|
Asus ZenFone 7
The ZenFone 7 and ZenFone 7 Pro are Android-based smartphones manufactured, released and marketed by Asus. The phones were unveiled on 26 August 2020, and succeed the ZenFone 6. Introduction On 26 August 2020, Asus launched the ZenFone 7 series in a Mandarin online press conference from their Taiwan headquarters. The ZenFone 7 series consists of the ZenFone 7 and ZenFone 7 Pro, retaining the hallmark flip camera form factor of the ZenFone 6 with the addition of a 3x telephoto camera, Sony IMX686 main sensor, 8K video recording capabilities, improved actuation mechanism, and optical image stabilisation Image stabilization (IS) is a family of techniques that reduce blurring associated with the motion of a camera or other imaging device during exposure. Generally, it compensates for pan and tilt (angular movement, equivalent to yaw and pit ... exclusive to the Pro model. The ZenFone 7 series features a 6.67-inch 90 Hz A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
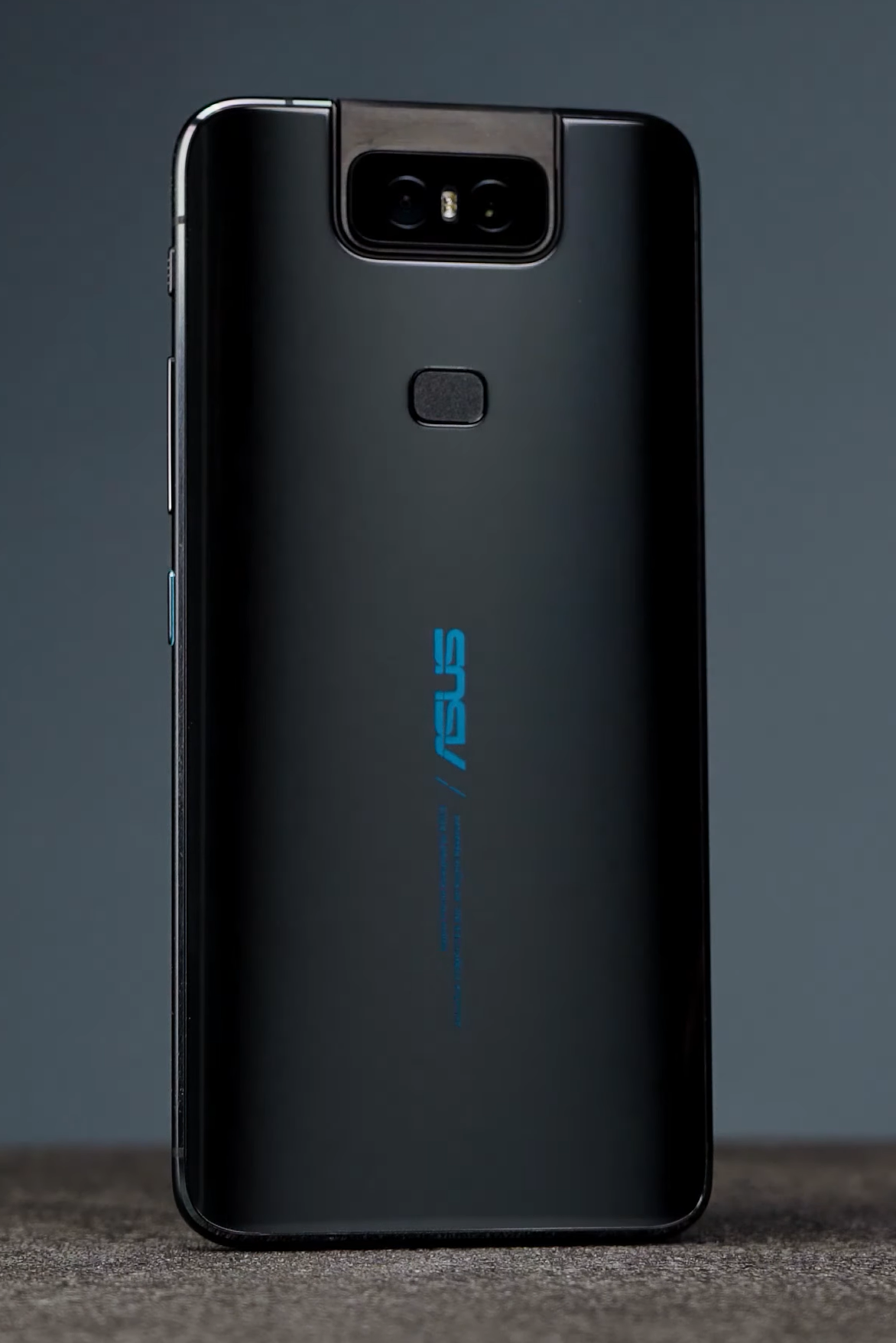
Asus ZenFone 6
The ZenFone 6 is a 2019 Android-based smartphone that was manufactured, released, and marketed by Asus. It is the only release in Asus' sixth-generation ZenFone lineup and directly succeeds the ZenFone 5Z. Asus chairman Jonney Shih unveiled the ZenFone 6 on 16 May 2019 in Valencia, Spain, and was released in Spain the following day. The ZenFone 6 has a larger display, a faster processor, and upgraded cameras than the ZenFone 5Z. The ZenFone 6's flip-up camera module doubles as a front-facing camera. It is the first mobile device Asus released after restructuring its smartphone division in late 2018. The ZenFone 6 was released in the Indian market as the "Asus 6Z". Despite positive reviews, the ZenFone 6 lacked broad appeal and attracted a niche market of power users and technology enthusiasts. Supply issues resulted in delays and stock shortages, which also interfered with its success. , Asus has not released sales figures for the device, only noting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5G NR Frequency Bands
Frequency bands for 5G New Radio (5G NR), which is the air interface or radio access technology of the 5G mobile networks, are separated into two different frequency ranges. First there is Frequency Range 1 (FR1), which includes sub-6 GHz frequency bands, some of which are traditionally used by previous standards, but has been extended to cover potential new spectrum offerings from 410 MHz to 7125 MHz. The other is Frequency Range 2 (FR2), which includes frequency bands from 24.25 GHz to 71.0 GHz. Frequency bands From the latest published version (Rel. 17) of the respective 3GPP technical standard (TS 38.101), the following tables list the specified frequency bands and the channel bandwidths of the 5G NR standard. Note that the NR bands are defined with prefix of "n". When the NR band is overlapping with the 4G LTE band, they share the same band number. Frequency Range 1 Frequency Range 2 See also * 5G * 5G NR * List of 5G NR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambient Light Sensor
An ambient light sensor is a component in smartphones, notebooks, other mobile devices, automotive displays and LCD TVs. It is a photodetector that is used to sense the amount of ambient light present, and appropriately dim the device's screen to match it. This avoids having the screen be too bright when the user's pupils are adapted for vision in a dark room, or too dim when the device is used outdoors in the daytime. Dimming the screen on a mobile device also prolongs the lifetime of the battery. The standard international unit for the illuminance of ambient light is the lux. The typical performance of an ambient light sensor is from less than 50 lux in dim light to over 10,000 lux at noon. There are three common types of ambient light sensor: phototransistors, photodiodes, and photonic integrated circuits, which integrate a photodetector and an amplifier in one device. By the end of 2004, about 30% of phones sold in Europe Europe is a large peninsula conventional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil. The first magnetometer capable of measuring the absolute magnetic intensity at a point in space was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall effect, which is still widely used. Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field, in geophysical surveys, to detect magnetic anomalies of various types, and to determine the dipole moment of magnetic materials. In an air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARCore
Arcore ( lmo, Arcor) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Monza and Brianza in the Italian region Lombardy, located about northeast of Milan. Arcore borders the following municipalities: Usmate Velate, Camparada, Lesmo, Biassono, Vimercate, Villasanta, Concorezzo. History The origin of the city is not clear: by the etymology of the name, it's probably datable during the Roman Empire. To endorse this hypothesis there are different elements: the presence of centuriations and the discovery, in the Middle Ages, of a Roman marble slab, now kept in the Archaeological Museum of Milan. The oldest documents so far discovered dates back to the 10th century. Arcore, in the Middle Ages, is under the control of the ''Pieve of Vimercate'', and is historically documented the presence of two monasteries, la Casa delle Umiliate in Sant'Apollinare and the Benedictine monastery of Saint Martin of Tours. By the 16th century, several noble lombard families (Casati, Durini, Giuli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, according to the conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submerged submarine. Due to their precision, gyroscopes are also used in gyrotheodolites to maintain direction in tunnel mining. Gyroscopes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USB On-The-Go
USB On-The-Go (USB OTG or just OTG) is a specification first used in late 2001 that allows USB devices, such as Tablet computer, tablets or smartphones, to act as a host, allowing other USB devices, such as USB flash drives, digital cameras, computer mouse, mouse or computer keyboard, keyboards, to be attached to them. Use of USB OTG allows those devices to switch back and forth between the roles of host and device. A mobile phone may read from removable media as the host device, but present itself as a USB Mass Storage Device when connected to a host computer. USB OTG introduces the concept of a device performing both Host and Peripheral roles whenever two USB devices are connected and one of them is a USB OTG device, they establish a communication link. The device controlling the link is called the Host, while the other is called the Peripheral. USB OTG defines two roles for devices: OTG A-device and OTG B-device, specifying which side supplies power to the link, and which in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USB Hardware
The initial versions of the USB standard specified connectors that were easy to use and that would have acceptable life spans; revisions of the standard added smaller connectors useful for compact portable devices. Higher-speed development of the USB standard gave rise to another family of connectors to permit additional data paths. All versions of USB specify cable properties; version 3.x cables include additional data paths. The USB standard included power supply to peripheral devices; modern versions of the standard extend the power delivery limits for battery charging and devices requiring up to 100 watts. USB has been selected as the standard charging format for many mobile phones, reducing the proliferation of proprietary chargers. Connectors The three sizes of USB connectors are the default or ''standard'' format intended for desktop or portable equipment, the ''mini'' intended for mobile equipment, which was deprecated when it was replaced by the thinner ''micro'' si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USB-C
USB-C (properly known as USB Type-C) is a 24-pin USB connector system with a rotationally symmetrical connector. The designation C refers only to the connector's physical configuration or form factor and should not be confused with the connector's specific capabilities, which are designated by its transfer specifications (such as USB 3.2). A notable feature of the USB-C connector is its ''reversibility''; a plug may be inserted into a receptacle in either orientation. The ''USB Type-C Specification 1.0'' was published by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) and was finalized in August 2014. It was developed at roughly the same time as the USB 3.1 specification. In July 2016, it was adopted by the IEC as "IEC 62680-1-3". A device with a Type-C connector does not necessarily implement USB, USB Power Delivery, or any Alternate Mode: the Type-C connector is common to several technologies while mandating only a few of them. USB 3.2, released in September 2017, replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Polymer Battery
A lithium polymer battery, or more correctly lithium-ion polymer battery (abbreviated as LiPo, LIP, Li-poly, lithium-poly and others), is a rechargeable battery of lithium-ion technology using a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte. High conductivity semisolid (gel) polymers form this electrolyte. These batteries provide higher specific energy than other lithium battery types and are used in applications where weight is a critical feature, such as mobile devices, radio-controlled aircraft and some electric vehicles. History LiPo cells follow the history of lithium-ion and lithium-metal cells which underwent extensive research during the 1980s, reaching a significant milestone with Sony's first commercial cylindrical Li-ion cell in 1991. After that, other packaging forms evolved, including the flat pouch format. Design origin and terminology Lithium polymer cells have evolved from lithium-ion and lithium-metal batteries. The primary difference is that instead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIM Card
file:SIM-Karte von Telefónica O2 Europe - Standard und Micro.jpg, A typical SIM card (mini-SIM with micro-SIM cutout) file:Sim card.png, A smart card taken from a Global System for Mobile Communications, GSM mobile phone file:Simkarte NFC SecureElement.jpg, T-Mobile nano-SIM card with NFC capabilities in the SIM tray of an iPhone 6s file:Tf sim both sides.png, A TracFone Wireless SIM card has no distinctive carrier markings and is only marked as a "SIM card" A SIM card (full form Subscriber Identity Module or Subscriber Identification Module) is an integrated circuit (IC) intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices (such as mobile phones and computers). Technically the actual physical card is known as a universal integrated circuit card (UICC); this smart card is usually made of PVC with embedded contacts and semiconductors, with the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |