|
Asterolepis (fish)
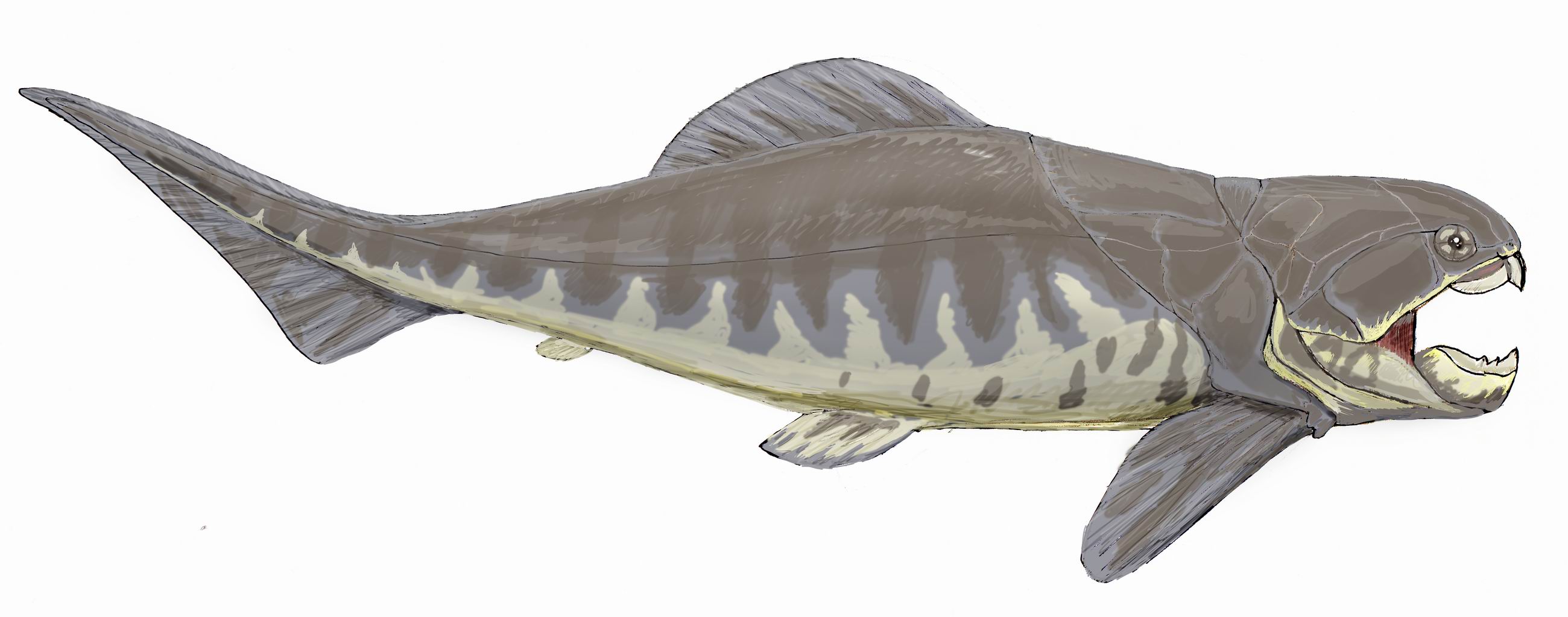
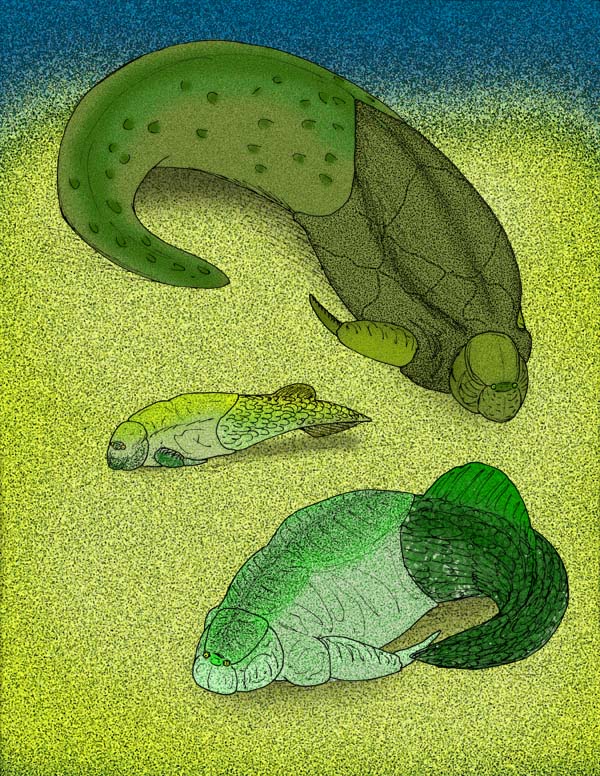
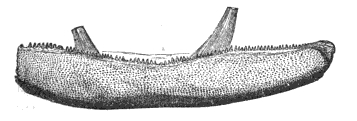
''Asterolepis'' is an extinct genus of antiarch placoderms from the Devonian of North and South America and Europe. They were heavily armored flat-headed benthic detritivores with distinctive jointed limb-like pectoral fins and hollow spine. The armor plate gives the ''Asterolepis'' a box-like shape. Its pectoral fins are also armored but the caudal and dorsal fin are not. The first fossils were named by M. Eichwald in 1840 after noticing star-like markings on the fossils. Etymology "Aster-" means star while "-lepis" means scales. Confusion surrounded the first fossils discovered of this genus, as naturalists were unable to ascertain their place among fishes and they were first named Chelonichthys. Later very fine specimens were found in the Old Red Sandstone of Russia and Professor Asmus of Dorpat sent them to the British Museum, noticing fossils exhibited star-like markings. That is when the name Chelonichthys was abandoned for ''Asterolepis'' which Eichwald proposed. Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterolepis Woodward 1889
''Asterolepis'' may refer to: * ''Asterolepis'' (fish), a genus of extinct armored fishes in the family Asterolepididae. * ''Asterolepis'' (moth), a genus of moths in the family Tortricidae. {{genus disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmoid Scales
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as well as possible hydrodynamic advantages. The term ''scale'' derives from the Old French , meaning a shell pod or husk. Scales vary enormously in size, shape, structure, and extent, ranging from strong and rigid armour plates in fishes such as shrimpfishes and boxfishes, to microscopic or absent in fishes such as eels and anglerfishes. The morphology of a scale can be used to identify the species of fish it came from. Scales originated within the jawless ostracoderms, ancestors to all jawed fishes today. Most bony fishes are covered with the cycloid scales of salmon and carp, or the ctenoid scales of perch, or the ganoid scales of sturgeons and gars. Cartilaginous fishes (sharks and rays) are covered with placoid scales. Some species are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganoid Scale
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as well as possible hydrodynamic advantages. The term ''scale'' derives from the Old French , meaning a shell pod or husk. Scales vary enormously in size, shape, structure, and extent, ranging from strong and rigid armour plates in fishes such as shrimpfishes and boxfishes, to microscopic or absent in fishes such as eels and anglerfishes. The morphology of a scale can be used to identify the species of fish it came from. Scales originated within the jawless ostracoderms, ancestors to all jawed fishes today. Most bony fishes are covered with the cycloid scales of salmon and carp, or the ctenoid scales of perch, or the ganoid scales of sturgeons and gars. Cartilaginous fishes (sharks and rays) are covered with placoid scales. Some species are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerotic Ring
Sclerotic rings are rings of bone found in the eyes of many animals in several groups of vertebrates, except for mammals and crocodilians. They can be made up of single bones or multiple segments and take their name from the sclera. They are believed to have a role in supporting the eye, especially in animals whose eyes are not spherical, or which live underwater. Fossil sclerotic rings are known for a variety of extinct animals, including ichthyosaurs, pterosaurs, and dinosaurs, but are often not preserved. File:Tawny Frogmouth Skull.jpg, A skull of an extant tawny frogmouth, showing large sclerotic rings. File:Uroplatus_phantasticus_skull1.jpg, A skull of an extant satanic leaf-tailed gecko, showing large sclerotic rings. File:Viatkogorgon skull.png, Skull and sclerotic ring of the gorgonopsian ''Viatkogorgon''. File:Prosaurolophus maximus3.JPG, Sclerotic ring of the hadrosaur ''Prosaurolophus ''Prosaurolophus'' (; meaning "before ''Saurolophus''", in comparison to the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endolymphatic Duct
From the posterior wall of the saccule a canal, the endolymphatic duct, is given off; this duct is joined by the ductus utriculosaccularis, and then passes along the aquaeductus vestibuli and ends in a blind pouch (endolymphatic sac) on the posterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone, where it is in contact with the dura mater In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. .... Disorders of the endolymphatic duct include Meniere's Disease and Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct. Additional images File:Gray902.png, Transverse section through head of fetal sheep, in the region of the labyrinth. X 30. File:Gray927.png, Transverse section of a human semicircular canal and duct References External links *The Endolymphatic Duct and Sac Vestibular system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal. In plants A tubercle is generally a wart-like projection, but it has slightly different meaning depending on which family of plants or animals it is used to refer to. In the case of certain orchids and cacti, it denotes a round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on the lip. They are also known as podaria (singular ''podarium''). When referring to some members of the pea family, it is used to refer to the wart-like excrescences that are found on the roots. In fungi In mycology, a tubercle is used to refer to a mass of hyphae from which a mushroom is made. In animals When it is used in relation to certain dorid nudibranchs such as '' Peltodoris nobilis'', it means the nodules on the dorsum of the animal. The tubercles in nudibranchs can present themselves in different ways: e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
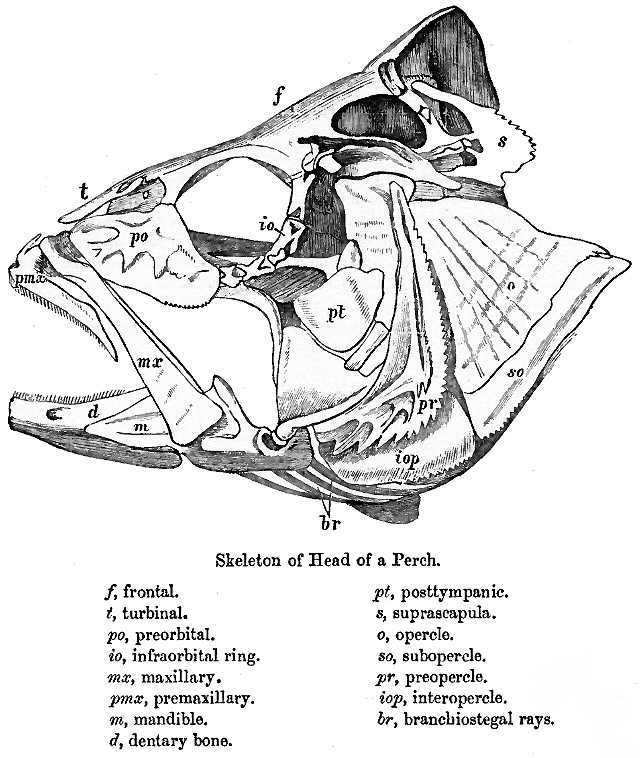
Endocranium
The endocranium in comparative anatomy is a part of the skull base in vertebrates and it represents the basal, inner part of the cranium. The term is also applied to the outer layer of the dura mater in human anatomy. Structure Structurally, the endocranium consists of a boxlike shape, open at the top. The posterior margin exhibit the '' foramen magnum'', an opening for the spinal cord. The floor of the endocranium has several paired openings for the cranial nerves, and the anterior margin holds a spongy construction, allowing for the external nasal nerves to pass through. Romer, A.S. & T.S. Parsons. 1977. ''The Vertebrate Body.'' 5th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia. (6th ed. 1985) All bones of the structure derive from the cranial neural crest during fetal development. Endocranial elements in humans In humans and other mammals, the endocranium forms during fetal development as a cartilaginous neurocranium, that ossifies from several centers. Several of these bones merge, and in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thorax'' "breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via la, thorax. Plural: ''thoraces'' or ''thoraxes''. Human thorax Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnathostomata
Gnathostomata (; from Greek: (') "jaw" + (') "mouth") are the jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all living vertebrates, including humans. In addition to opposing jaws, living gnathostomes have true teeth (a characteristic which has subsequently been lost in some), paired appendages (pectoral and pelvic fins, arms, legs, wings, etc.), the elastomeric protein of elastin, and a horizontal semicircular canal of the inner ear, along with physiological and cellular anatomical characters such as the myelin sheaths of neurons, and an adaptive immune system that has the discrete lymphoid organs of spleen and thymus, and uses V(D)J recombination to create antigen recognition sites, rather than using genetic recombination in the variable lymphocyte receptor gene. It is now assumed that Gnathostomata evolved from ancestors that already possessed a pair of both pectoral and pelvic fins. Until recently these ancestors, know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiarchi
Antiarchi ("opposite anus") is an order (biology), order of heavily armored placoderms. The antiarchs form the second-most successful group of placoderms after the arthrodires in terms of numbers of species and range of environments. The order's name was coined by Edward Drinker Cope, who, when examining some fossils that he thought were armored tunicates related to ''Chelysoma'', mistakenly thought that the orbital fenestra (i.e., the hole in the headshield for the eyes, nose and pineal foramen) was the opening for the mouth, or oral siphon, and that the opening for the anal siphon was on the other side of the body, as opposed to having both oral and anal siphons together at one end. The front portions of their bodies were heavily armored, to the point of literally resembling a box with eyes, with the sometimes scaled, sometimes naked rear portions often becoming wiktionary:sinuous, sinuous, particularly with later forms. The pair of pectoral fins were modified into a pair of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |