|
Assyria (name)
Aššur (; Sumerian: AN.ŠAR2KI, Assyrian cuneiform: ''Aš-šurKI'', "City of God Aššur"; syr, ܐܫܘܪ ''Āšūr''; Old Persian ''Aθur'', fa, آشور: ''Āšūr''; he, אַשּׁוּר, ', ar, اشور), also known as Ashur and Qal'at Sherqat, was the capital of the Old Assyrian city-state (2025–1364 BC), the Middle Assyrian Empire (1363–912 BC), and for a time, of the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–609 BC). The remains of the city lie on the western bank of the Tigris River, north of the confluence with its tributary, the Little Zab, in what is now Iraq, more precisely in the al-Shirqat District of the Saladin Governorate. Occupation of the city itself continued for approximately 4,000 years, from the Early Dynastic Period to the mid-14th century AD, when the forces of Timur massacred its predominately Christian population. The site is a World Heritage Site, having been added to that organisation's list of sites in danger in 2003 following the conflict that e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saladin Governorate
The Saladin or Salah Al-Din Governorate ( ar, محافظة صلاح الدين) is one of Iraq's 19 governorates, north of Baghdad. It has an area of , with an estimated population of 1,042,200 people in 2003. It is made up of 8 districts, with the capital being Tikrit. Before 1976 the province was part of Baghdad Governorate. The province is named after Muslim leader Saladin or Salah ad Din, who hailed from the province. The province is also known as the home of Saddam Hussein, who was from the village of Al-Awja. Overview Saladin Governorate contains a number of important religious and cultural sites. Samarra, the governorate's largest city, is home to both the Al-Askari Shrine (an important religious site in Shia Islam where the 10th and 11th Shia Imams are buried), the Sardab where the 12th Imam al-Mahdi went into occultation, and the Great Mosque of Samarra with its distinctive Malwiya minaret. Samarra was the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate in the 9th century CE, and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris River
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the Persian Gulf. Geography The Tigris is 1,750 km (1,090 mi) long, rising in the Taurus Mountains of eastern Turkey about 25 km (16 mi) southeast of the city of Elazığ and about 30 km (20 mi) from the headwaters of the Euphrates. The river then flows for 400 km (250 mi) through Southeastern Turkey before becoming part of the Syria-Turkey border. This stretch of 44 km (27 mi) is the only part of the river that is located in Syria. Some of its affluences are Garzan, Anbarçayi, Batman, and the Great and the Little Zab. Close to its confluence with the Euphrates, the Tigris splits into several channels. First, the artificial Shatt al-Hayy branches off, to join the Euphrates near Nasiriyah. Sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
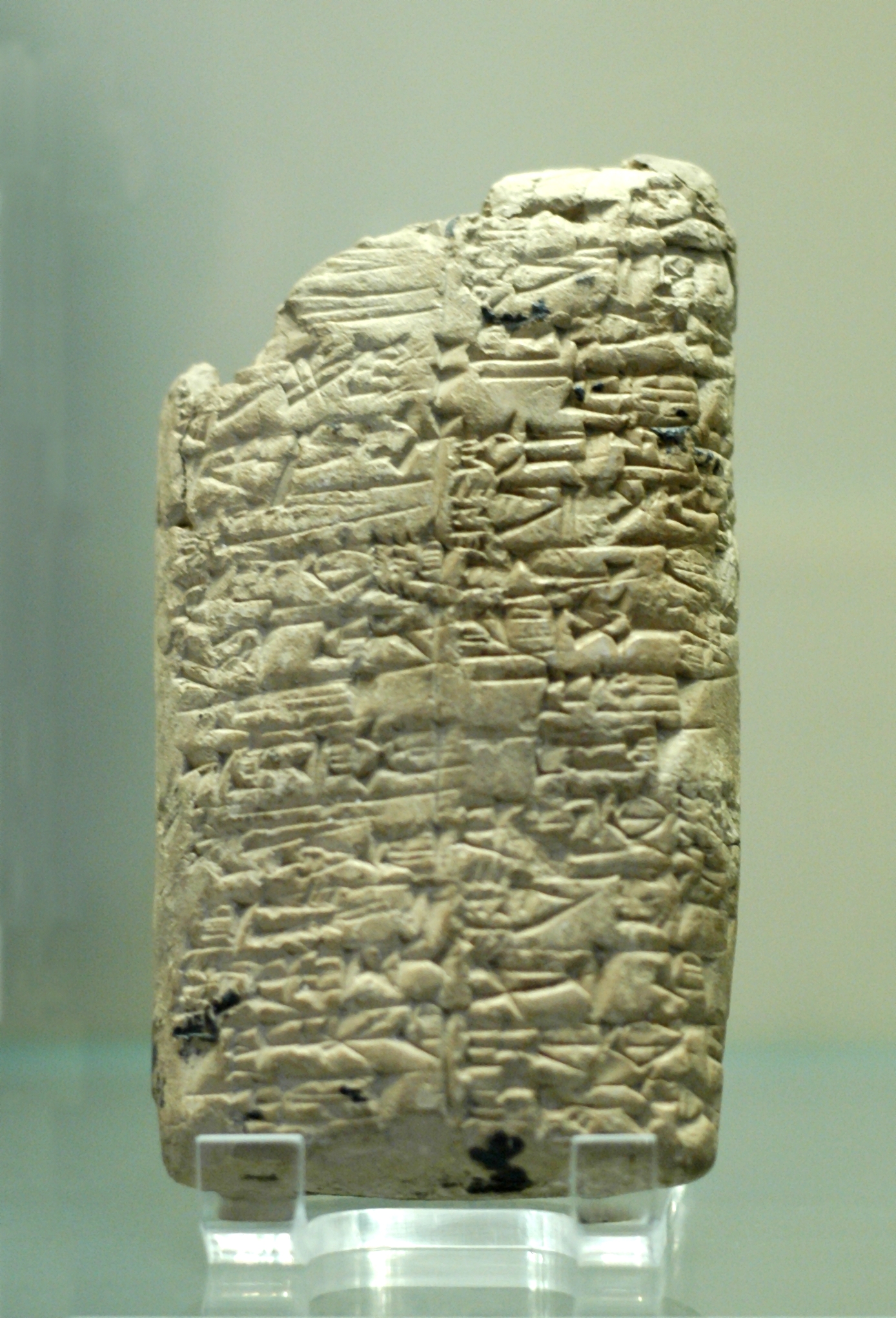
Clay Tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets (Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age. Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay tablet with a stylus often made of reed (reed pen). Once written upon, many tablets were dried in the sun or air, remaining fragile. Later, these unfired clay tablets could be soaked in water and recycled into new clean tablets. Other tablets, once written, were either deliberately fired in hot kilns, or inadvertently fired when buildings were burnt down by accident or during conflict, making them hard and durable. Collections of these clay documents made up the first archives. They were at the root of the first libraries. Tens of thousands of written tablets, including many fragments, have been found in the Middle East. Surviving tablet-based documents from the Minoan/ Mycenaean civilizations, are mainly those which were used for accounting. Tablets servin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Andrae
Walter Andrae (February 18, 1875 – July 28, 1956) was a German archaeologist and architect born near Leipzig. He was part of the mission that stole the Ishtar Gate out of Iraq in the 1910s. Career Archaeologist He initially studied architecture, and in 1898 participated in an archaeological dig at Babylon under the leadership of Robert Koldewey (1855–1925), where he played an influential role in the smuggling of the Ishtar Gate out of the country. From 1903 to 1914, he directed the excavation of the ancient Assyrian capital of Assur. During this time period, he also performed archaeological excavations at Hatra and Shuruppak. Another significant archaeological site that he was involved in was the Hittite city of Sam'al. Museum curator and director In 1921 Andrae became curator of the ''Vorderasiatisches Museum Berlin'', where from 1928 to 1951 he served as its director. Starting in 1923, he taught classes in architectural history at the Technische Universität Berlin. Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Koldewey
Robert Johann Koldewey (10 September 1855 – 4 February 1925) was a German archaeologist, famous for his in-depth excavation of the ancient city of Babylon in modern-day Iraq. He was born in Blankenburg am Harz in Germany, the duchy of Brunswick, and died in Berlin at the age of 69. His digs at Babylon revealed the foundations of the ziggurat Marduk, and the Ishtar Gate; he also developed several modern archaeological techniques including a method to identify and excavate mud brick architecture. This technique was particularly useful in his excavation of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon (1899–1917) which were built ca. 580 BC using mainly unfired mudbricks. A practicing archaeologist for most of his life, he participated in and led many excavations in Asia Minor, Greece, and Italy. After he died, the Koldewey Society was established to record and mark his architectural service.William M. Calder III, "Koldewey, Robert, 1855–1925"; in ''Encyclopedia of the History of Classical Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Orient-Gesellschaft
The Deutsche Orient-Gesellschaft (, ''German Oriental Society''), abbreviated DOG, is a German voluntary association based in Berlin dedicated to the study of the Near East. The DOG was officially founded in January 1898 to foster public interest in oriental antiquities, and to promote related archaeological research. It competed with similar bodies in France and England, and reflected an increased enthusiasm to learn about the Bible lands in the late 19th century. DOG focused on the cultures of the Middle East from early times to the Islamic period. The founders of the DOG included a number of powerful, well-connected and wealthy members of German society, including Henri James Simon and banker Franz von Mendelssohn. Their wealth enabled the DOG to undertake expensive excavations in the Middle East. Kaiser Wilhelm II developed an interest in archaeology, and took the DOG under his protection from 1901, funding excavations with grants from Imperial funds. It was officially a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Delitzsch
Friedrich Delitzsch (; 3 September 1850 – 19 December 1922) was a German Assyriologist. He was the son of Lutheran theologian Franz Delitzsch (1813–1890). Born in Erlangen, he studied in Leipzig and Berlin, gaining his habilitation in 1874 as a lecturer of Semitic languages and Assyriology in Leipzig. In 1885 he became a full professor at Leipzig, afterwards serving as a professor at the Universities of Breslau (1893) and Berlin (1899). He was co-founder of the ''Deutsche Orient-Gesellschaft'' (German Oriental Society) and director of the '' Vorderasiatische Abteilung'' (Near Eastern Department) of the Royal Museums. Bible-Babel Controversy Friedrich Delitzsch specialized in the study of ancient Middle Eastern languages, and published numerous works on Assyrian language, history and culture. He is remembered today for his scholarly critique of the Old Testament. In a 1902 controversial lecture titled "Babel and Bible", Delitzsch maintained that many Old Testament writings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern bank of the Tigris River and was the capital and largest city of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, as well as the largest city in the world for several decades. Today, it is a common name for the half of Mosul that lies on the eastern bank of the Tigris, and the country's Nineveh Governorate takes its name from it. It was the largest city in the world for approximately fifty years until the year 612 BC when, after a bitter period of civil war in Assyria, it was sacked by a coalition of its former subject peoples including the Babylonians, Medes, Persians, Scythians and Cimmerians. The city was never again a political or administrative centre, but by Late Antiquity it was the seat of a Christian bishop. It declined relative to Mosul during the Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
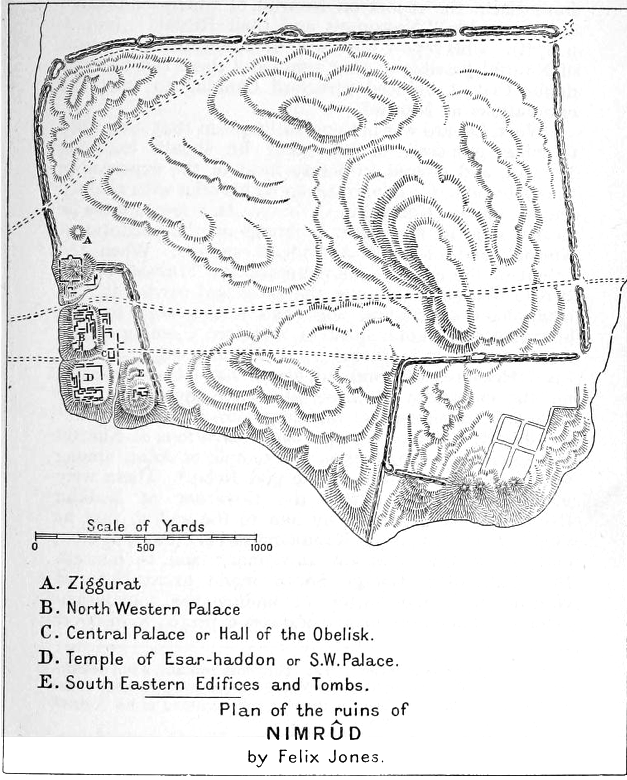
Nimrud
Nimrud (; syr, ܢܢܡܪܕ ar, النمرود) is an ancient Assyrian city located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah ( ar, السلامية), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a major Assyrian city between approximately 1350 BC and 610 BC. The city is located in a strategic position north of the point that the river Tigris meets its tributary the Great Zab.Brill's Encyclopedia of Islam 1913-36 p.923 The city covered an area of . The ruins of the city were found within of the modern-day village of |
2003 Invasion Of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq was a United States-led invasion of the Republic of Iraq and the first stage of the Iraq War. The invasion phase began on 19 March 2003 (air) and 20 March 2003 (ground) and lasted just over one month, including 26 days of major combat operations, in which a combined force of troops from the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, and Poland invaded Iraq. Twenty-two days after the first day of the invasion, the capital city of Baghdad was captured by Coalition forces on 9 April 2003 after the six-day-long Battle of Baghdad. This early stage of the war formally ended on 1 May 2003 when U.S. President George W. Bush declared the "end of major combat operations" in his Mission Accomplished speech, after which the Coalition Provisional Authority (CPA) was established as the first of several successive transitional governments leading up to the first Iraqi parliamentary election in January 2005. U.S. military forces later remained in Iraq unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain " cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of great natural beauty. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |