek mythology), Althaea and the vintner King OeneusAntoninus Liberalis2as cited in Nicander, Nicander's ''Metamorphoses'' or according to some, of the god Ares. He was the brother of Deianira, Deianeira, Toxeus, Clymenus, Periphas, Agelaus (or Ageleus), Thyreus (mythology), Thyreus (or Phereus or Pheres), Gorge (mythology), Gorge, Eurymede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippomenes
:''The name Hippomenes may also refer to the father of Leimone.'' In Greek mythology, Hippomenes (; grc, Ἱππομένης), also known as Melanion (; Μελανίων or Μειλανίων), was a son of the Arcadian AmphidamasApollodorus, 3.9.2 or of King Megareus of Onchestus and the husband of Atalanta. He was known to have been one of the disciples of Chiron, and to have surpassed other disciples in his eagerness to undertake hard challenges. Inscriptions mention him as one of the Calydonian hunters. Mythology The main myth of Hippomenes' courtship of Atalanta, narrated by Pseudo-Apollodorus, Ovid, Servius, and Hyginus was as follows. Hippomenes fell in love with Atalanta, the virgin huntress who strongly disliked the idea of getting married. After a warning from an oracle about getting married, she declared that whoever wanted to marry her was to beat her in a footrace (herself being a notoriously swift runner), and that those who should try and lose would be pun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanion
:''The name Hippomenes may also refer to the father of Leimone.'' In Greek mythology, Hippomenes (; grc, Ἱππομένης), also known as Melanion (; Μελανίων or Μειλανίων), was a son of the Arcadian AmphidamasApollodorus, 3.9.2 or of King Megareus of Onchestus and the husband of Atalanta. He was known to have been one of the disciples of Chiron, and to have surpassed other disciples in his eagerness to undertake hard challenges. Inscriptions mention him as one of the Calydonian hunters. Mythology The main myth of Hippomenes' courtship of Atalanta, narrated by Pseudo-Apollodorus, Ovid, Servius, and Hyginus was as follows. Hippomenes fell in love with Atalanta, the virgin huntress who strongly disliked the idea of getting married. After a warning from an oracle about getting married, she declared that whoever wanted to marry her was to beat her in a footrace (herself being a notoriously swift runner), and that those who should try and lose would be pun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Apple
The golden apple is an element that appears in various national and ethnic folk legends or fairy tales. Recurring themes depict a hero (for example Hercules or Făt-Frumos) retrieving the golden apples hidden or stolen by a monstrous antagonist. Gold apples also appear on the Silver Branch of the Otherworld in Irish mythology. Greek mythology Golden apples appear in three Greek myths: Atalanta and Melanion A huntress named Atalanta who raced against a suitor named Melanion, also known as Hippomenes. Melanion used golden apples to distract Atalanta so that he could win the race. Though abandoned by her father as an infant, Atalanta became a skilled hunter and received acclaim for her role in the hunt for the Calydonian boar. Her father claimed her as his daughter and wished to marry her off. However, Atalanta was reluctant to marry due to a prophecy that marriage would be her downfall. Because of her beauty, she gained a number of suitors and finally agreed to marry, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calydonian Boar Hunt
The Calydonian boar hunt is one of the great heroic adventures in Greek legend. It occurred in the generation prior to that of the Trojan War, and stands alongside the other great heroic adventure of that generation, the voyage of the Argonauts, which preceded it. The purpose of the hunt was to kill the Calydonian boar (also called the Aetolian boar), which had been sent by Artemis to ravage the region of Calydon in Aetolia, because its king Oeneus had failed to honour her in his rites to the gods. The hunters, led by the hero Meleager, included many of the foremost heroes of Greece. In most accounts, it also included a great heroine, Atalanta, who won its hide by first wounding it with an arrow. This outraged some of the men, leading to a tragic dispute. Importance in Greek mythology and art Since the Calydonian boar hunt drew together numerous heroes—among whom were many who were venerated as progenitors of their local ruling houses among tribal groups of Hellenes into Clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemis
In ancient Greek mythology and Ancient Greek religion, religion, Artemis (; grc-gre, Ἄρτεμις) is the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. She was heavily identified with Selene, the Moon, and Hecate, another Moon goddess, and was thus regarded as one of the most prominent lunar deities in mythology, alongside the aforementioned two.Smiths.v. Artemis/ref> She would often roam the forests of Greece, attended by her large entourage, mostly made up of nymphs, some mortals, and hunters. The goddess Diana (mythology), Diana is her Religion in ancient Rome, Roman equivalent. In Greek tradition, Artemis is the daughter of the sky god and king of gods Zeus and Leto, and the twin sister of Apollo. In most accounts, the twins are the products of an extramarital liaison. For this, Zeus' wife Hera forbade Leto from giving birth anywhere on land. Only the island of Delos gave refuge to Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthenopaeus
In Greek mythology, Parthenopaeus or Parthenopaios (; Ancient Greek: Παρθενοπαῖος, ''Parthenopaîos'') was one of the Seven against Thebes, a native of Arcadia, described as young and outstandingly good-looking, but at the same time arrogant, ruthless and over-confident, although an unproblematic ally for the Argives.Euripides, '' Suppliant Women'', 890 ff. Mythology Early life Parthenopaeus was the son of Atalanta by either her husband Hippomenes (Melanion), or by Meleager, or Ares. A less common version makes him a son of Talaus and Lysimache (which makes him a close relative of the other members of the Seven and thereby motivates his involvement in the war). Hyginus writes that he was left exposed by Atalanta on Mount Parthenius ("virginal") in Arcadia, so that she could conceal the fact that she was not a virgin anymore; the name Parthenopaeus is accordingly interpreted by Hyginus as "seemingly-virginal" or the like, as if referring to the fact that his moth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clymene (mythology)
In Greek mythology, the name Clymene or Klymene (; grc, Κλυμένη ''Kluménē'' means 'fame') may refer to: * Clymene, the wife of the Titan Iapetus, was one of the 3,000 Oceanids, the daughters of the Titans Oceanus and his sister-spouse Tethys. She was the mother of Atlas, Epimetheus, Prometheus, and Menoetius; other authors relate the same of her sister Asia. A less common genealogy makes Clymene the mother of Deucalion by Prometheus. She may also be the Clymene referred to as the mother of Mnemosyne by Zeus.Hyginus, ''Fabulae'Preface/ref> In some myths, Clymene was one of the nymphs in the train of Cyrene. * Clymene, another Oceanid, was given as the wife to King Merops of Aethiopia and was, by Helios, the mother of Phaethon and the Heliades. Others include: * Clymene, the name of one or two Nereid(s), 50 sea-nymph daughters of the ' Old Man of the Sea' Nereus and the Oceanid Doris. Clymene and her other sisters appeared to Thetis when she cries out in sympathy f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iasus
In Greek mythology, Iasus (; Ancient Greek: Ἴασος) or Iasius (; Ἰάσιος) was the name of several people: *Iasus (Iasius), one of the Dactyli or Curetes. * Iasus, king of Argos. *Iasus, son of Io *Iasius ( Iasion), son of Eleuther and brother of Pierus. He was the father of Chaeresilaus and Astreis. *Iasius, another name of Iasion. *Iasus (Iasius), the Arcadian father of Atalanta by Clymene, daughter of Minyas; he was the son of King Lycurgus of Arcadia by either Eurynome or Cleophyle. His brothers were Ancaeus, Epochus and Amphidamas. *Iasus, father of Nepeia, who married King Olympus and gave her name to the plain of Nepeia near Cyzicus. *Iasius, winner of the horse-racing contest at the Olympic games held by Heracles. *Iasus (Iasius), king of Orchomenus and son of Persephone, daughter of Minyas. He was the father of Amphion, father of Chloris, wife of Neleus and Phylomache, wife of Pelias. *Iasus, father of Phaedimus. His son was killed by Amy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argonauts
The Argonauts (; Ancient Greek: ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, '' Argo'', named after its builder, Argus. They were sometimes called Minyans, after a prehistoric tribe in the area. Mythology The Golden Fleece After the death of King Cretheus, the Aeolian Pelias usurped the throne from his half-brother Aeson and became king of Iolcus in Thessaly (near the modern city of Volos). Because of this unlawful act, an oracle warned him that a descendant of Aeolus would seek revenge. Pelias put to death every prominent descendant of Aeolus he could, but spared Aeson because of the pleas of their mother Tyro. Instead, Pelias kept Aeson prisoner and forced him to renounce his inheritance. Aeson married Alcimede, who bore him a son named Jason. Pelias intended to kill the baby at once, but Alcimede summoned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcadia (regional Unit)
Arcadia ( el, Αρκαδία, ''Arkadía'' ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Peloponnese. It is in the central and eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. It takes its name from the mythological figure Arcas. In Greek mythology, it was the home of the god Pan. In European Renaissance arts, Arcadia was celebrated as an unspoiled, harmonious wilderness. Geography Arcadia is a rural, mountainous regional unit comprising about 18% of the land area of the Peloponnese peninsula. It is the peninsula's largest regional unit. According to the 2011 census, it has about 86,000 inhabitants; its capital, Tripoli, has about 30,000 residents in the city proper, and about 47,500 total in the greater metropolitan area. Arcadia consists partly of farmland, and to a larger extent grassland and degenerated shrubland. It also has three mountain ranges, with forestation mainly at altitudes above 1000 meters: Mainalo, a winter ski resort, situa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |