|
Astelin
Azelastine, sold under the brand name Optivar among others, is a H1 receptor-blocking medication primarily used as a nasal spray to treat allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and as eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis. Other uses may include asthma and skin rashes for which it is taken by mouth. Onset of effects is within minutes when used in the eyes and within an hour when used in the nose. Effects last for up to 12 hours. Common side effects include headache, sleepiness, change in taste, and sore throat. It is unclear if use is safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding. It is a second-generation antihistamine and works by blocking the release of a number of inflammatory mediators including histamine. Azelastine was patented in 1971 and came into medical use in 1986. It is available as a generic medication in the United States. In 2020, it was the 173rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3million prescriptions. Medical uses Azelastine nasal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasomotor Rhinitis
Nonallergic rhinitis is rhinitis—inflammation of the inner part of the nose—not caused by an allergy. Nonallergic rhinitis displays symptoms including chronic sneezing or having a congested, drippy nose, without an identified allergic reaction. Other common terms for nonallergic rhinitis are vasomotor rhinitis and perennial rhinitis. The prevalence of nonallergic rhinitis in Otorhinolaryngology, otolaryngology is 40%. Allergic rhinitis is more common than nonallergic rhinitis; however, both conditions have similar presentation, manifestation and treatment. Nasal itching and paroxysmal sneezing are usually associated with nonallergic rhinitis rather than allergic rhinitis. Types * Rhinitis medicamentosa – rebound nasal congestion suspected to be brought on by extended use of topical decongestants and certain oral medications that constrict blood vessels in the nose. Treatment includes withdrawal of nasal drops, short courses of systemic steroid therapy and in some cases, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
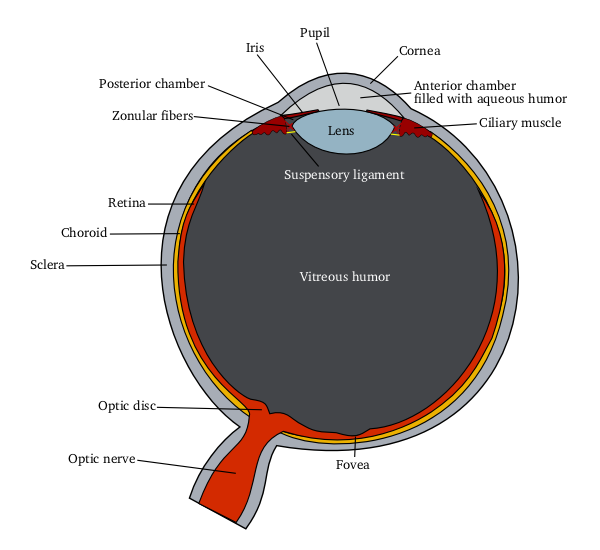
Ophthalmic Drug Administration
Ophthalmic drug administration is the administration of a drug to the eyes, most typically as an eye drop formulation. Topical formulations are used to combat a multitude of diseased states of the eye. These states may include bacterial infections, eye injury, glaucoma, and dry eye. However, there are many challenges associated with topical delivery of drugs to the cornea of the eye. Eye drop formulations Two of the largest challenges faced when using topicals to treat pathological states of the eye include patient compliance and ineffective absorbance of drugs into the cornea. In fact, researchers in this field of drug delivery agree that less than 7% of drugs delivered to the eye reach and penetrate the corneal barrier, therefore, increasing the frequency of dosing used for topicals. This is one of the fundamental problem associated with using topicals to deliver drugs to the cornea and therefore leads to the increased demand for patient compliance. Together, these two factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis
Rhinitis, also known as coryza, is irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. Common symptoms are a stuffy nose, runny nose, sneezing, and post-nasal drip. The inflammation is caused by viruses, bacteria, irritants or allergens. The most common kind of rhinitis is allergic rhinitis, which is usually triggered by airborne allergens such as pollen and dander. Allergic rhinitis may cause additional symptoms, such as sneezing and nasal itching, coughing, headache, fatigue, malaise, and cognitive impairment. The allergens may also affect the eyes, causing watery, reddened, or itchy eyes and puffiness around the eyes. The inflammation results in the generation of large amounts of mucus, commonly producing a runny nose, as well as a stuffy nose and post-nasal drip. In the case of allergic rhinitis, the inflammation is caused by the degranulation of mast cells in the nose. When mast cells degranulate, they release histamine and other chemicals, starting an infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered to a living organism. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as: pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects a drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects, as seen in PK/PD models. Overview Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific xenobiotic/chemical after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume Of Distribution
In pharmacology, the volume of distribution (VD, also known as apparent volume of distribution, literally, ''volume of dilution'') is the theoretical volume that would be necessary to contain the total amount of an administered drug at the same concentration that it is observed in the blood plasma. In other words, it is the ratio of ''amount of drug in a body (dose)'' to ''concentration of the drug that is measured in blood, plasma, and un-bound in interstitial fluid''. The VD of a drug represents the degree to which a drug is distributed in body tissue rather than the plasma. VD is directly proportional with the amount of drug distributed into tissue; a higher VD indicates a greater amount of tissue distribution. A VD greater than the total volume of body water (approximately 42 liters in humans) is possible, and would indicate that the drug is highly distributed into tissue. In other words, the volume of distribution is smaller in the drug staying in the plasma than that of a dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elimination Half Life
Biological half-life (also known as elimination half-life, pharmacologic half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration ( Cmax) to half of Cmax in the blood plasma, and is denoted by the abbreviation t_. This is used to measure the removal of things such as metabolites, drugs, and signalling molecules from the body. Typically, the biological half-life refers to the body's natural cleansing through the function of the liver and through the excretion of the measured substance through the kidneys and intestines. This concept is used when the rate of removal is roughly exponential. In a medical context, half-life explicitly describes the time it takes for the blood plasma concentration of a substance to halve (''plasma half-life'') its steady-state when circulating in the full blood of an organism. This measurement is useful in medicine, pharmacology and pharmacokinetics because it helps det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation. By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. However, when a medication is administered via routes other than intravenous, its bioavailability is generally lower than that of intravenous due to intestinal endothelium absorption and first-pass metabolism. Thereby, mathematically, bioavailability equals the ratio of comparing the area under the plasma drug concentration curve versus time (AUC) for the extravascular formulation to the AUC for the intravascular formulation. AUC is used because AUC is proportional to the dose that has entered the systemic circulation. Bioavailability of a drug is an average value; to take population variability into account, deviation range is shown as ±. To ensure that the drug taker who has poor absorption is dosed appropriately, the bottom value o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system to block pain signaling to the brain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) alleviate pain by counteracting the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme. On its own, COX enzyme synthesizes prostaglandins, creating inflammation. In whole, the NSAIDs prevent the prostaglandins from ever being synthesized, reducing or eliminating the inflammation and resulting pain. Some common examples of NSAIDs are aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen. The newer specific COX-inhibitors are not classified together with the traditional NSAIDs, even though they presumably share the same mode of action. On the other hand, there are analgesics that are commonly associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mast Cell Stabilizer
Mast cell stabilizers are medications used to prevent or control certain allergic disorders. They block mast cell degranulation, stabilizing the cell and thereby preventing the release of histamine and related mediators. One suspected pharmacodynamic mechanism is the blocking of IgE-regulated calcium channels. Without intracellular calcium, the histamine vesicles cannot fuse to the cell membrane and degranulate. As inhalers they are used to treat asthma, as nasal sprays to treat hay fever (allergic rhinitis) and as eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis. Finally, in oral form, they are used to treat the rare condition of mastocytosis. Examples Mast cell stabilizer medications include: * β2-adrenergic agonists * Cromoglicic acid * Ketotifen * Loratadine * Desloratadine * Methylxanthines * Olopatadine * Rupatadine *Mepolizumab * Omalizumab * Pemirolast * Quercetin * Nedocromil * Azelastine * Tranilast * Palmitoylethanolamide * Vitamin D * Bilastine Bilastine is an antih ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides relief from nasal congestion, sneezing A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth and ..., or hives caused by pollen, dust mites, or animal allergy with few side effects. Antihistamines are usually for short-term treatment. Chronic allergies increase the risk of health problems which antihistamines might not treat, including asthma, sinusitis, and lower respiratory tract infection. Consultation of a medical professional is recommended for those who intend to take antihistamines for longer-term use. Although people typically use the word "anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anosmia
Anosmia, also known as smell blindness, is the loss of the ability to detect one or more smells. Anosmia may be temporary or permanent. It differs from hyposmia, which is a decreased sensitivity to some or all smells. Anosmia can be due to a number of factors, including an inflammation of the nasal mucosa, blockage of nasal passages or a destruction of one temporal lobe. Inflammation is due to chronic mucosa changes in the lining of the paranasal sinus and in the middle and superior turbinates. When anosmia is caused by inflammatory changes in the nasal passageways, it is treated simply by reducing inflammation. It can be caused by chronic meningitis and neurosyphilis that would increase intracranial pressure over a long period of time, and in some cases by ciliopathy, including ciliopathy due to primary ciliary dyskinesia. The term derives from the New Latin ''anosmia'', based on Ancient Greek ἀν- (''an''-) + ὀσμή (''osmḗ'' 'smell'; another related term, hyperosmia, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somnolence
Somnolence (alternatively sleepiness or drowsiness) is a state of strong desire for sleep, or sleeping for unusually long periods (compare hypersomnia). It has distinct meanings and causes. It can refer to the usual state preceding falling asleep, the condition of being in a drowsy state due to circadian rhythm disorders, or a symptom of other health problems. It can be accompanied by lethargy, weakness and lack of mental agility. Somnolence is often viewed as a symptom rather than a disorder by itself. However, the concept of somnolence recurring at certain times for certain reasons constitutes various disorders, such as excessive daytime sleepiness, shift work sleep disorder, and others; and there are medical codes for somnolence as viewed as a disorder. Sleepiness can be dangerous when performing tasks that require constant concentration, such as driving a vehicle. When a person is sufficiently fatigued, microsleeps may be experienced. In individuals deprived of sleep, somno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |