|
Asset Location
Asset location (AL) is a term used in personal finance to refer to how investors distribute their investments across savings vehicles including taxable accounts, tax-exempt accounts (e.g., TFSA, Roth IRA, ISAs, TESSAs), tax-deferred accounts (e.g., Canadian RRSP, American 401(k) and IRAs, British SIPPs, Irish Personal Retirement Savings Accounts (RPSA), and German Riester pensions), trust accounts (e.g., grantor retainer annuity trusts, generation-skipping trusts, charitable remainder trusts, charitable lead trusts), variable life insurance policies, foundations, and onshore vs. offshore accounts. While asset allocation (AA) determines what assets to own and in what proportions, AL determines where those assets are held. While the objective of AA is to create portfolios with the greatest return for a level of risk, and to optimize individuals' risk exposure according to their risk tolerance, goals and investment time frame, the objective of AL is to maximize the benefits of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Finance
Personal finance is the financial management which an individual or a family unit performs to budget, save, and spend monetary resources over time, taking into account various financial risks and future life events. When planning personal finances, the individual would consider the suitability to his or her needs of a range of banking products ( checking, savings accounts, credit cards and consumer loans) or investment in private equity, ( companies' shares, bonds, mutual funds) and insurance (life insurance, health insurance, disability insurance) products or participation and monitoring of and- or employer-sponsored retirement plans, social security benefits, and income tax management. History Before a specialty in personal finance was developed, various disciplines which are closely related to it, such as family economics, and consumer economics were taught in various colleges as part of home economics for over 100 years. The earliest known research in personal financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is the implementation of an investment strategy that attempts to balance risk versus reward by adjusting the percentage of each asset in an investment portfolio according to the investor's risk tolerance, goals and investment time frame. The focus is on the characteristics of the overall portfolio. Such a strategy contrasts with an approach that focuses on individual assets. Description Many financial experts argue that asset allocation is an important factor in determining returns for an investment portfolio. Asset allocation is based on the principle that different assets perform differently in different market and economic conditions. A fundamental justification for asset allocation is the notion that different asset classes offer returns that are not perfectly correlated, hence diversification reduces the overall risk in terms of the variability of returns for a given level of expected return. Asset diversification has been described as "the only free lunch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income Tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Taxation rates may vary by type or characteristics of the taxpayer and the type of income. The tax rate may increase as taxable income increases (referred to as graduated or progressive tax rates). The tax imposed on companies is usually known as corporate tax and is commonly levied at a flat rate. Individual income is often taxed at progressive rates where the tax rate applied to each additional unit of income increases (e.g., the first $10,000 of income taxed at 0%, the next $10,000 taxed at 1%, etc.). Most jurisdictions exempt local charitable organizations from tax. Income from investments may be taxed at different (generally lower) rates than other types of income. Credits of various sorts may be allowed that reduce tax. Some jurisdicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is the implementation of an investment strategy that attempts to balance risk versus reward by adjusting the percentage of each asset in an investment portfolio according to the investor's risk tolerance, goals and investment time frame. The focus is on the characteristics of the overall portfolio. Such a strategy contrasts with an approach that focuses on individual assets. Description Many financial experts argue that asset allocation is an important factor in determining returns for an investment portfolio. Asset allocation is based on the principle that different assets perform differently in different market and economic conditions. A fundamental justification for asset allocation is the notion that different asset classes offer returns that are not perfectly correlated, hence diversification reduces the overall risk in terms of the variability of returns for a given level of expected return. Asset diversification has been described as "the only free lunch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Portfolio Theory
Modern portfolio theory (MPT), or mean-variance analysis, is a mathematical framework for assembling a portfolio of assets such that the expected return is maximized for a given level of risk. It is a formalization and extension of diversification in investing, the idea that owning different kinds of financial assets is less risky than owning only one type. Its key insight is that an asset's risk and return should not be assessed by itself, but by how it contributes to a portfolio's overall risk and return. It uses the variance of asset prices as a proxy for risk. Economist Harry Markowitz introduced MPT in a 1952 essay, for which he was later awarded a Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences; see Markowitz model. Mathematical model Risk and expected return MPT assumes that investors are risk averse, meaning that given two portfolios that offer the same expected return, investors will prefer the less risky one. Thus, an investor will take on increased risk only if compensat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Trust
A unit trust is a form of collective investment constituted under a trust deed. A unit trust pools investors' money into a single fund, which is managed by a fund manager. Unit trusts offer access to a wide range of investments, and depending on the trust, it may invest in securities such as shares, bonds, gilts, and also properties, mortgage and cash equivalents. Those investing in the trust own "units" whose price is called the "net asset value" (NAV). The number of these units is not fixed and when more is invested in a unit trust (by investors opening accounts or adding to their accounts), more units are created. In addition to the UK, trusts are found in Fiji, Ireland, the Isle of Man, Guernsey, Jersey, New Zealand, Australia, Kenya, Uganda, Namibia, South Africa, Singapore, Malaysia and Zimbabwe. History The first unit trust was launched in the UK in 1931 by M&G under the inspiration of Ian Fairbairn. The rationale behind the launch was to emulate the comparative robu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Fund
A mutual fund is a professionally managed investment fund that pools money from many investors to purchase securities. The term is typically used in the United States, Canada, and India, while similar structures across the globe include the SICAV in Europe ('investment company with variable capital') and open-ended investment company (OEIC) in the UK. Mutual funds are often classified by their principal investments: money market funds, bond or fixed income funds, stock or equity funds, or hybrid funds. Funds may also be categorized as index funds, which are passively managed funds that track the performance of an index, such as a stock market index or bond market index, or actively managed funds, which seek to outperform stock market indices but generally charge higher fees. Primary structures of mutual funds are open-end funds, closed-end funds, unit investment trusts. Open-end funds are purchased from or sold to the issuer at the net asset value of each share as of the close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Estate Investment Trust
A real estate investment trust (REIT) is a company that owns, and in most cases operates, income-producing real estate. REITs own many types of commercial real estate, including office and apartment buildings, warehouses, hospitals, shopping centers, hotels and commercial forests. Some REITs engage in financing real estate. Most countries' laws on REITs entitle a real estate company to pay less in corporation tax and capital gains tax. REITs have been criticised as enabling speculation on housing, and reducing housing affordability, without increasing finance for building. REITs can be publicly traded on major exchanges, publicly registered but non-listed, or private. The two main types of REITs are equity REITs and mortgage REITs (mREITs). In November 2014, equity REITs were recognized as a distinct asset class in the Global Industry Classification Standard by S&P Dow Jones Indices and MSCI. The key statistics to examine the financial position and operation of a REIT include n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
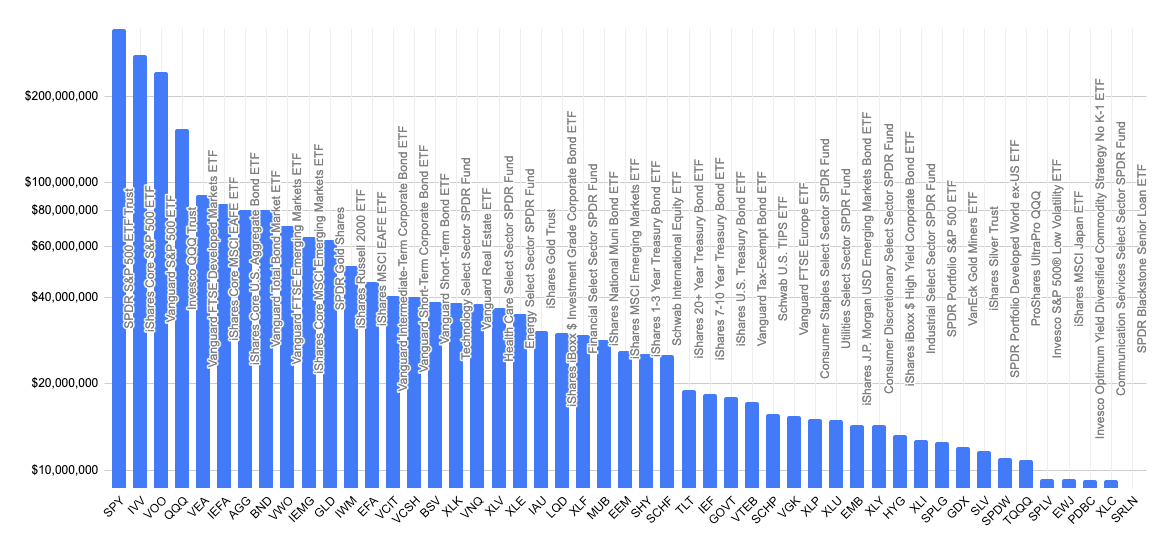
Exchange-traded Fund
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund and exchange-traded product, i.e. they are traded on stock exchanges. ETFs are similar in many ways to mutual funds, except that ETFs are bought and sold from other owners throughout the day on stock exchanges whereas mutual funds are bought and sold from the issuer based on their price at day's end. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, futures contracts, and/or commodities such as gold bars, and generally operates with an arbitrage mechanism designed to keep it trading close to its net asset value, although deviations can occasionally occur. Most ETFs are index funds: that is, they hold the same securities in the same proportions as a certain stock market index or bond market index. The most popular ETFs in the U.S. replicate the S&P 500, the total market index, the NASDAQ-100 index, the price of gold, the "growth" stocks in the Russell 1000 Index, or the index of the largest technology companies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Savings And Investments
National Savings and Investments (NS&I), formerly called the Post Office Savings Bank and National Savings, is a state-owned savings bank in the United Kingdom. It is both a non-ministerial government department and an executive agency of HM Treasury. The aim of NS&I has been to attract funds from individual savers in the UK for the purpose of funding the government's deficit. NS&I attracts savers through offering savings products with tax-free elements on some products, and a 100% guarantee from HM Treasury on all deposits. As of 2017, approximately 9% of the government's debt is met by funds raised through NS&I, around half of which is from the Premium Bond offering. History National Savings and Investments was founded by the Palmerston government in 1861 as the Post Office Savings Bank, the world's first postal savings system. The aim of the bank was to allow ordinary workers a facility "to provide for themselves against adversity and ill-health", and to provide the government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipal Bond
A municipal bond, commonly known as a muni, is a Bond (finance), bond issued by state or local governments, or entities they create such as authorities and special districts. In the United States, interest income received by holders of municipal bonds is often, but not always, exempt from federal and state income taxation. Typically, only investors in the highest tax brackets benefit from buying tax-exempt municipal bonds instead of taxable bonds. Taxable equivalent yield calculations are required to make fair comparisons between the two categories. The U.S. municipal debt market is relatively small compared to the corporate market. Total municipal debt outstanding was $4 trillion as of the first quarter of 2021, compared to nearly $15 trillion in the corporate and foreign markets. Local authorities in many #In other countries, other countries in the world issue similar bonds, sometimes called local authority bonds or other names. History Municipal debt predates corporate debt b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CFA Institute
The CFA Institute is a global, not-for-profit professional organization that provides investment professionals with finance education. The institute aims to promote standards in ethics, education, and professional excellence in the global investment services industry. Since 1945, the institute has published the peer-reviewed, quarterly journal, the ''Financial Analysts Journal''. It also publishes the ''CFA Digest'' and the ''CFA Magazine''. Structure The organization offers the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation, the Certificate in Investment Performance Measurement (CIPM), the Certificate in ESG Investing, and until December 2021, the Investment Foundations Certificate. It provides continuing education conferences, seminars, webcasts, and publications to allow members and other participants to stay current on developments in the investment industry. CFA Institute also oversees the CFA Institute Research Challenge for university students and the Research Foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |