|
Aspidochelone
According to the tradition of the ''Physiologus'' and medieval bestiaries, the aspidochelone is a fabled sea creature, variously described as a large whale or vast sea turtle, and a giant sea monster with huge spines on the ridge of its back. No matter what form it is, it is always described as being so huge that it is often mistaken for an island and appears to be rocky with crevices and valleys with trees and greenery and having sand dunes all over it. The name ''aspidochelone'' appears to be a compound word combining Greek '' aspis'' (which means either " asp" or " shield"), and ''chelone'', the turtle. It rises to the surface from the depths of the sea, and entices unwitting sailors with its island appearance to make landfall on its huge shell and then the whale is able to pull them under the ocean, ship and all the people, drowning them. It also emits a sweet smell that lures fish into its trap where it then devours them. In the moralistic allegory of the ''Physiologus'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiologus
The ''Physiologus'' () is a didactic Christian text written or compiled in Greek by an unknown author, in Alexandria; its composition has been traditionally dated to the 2nd century AD by readers who saw parallels with writings of Clement of Alexandria, who is asserted to have known the text, though Alan Scott has made a case for a date at the end of the 3rd or in the 4th century. The ''Physiologus'' consists of descriptions of animals, birds, and fantastic creatures, sometimes stones and plants, provided with moral content. Each animal is described, and an anecdote follows, from which the moral and symbolic qualities of the animal are derived. Manuscripts are often, but not always, given illustrations, often lavish. The book was translated into Armenian in 5th century, into Latin by the early 6th century or possibly even by the mid-4th century and into Ethiopic and Syriac, then into many European and Middle-Eastern languages, and many illuminated manuscript copies such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
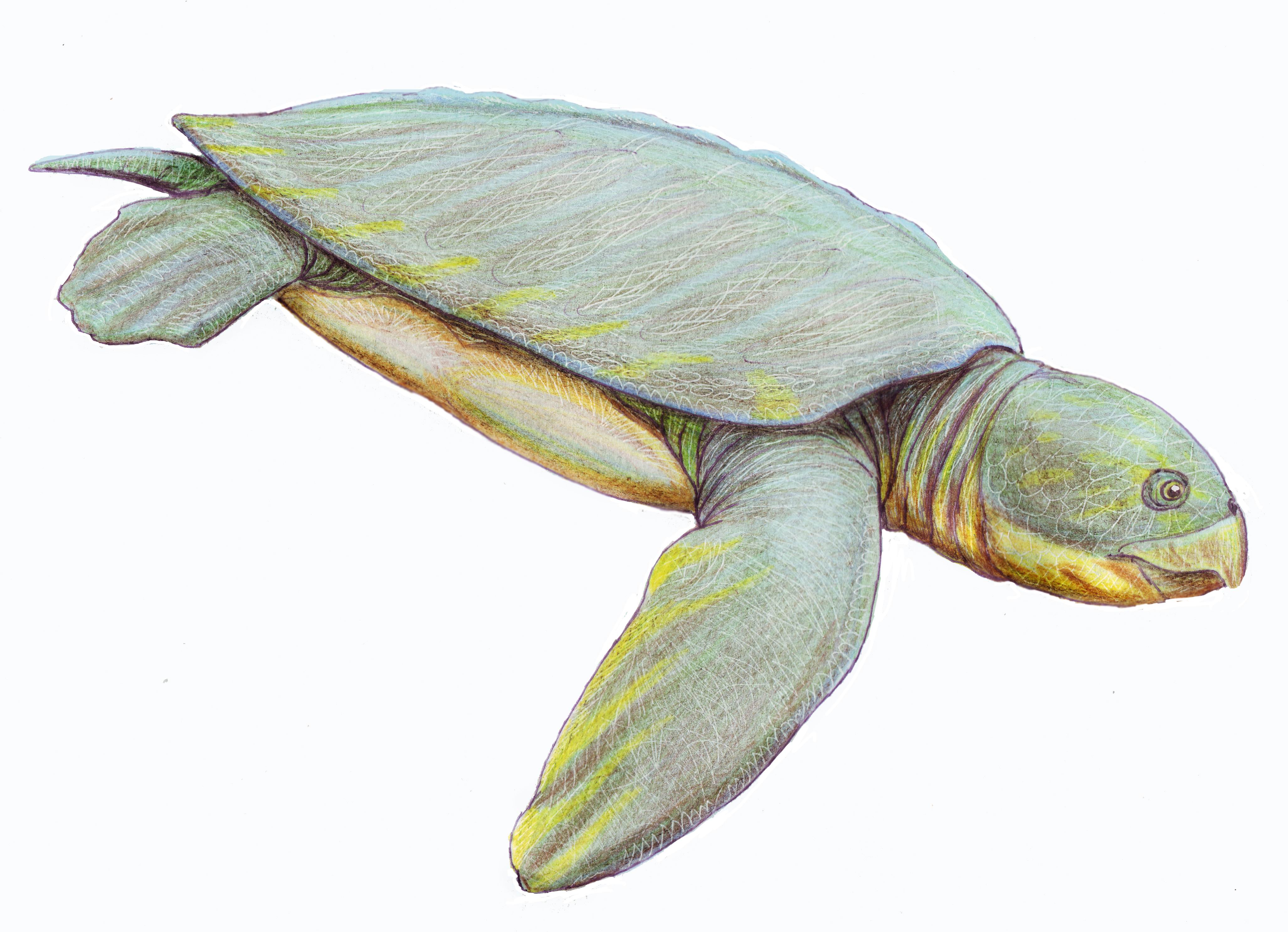
Sea Turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley sea turtles. All six of the sea turtle species present in US waters (all of those listed above except the flatback) are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. The seventh sea turtle species is the flatback, which exists in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. Sea turtles can be separated into the categories of hard-shelled (cheloniid) and leathery-shelled ( dermochelyid).Wyneken, J. 2001. The Anatomy of Sea Turtles. U.S Department of Commerce NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-470, 1-172 pp. There is only one dermochelyid species which is the leatherback sea turtle. Description For each of the seven types of sea turtles, females and males are the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Monster
Sea monsters are beings from folklore believed to dwell in the sea and often imagined to be of immense size. Marine monsters can take many forms, including sea dragons, sea serpents, or tentacled beasts. They can be slimy and scaly and are often pictured threatening ships or spouting jets of water. The definition of a "monster" is subjective; further, some sea monsters may have been based on scientifically accepted creatures, such as whales and types of giant and colossal squid. Sightings and legends Sea monster accounts are found in virtually all cultures that have contact with the sea. For example, Avienius relates of Carthaginian explorer Himilco's voyage "...there monsters of the deep, and beasts swim amid the slow and sluggishly crawling ships." (lines 117–29 of ''Ora Maritima''). Sir Humphrey Gilbert claimed to have encountered a lion-like monster with "glaring eyes" on his return voyage after formally claiming St. John's, Newfoundland (1583) for England. Another ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbah Bar Bar Hana
Rabbah bar bar Hana (רבה בר בר חנה) was a Jewish Talmudist who lived in Babylonia, known as an Amora of the second generation. Biography He was the grandson of Hana and the brother of Hiyya. He went to Palestine and became a pupil of Rabbi Yochanan, whose sayings he transmitted. He does not seem to have enjoyed high regard in Palestine, for it was taken as a matter of course that Rav Shimon ben Lakish should not do him the honor of addressing him in public. After a somewhat prolonged sojourn in Palestine he returned to Babylonia, residing both at Pumbedita and at Sura. In Pumbedita he at first refused to attend the lectures of Rav Judah ben Ezekiel, but he soon became his friend, and was consulted by him in difficult cases. Judah and his pupil Rabbah bar Nahmani once visited Rabbah, who was ill, and submitted a halakhic question to him. While they were there a Zoroastrian priest ("geber") suddenly appeared and extinguished the lamp, the day being a festival of Ormuzd, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Romance, Armenian Manuscript, 1538–1544
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander and Aleksandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexandre, Aleks, Aleksa and Sander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria, and Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). It is an example of the widespread motif of Greek names expressing "battle-prowess", in this case the ability to withstand or push back an enemy battle line. The earliest attested form of the name, is the Mycenaean Greek feminine anthroponym , , (/Alexandra/), written in the Linear B syllabic script. Alaksandu, alternatively called ''Alakasandu'' or ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epistola Alexandri Ad Aristotelem
The ''Epistola Alexandri ad Aristotelem'' ("Letter of Alexander to Aristotle") is a purported letter from Alexander the Great to the philosopher Aristotle concerning his adventures in India. Although accepted for centuries as genuine, it is today regarded as apocryphal. It is the primary source for most of the tales of the marvellous and fabulous found in later Alexander traditions. Textual history The ''Epistola'' was composed in Greek. The original version may have adhered more closely to historical fact than later versions. An abridged version, including much fabulous material, was incorporated into the '' Alexander Romance'' no later than the third century AD. In the Greek alpha recension of the ''Romance'', the letter is chapter 17 of book III. The ''Epistola'' was widely translated and circulated both with the various versions of the ''Romance'' and independently of it. In some later Greek recensions of the ''Romance'', the letter is switched from the first person to the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Of Naples
Leo of Naples ( fl. 950s), also called Leo the Archpriest ( it, Leone Arciprete), was a diplomat and translator in the service of Dukes John III and Marinus II of Naples. He undertook a diplomatic mission to Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, during the joint reign of Constantine VII and Romanus II between 945 and 959. During his time in the capital, he came across the '' Alexander Romance'', a collection of Greek stories about Alexander the Great, and had a copy made for Theodora, the wife of John III. After Theodora's death, John commissioned Leo to translate the ''Romance'' into Latin. The date of Theodora's death is unknown, but she was still living in 951. John died in 968 or 969. All that is known of Leo comes from the prologue he wrote to this translation, in which he calls himself an ''archipresbyter''. Leo entitled his work ''Nativitas et victoria Alexandri magni'' (Birth and Victory of Alexander the Great). The autograph does not survive and all survivin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonian Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The term ''Talmud'' normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (). It may also traditionally be called (), a Hebrew abbreviation of , or the "six orders" of the Mishnah. The Talmud has two components: the Mishnah (, 200 CE), a written compendium of the Oral Torah; and the Gemara (, 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may refer to eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two Fishermen On An Aspidochelone, C
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultures. Evolution Arabic digit The digit used in the modern Western world to represent the number 2 traces its roots back to the Indic Brahmic script, where "2" was written as two horizontal lines. The modern Chinese and Japanese languages (and Korean Hanja) still use this method. The Gupta script rotated the two lines 45 degrees, making them diagonal. The top line was sometimes also shortened and had its bottom end curve towards the center of the bottom line. In the Nagari script, the top line was written more like a curve connecting to the bottom line. In the Arabic Ghubar writing, the bottom line was completely vertical, and the digit looked like a dotless closing question mark. Restoring the bottom line to its original horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Ibn Naghrillah
Samuel ibn Naghrillah (, ''Sh'muel HaLevi ben Yosef HaNagid''; ''ʾAbū ʾIsḥāq ʾIsmāʿīl bin an-Naghrīlah''), also known as Samuel HaNagid (, ''Shmuel HaNagid'', lit. ''Samuel the Prince'') and Isma’il ibn Naghrilla (born 993; died 1056), was a medieval Jewish Spanish Talmudic scholar, grammarian, philologist, soldier, merchant, politician, and an influential poet who lived in Iberia at the time of the Moorish rule. His poetry was one area through which he was well known. Marcus, Jacob Rader. "59: Samuel Ha-Nagid, Vizier of Granada." ''The Jew in the Medieval World: A Source Book, 315-1791.'' Cincinnati: Union of American Hebrew Congregations, 1938. 335-38. He was perhaps the most politically influential Jew in Muslim Spain. Stillman, Norman A. ''The Jews of Arab Lands: A History and Source Book'', The Jewish Publication Society of America,1979. 56 He was also the Prime Minister of the Muslim state of Granada and battlefield commander of the non-Jewish Granadan army. Lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commentary On The Hexameron
The ''Commentary on the Hexameron'' of Pseudo-Eustathius is an anonymous commentary on the ''Genesis'' creation narrative written in Greek between 375 and 500 AD. More than 26 medieval manuscripts exist containing it, all of which give Eustathius of Antioch as the author. The work contains rather more material than a typical commentary on creation, including historical material down to the time of Alexander the Great, all excerpted from earlier Christian writers. Consequently, it has been given the Latin title ''Liber chronicorum'' ('book of chronicles'). The ''Commentary'' includes extracts from the lost writings of Alexander Polyhistor, and the author appears to have had direct access to copies of Polyhistor. It is also a useful early witness to the ''Physiologus''. That it could not have been written by Eustathius of Antioch, who was deposed in 330, is clear from the material it draws from the ''Homilies on the Hexameron'' of Basil the Great, delivered around 370. In addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |