|
Asus Media Bus
The Asus Media Bus is a proprietary computer bus developed by Asus, which was used on some Socket 7 motherboards in the middle 1990s. It is a combined PCI and ISA slot. It was developed to provide a cost-efficient solution to a complete multimedia system. Using Media Bus cards for building a system reduced slot requirements and compatibility problems. Expansion cards supporting this interface were only manufactured by Asus for a very limited time. This bus is now obsolete. While similar to PCI-X in appearance, the extension contains 4 additional pins (2 on each side) for a total of 68. The divider between the PCI slot and Media Bus extension is too wide to support a properly-keyed PCI-X card. Despite the very short lifespan, there were at least two revisions of Asus Media Bus – revision 1.2 and 2.0. The difference between them is that the latter revision has 72 pins instead of 68 so it does not have to use any PCI slot signals reserved for PCI cards and PCI slot shared wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the brain. Only acoustic waves that have frequencies lying between about 20 Hz and 20 kHz, the audio frequency range, elicit an auditory percept in humans. In air at atmospheric pressure, these represent sound waves with wavelengths of to . Sound waves above 20 kHz are known as ultrasound and are not audible to humans. Sound waves below 20 Hz are known as infrasound. Different animal species have varying hearing ranges. Acoustics Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gasses, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound, and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an ''acoustician'', while someone working in the field of acoustica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATI Rage Series
The ATI Rage (stylized as RAGE or rage) is a series of graphics chipsets developed by ATI Technologies offering graphical user interface (GUI) 2D acceleration, video acceleration, and 3D acceleration developed by ATI Technologies. It is the successor to the ATI Mach series of 2D accelerators. 3D RAGE (I) The original 3D RAGE (also known as Mach64 GT) chip was based upon a Mach64 2D core with new 3D functionality and MPEG-1 acceleration. The 3D RAGE was released in April 1996. The 3D RAGE was used in ATI's ''3D Xpression'' video board. Additionally, this chip was found integrated into the IBM Aptiva 2176 line with the Stealth case, and came with a Free Copy of MechWarrior 2: 31st Century Combat that only worked with this graphics chip to showcase its abilities. The memory configuration on this integrated chip was 2 Megabytes. 3D RAGE II (II+, II+DVD, IIc) The second generation Rage (aka Mach64 GT-B) offered roughly two times greater 3D performance. Its graphics proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATI Mach Series
The ATI Mach line was a series of 2D graphics accelerators for personal computers developed by ATI Technologies. It became an extension (and eventual successor) to the ATI Wonder series of cards. The first chip in the series was the ATI Mach8. It was essentially a clone of the IBM 8514/A with a few notable extensions such as Crystal fonts. Being one of the first graphics accelerator chips on the market, the Mach8 did not have an integrated VGA core. In order to use the first Mach8 coprocessor cards, a separate VGA card was required. This increased the cost of ownership as one had to purchase two rather than one expansion card for graphics. A temporary solution was presented with the ATI Graphics Ultra/Vantage cards, which combined an ATI 8514 Ultra and VGA Wonder+ into a single card (though using discrete ICs). The Mach32 chip was the follow-up to the Mach8, which finally featured an integrated VGA core, true colour support and a 64-bit datapath to internal memory. Models Mach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamaha YMF262
The OPL (FM Operator Type-L) series are a family of sound chips developed by Yamaha. The OPL series are low-cost sound chips providing FM synthesis for use in computing, music and video game applications. Internal operation The internal operation of the chips is completely digital. Each FM-tone is generated by a digital oscillator using a form of direct digital synthesis. A low-frequency oscillator and an envelope generator drive an FM operator to produce floating-point output for the DAC. Decapsulation of the chips shows two look-up tables, one for calculating exponents and one for log-sine. This allows the FM operator to calculate its output without any multipliers, using the formula \exp log \sin[\varphi_2 + \exp [\log \sin [\varphi_1+ A_1">varphi_2_+_\exp_[\log_\sin_[\varphi_1.html" ;"title="log \sin[\varphi_2 + \exp [\log \sin [\varphi_1">log \sin[\varphi_2 + \exp [\log \sin [\varphi_1+ A_1 + A_2] and two 256-entry look-up tables. Both tables are stored as pairs of values r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Blaster
Sound Blaster is a family of sound cards designed by Singaporean technology company Creative Technology (known in the US as Creative Labs). Sound Blaster sound cards were the de facto standard for consumer audio on the IBM PC compatible system platform, until the widespread transition to ''Microsoft'' Windows 95, which standardized the programming interface at application level (eliminating the importance of backward compatibility with Sound Blaster), and the evolution in PC design led to onboard audio electronics, which commoditized PC audio functionality. By 1995, Sound Blaster cards had sold over 15 million units worldwide and accounted for seven out of ten sound card sales. Creative Music System and Game Blaster Creative Music System The history of Creative sound cards started with the release of the Creative Music System ("C/MS") CT-1300 board in August 1987. It contained two Philips SAA1099 integrated circuits, which, together, provided 12 channels of square-wave "bee-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems which, in turn, were replaced by flat panel displays of several types. Video systems vary in display resolution, aspect ratio, refresh rate, color capabilities and other qualities. Analog and digital variants exist and can be carried on a variety of media, including radio broadcast, magnetic tape, optical discs, computer files, and network streaming. History Analog video Video technology was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) television systems, but several new technologies for video display devices have since been invented. Video was originally exclusively a live technology. Charles Ginsburg led an Ampex research team developing one of the first practical vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
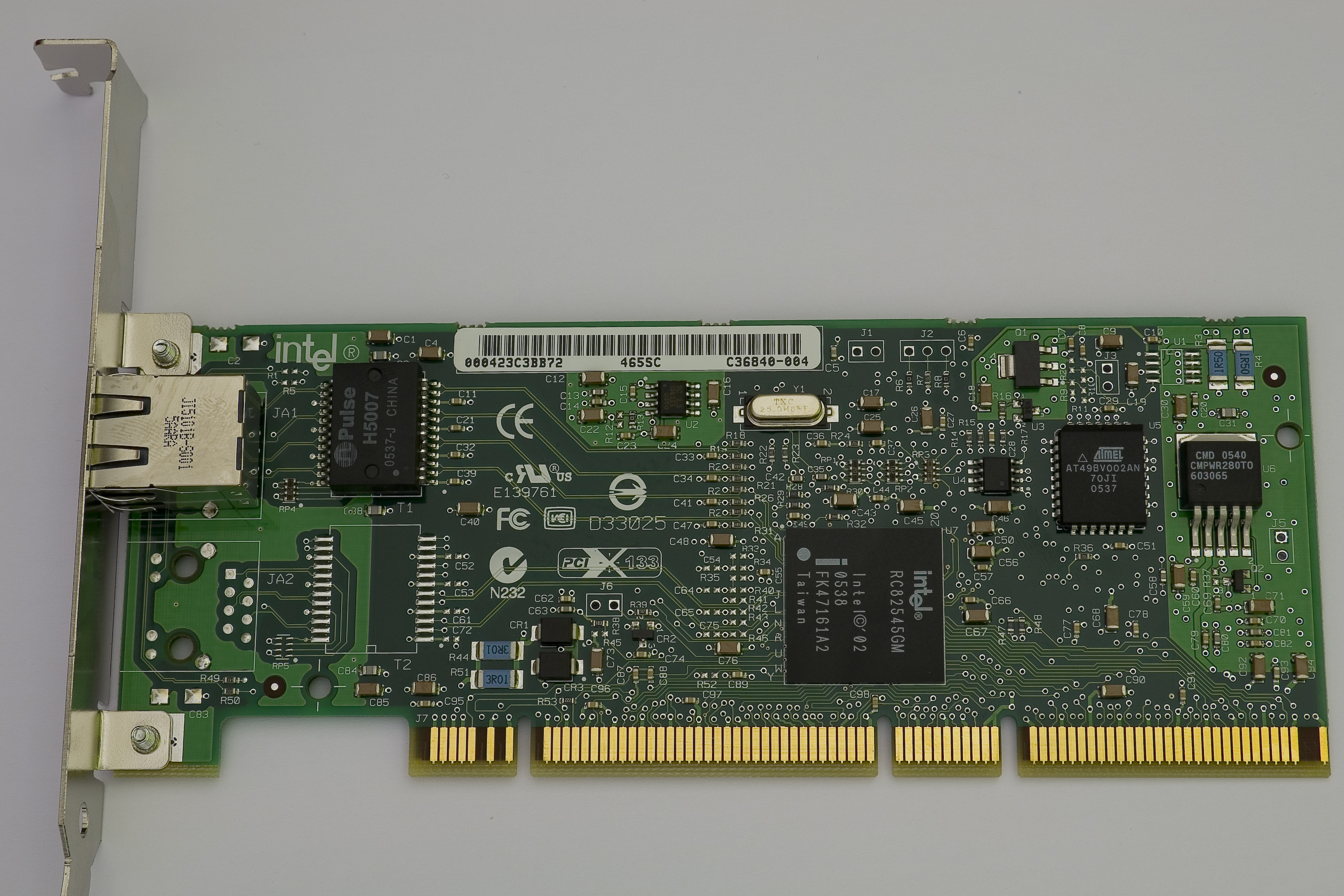
PCI-X
PCI-X, short for Peripheral Component Interconnect eXtended, is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI local bus for higher bandwidth demanded mostly by servers and workstations. It uses a modified protocol to support higher clock speeds (up to 133 MHz), but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation. PCI-X 2.0 added speeds up to 533 MHz, with a reduction in electrical signal levels. The slot is physically a 3.3 V PCI slot, with exactly the same size, location and pin assignments. The electrical specifications are compatible, but stricter. However, while most conventional PCI slots are the 85 mm long 32-bit version, most PCI-X devices use the 130 mm long 64-bit slot, to the point that 64-bit PCI connectors and PCI-X support are seen as synonymous. PCI-X is in fact fully specified for both 32- and 64-bit PCI connectors, and PCI-X 2.0 added a 16-bit variant for embedded applications. It has been replaced in mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Media Bus P55tp4xe
Media may refer to: Communication * Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data ** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising ** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass electronic communication networks ** Digital media, electronic media used to store, transmit, and receive digitized information ** Electronic media, communications delivered via electronic or electromechanical energy ** Hypermedia, media with hyperlinks ** Interactive media, media that is interactive ** Mass media, technologies that reach a large audience via mass communication ** MEDIA Programme, a European Union initiative to support the European audiovisual sector ** Multimedia, communications that incorporate multiple forms of information content and processing ** New media, the combination of traditional media and computer and communications technology ** News media, mass media focused on communicating news ** Print media, communications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industry Standard Architecture
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles. Originally referred to as the PC bus (8-bit) or AT bus (16-bit), it was also termed ''I/O Channel'' by IBM. The ISA term was coined as a retronym by competing PC-clone manufacturers in the late 1980s or early 1990s as a reaction to IBM attempts to replace the AT-bus with its new and incompatible Micro Channel architecture. The 16-bit ISA bus was also used with 32-bit processors for several years. An attempt to extend it to 32 bits, called Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA), was not very successful, however. Later buses such as VESA Local Bus and PCI were used instead, often along with ISA slots on the same mainboard. Derivatives of the AT bus structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer and is part of the PCI Local Bus standard. The PCI bus supports the functions found on a processor bus but in a standardized format that is independent of any given processor's native bus. Devices connected to the PCI bus appear to a bus master to be connected directly to its own bus and are assigned addresses in the processor's address space. It is a parallel bus, synchronous to a single bus clock. Attached devices can take either the form of an integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard (called a ''planar device'' in the PCI specification) or an expansion card that fits into a slot. The PCI Local Bus was first implemented in IBM PC compatibles, where it displaced the combination of several slow Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) slots and one fast VESA Local Bus (VLB) slot as the bus configuration. It has subsequently been adopted for other computer types. Typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |