|
Aspy Fault
The Aspy Fault () is a strike-slip fault that runs through 40 km of Cape Breton, Nova Scotia and is often thought to be a part of the Cabot Fault/ Great Glen Fault system of Avalonia. Part of the fault runs through Cape Breton Highlands National Park. This fault runs southward from Cape North through the Margaree Valley. The Aspy River and the upper section of the Margaree River follows the trace of the fault. Evidence shows movement in this fault dating back to the Ordovician period when it was probably created when two continental plates collided and pushed the seafloor upwards, also creating the Appalachian Mountains. Erosion and the presence of this fault have created much of the scenery known today as the Cape Breton Highlands The Cape Breton Highlands (french: Plateau du Cap-Breton, gd, Àrd-thalamh Cheap Bhreatainn), commonly called the Highlands, refer to a highland or mountainous plateau across the northern part of Cape Breton Island in the Canadian province of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspy Fault
The Aspy Fault () is a strike-slip fault that runs through 40 km of Cape Breton, Nova Scotia and is often thought to be a part of the Cabot Fault/ Great Glen Fault system of Avalonia. Part of the fault runs through Cape Breton Highlands National Park. This fault runs southward from Cape North through the Margaree Valley. The Aspy River and the upper section of the Margaree River follows the trace of the fault. Evidence shows movement in this fault dating back to the Ordovician period when it was probably created when two continental plates collided and pushed the seafloor upwards, also creating the Appalachian Mountains. Erosion and the presence of this fault have created much of the scenery known today as the Cape Breton Highlands The Cape Breton Highlands (french: Plateau du Cap-Breton, gd, Àrd-thalamh Cheap Bhreatainn), commonly called the Highlands, refer to a highland or mountainous plateau across the northern part of Cape Breton Island in the Canadian province of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Breton Highlands National Park
Cape Breton Highlands National Park is a Canadian national park on northern Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia. The park was the first national park in the Atlantic provinces of Canada and covers an area of . It is one of 42 in Canada's system of national parks. It consists of mountains, valleys, waterfalls, rocky coastlines and the Cape Breton Highlands, a tundra-esque plateau. Forest types include Acadian and Boreal. The park includes the highest point in Nova Scotia, White Hill, at above sea level. Rivers in the park include the Chéticamp River and the North Aspy River. In 2014, Parks Canada started a four-year project with the Unama'ki Institute of Natural Resources, among other partners, to begin regional boreal forest restorations within this park. Recreation One-third of the Cabot Trail passing through the park features ocean and mountain views. The park is known for its "steep cliffs and deep river canyons that carve into a forested plateau bordering the Atlantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Of Nova Scotia
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant " birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word '' physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Breton Highlands
The Cape Breton Highlands (french: Plateau du Cap-Breton, gd, Àrd-thalamh Cheap Bhreatainn), commonly called the Highlands, refer to a highland or mountainous plateau across the northern part of Cape Breton Island in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. Considered an extension of the Appalachian mountain chain, the Highlands comprise the northern portions of Inverness and Victoria counties. The Highlands are surrounded by water with the Atlantic Ocean on the east, the Cabot Strait to the north and east, the Gulf of St. Lawrence on the north and west, and Bras d'Or Lake to the south. Elevations average 350 metres at the edges of the plateau (i.e. at the above-mentioned water bodies), and rise to more than 500 metres at the centre, including the highest elevation point in the province at White Hill, at 533 metres. The plateau consists of numerous broad, gently rolling hills bisected with deep valleys and steep-walled river canyons. The southern and western edges of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west. Definitions vary on the precise boundaries of the Appalachians. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines the ''Appalachian Highlands'' physiographic division as consisting of 13 provinces: the Atlantic Coast Uplands, Eastern Newfoundland Atlantic, Maritime Acadian Highlands, Maritime Plain, Notre Dame and Mégantic Mountains, Western Newfoundland Mountains, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, St. Lawrence Valley, Appalac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician Period
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambrian P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaree River
The Margaree River (''Abhainn Mhargaraidh'') is a river on Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia. The northeast branch of the river derives from the watershed of the Cape Breton Highlands, while the Southwest Margaree flows northeast from Lake Ainslie. The two branches join at Margaree Forks. The river then flows north to empty into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence at Margaree Harbour, Nova Scotia. The river is 120 km in length and drains an area of 1,375 km². The Margaree has been well known for a century for its trout and Atlantic salmon sport fishery, that draws anglers from near and far. Fishing is highly regulated now and is restricted to fly fishing only, with barbless hooks, in the main stem of the river. Famed American angler and Atlantic salmon conservationist Lee Wulff caught his first salmon on a fly on the Margaree in 1933. The gravel bars of the upper Northeast Margaree provide spawning grounds for Atlantic salmon; its steep valleys provide habitat for American ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspy River
The Aspy River () is a river on northeastern Cape Breton Island which rises in the Cape Breton Highlands and empties into Aspy Bay. The North Aspy follows the ancient Aspy Fault which extends for 40 km inland from the coast and extends along the upper section of the northeast Margaree River. This geological fault is thought to be a part of the Cabot Fault (Newfoundland)/ Great Glen Fault (Scotland) system of Avalonia. It is believed by some sources that John Cabot landed at Aspy Bay in 1497. In 1856, a submarine cable was laid across the Cabot Strait from Aspy Bay to Newfoundland establishing a telegraph link between St. John's, Newfoundland and New York City. A dirt road in Cape Breton Highlands National Park leads to the Beulach Ban falls on the North Aspy River. "Beulach Ban" is Gaelic for "white gorge". See also * List of rivers of Nova Scotia Nova Scotia's rivers all flow into the Atlantic Ocean through four unique watersheds: the Gulf of Maine, the Northumberland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
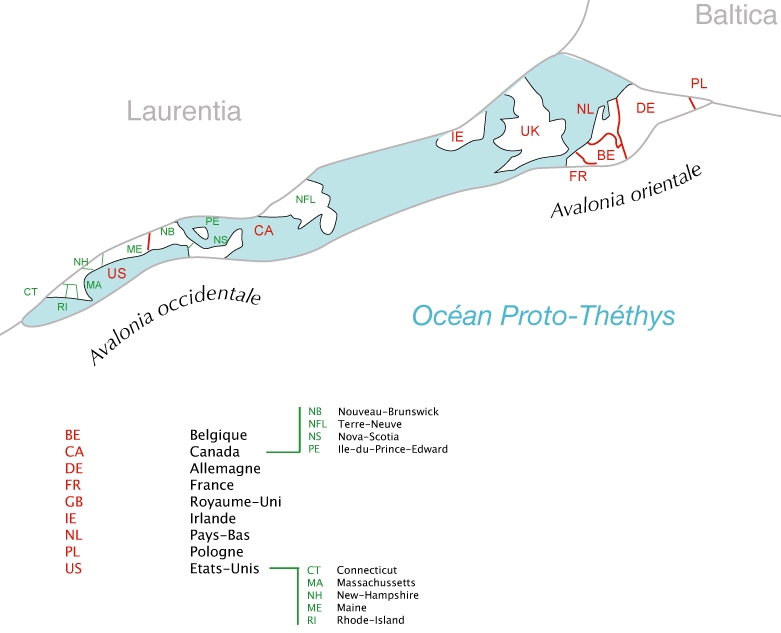
Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent underlie south-west Great Britain, southern Ireland, and the eastern coast of North America. It is the source of many of the older rocks of Western Europe, Atlantic Canada, and parts of the coastal United States. Avalonia is named for the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland. Avalonia developed as a volcanic arc on the northern margin of Gondwana. It eventually rifted off, becoming a drifting microcontinent. The Rheic Ocean formed behind it, and the Iapetus Ocean shrank in front. It collided with the continents Baltica, then Laurentia, and finally with Gondwana, ending up in the interior of Pangea. When Pangea broke up, Avalonia's remains were divided by the rift which became the Atlantic Ocean. Extent When the term "Avalon" was first coined by Canadian geologist Harold Williams in 1964, he included only Precambrian rocks in eastern Newfoundland. More than a decade later he ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AVALONIA
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent underlie south-west Great Britain, southern Ireland, and the eastern coast of North America. It is the source of many of the older rocks of Western Europe, Atlantic Canada, and parts of the coastal United States. Avalonia is named for the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland. Avalonia developed as a volcanic arc on the northern margin of Gondwana. It eventually rifted off, becoming a drifting microcontinent. The Rheic Ocean formed behind it, and the Iapetus Ocean shrank in front. It collided with the continents Baltica, then Laurentia, and finally with Gondwana, ending up in the interior of Pangea. When Pangea broke up, Avalonia's remains were divided by the rift which became the Atlantic Ocean. Extent When the term "Avalon" was first coined by Canadian geologist Harold Williams in 1964, he included only Precambrian rocks in eastern Newfoundland. More than a decade later he ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Glen Fault
The Great Glen Fault is a strike-slip fault that runs through the Great Glen in Scotland. The fault is mostly inactive today, but occasional moderate tremors have been recorded over the past 150 years. Location Aligned northeast to southwest, the Great Glen Fault extends further southwest in a straight line through Loch Linnhe and the Firth of Lorne, and then on into northwestern Ireland, directly through Lough Swilly, Donegal Bay and Clew Bay as the Leannan Fault. To the northeast the fault connects to the Walls Boundary Fault and the associated Melby Fault and Nestings Fault, before becoming obscured by the effects of Mesozoic rifting to the north of Shetland. The fault continues on the North American side of the North Atlantic Ocean, but is no longer part of a contiguous fault, as the complete fault was broken when the Mid-Atlantic Ridge formed 200 million years ago. The North American side of the fault runs through the length of northwestern Newfoundland, Canada, as the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabot Fault
Cabot may refer to: Businesses * Cabot Corporation, an American chemicals company * Cabot Creamery, an American dairy cooperative Fictional characters * Alexandra Cabot, in the ''Law & Order'' universe * Leigh Cabot, from Stephen King's 1983 novel ''Christine'' * Rosanna Cabot, in the soap opera ''As the World Turns'' * Tarl Cabot, protagonist of ''Gor'' novels * William Cabot, in the film '' The Sum of All Fears'' * Ephraim Cabot, in the play '' Desire Under the Elms'' by Eugene O'Neill People * Cabot family, of the Boston Brahmins, or "first families of Boston" * Bruce Cabot (1904–1972), American actor * Dolce Ann Cabot (1862–1943), New Zealand journalist, newspaper editor, feminist and teacher * John Cabot (c. 1450 – c. 1499), Italian navigator and explorer, father of Sebastian Cabot * Godfrey Lowell Cabot (1861-1962), American industrialist who founded the Cabot Corporation * George Cabot (1752–1823), American merchant, seaman, and politician * John Moors Cabo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


