|
Arzamas 16
Sarov (russian: Саро́в) is a closed town in Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It was known as Gorkiy-130 (Горький-130) and Arzamas-16 (), after a (somewhat) nearby town of Arzamas,SarovLabsCreation of Nuclear Center Arzamas-16/ref> from 1946 to 1991. Until 1995, it was known as Kremlyov/Kremlev/Kremljov (). The town is closed as it is the Russian center for nuclear research. Population: 92,047 ( 2010 Census); 87,652 ( 2002 Census) History The history of the town can be divided into two different periods. In the earlier history of Russia it was known as one of the holy places of the Russian Orthodox Church, because of its monastery, that gave Russia one of its greatest saints, St. Seraphim. Since the 1940s, it has gradually become the center for research and production of Soviet and later Russian nuclear weapons. The history of human settlement in the area around Sarov goes back at least to the 12th–13th centuries, when a large Mordvin settlement was foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
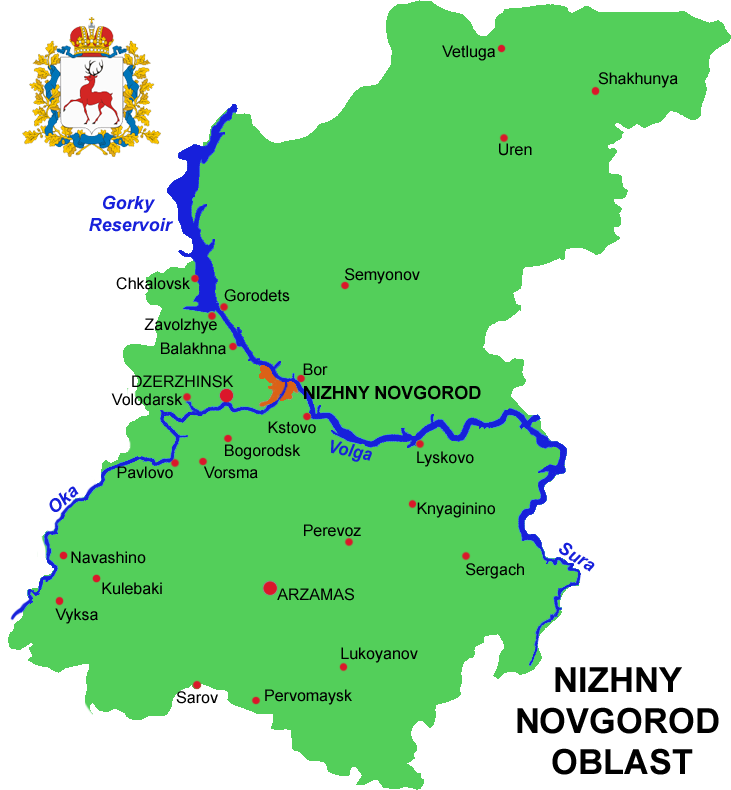
Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Nizhny Novgorod Oblast (russian: link=no, Нижегородская область, ''Nizhegorodskaya oblast''), is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Nizhny Novgorod. It has a population of 3,310,597 as of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census. From 1932 to 1990 it was known as Gorky Oblast. The oblast is crossed by the Volga River. Apart from Nizhny Novgorod's metropolitan area (including Dzerzhinsk, Russia, Dzerzhinsk, Bor, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Bor and Kstovo) the biggest city is Arzamas. Near the town of Sarov there is the Serafimo-Diveyevsky Monastery, one of the largest convents in Russia, established by Seraphim of Sarov, Saint Seraphim of Sarov. The Makaryev Monastery opposite of the town of Lyskovo, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Lyskovo used to be the location of the largest fair in Eastern Europe. Other historic towns include Gorodets, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
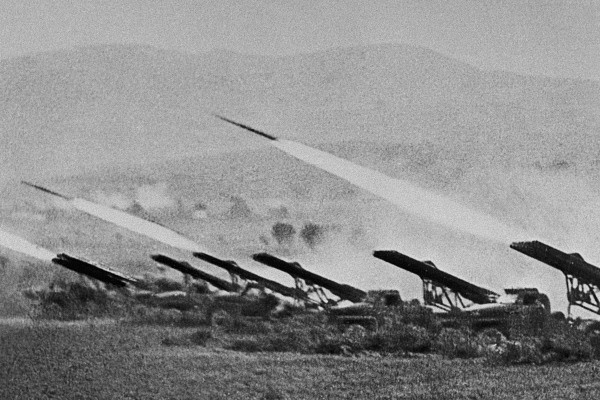
Katyusha Rocket Launcher
The Katyusha ( rus, Катю́ша, p=kɐˈtʲuʂə, a=Ru-Катюша.ogg) is a type of rocket artillery first built and fielded by the Soviet Union in World War II. Multiple rocket launchers such as these deliver explosives to a target area more intensively than conventional artillery, but with lower accuracy and requiring a longer time to reload. They are fragile compared to artillery guns, but are cheap, easy to produce, and usable on almost any chassis. The Katyushas of World War II, the first self-propelled artillery mass-produced by the Soviet Union,Zaloga, p 150. were usually mounted on ordinary trucks. This mobility gave the Katyusha, and other self-propelled artillery, another advantage: being able to deliver a large blow all at once, and then move before being located and attacked with counter-battery fire. Katyusha weapons of World War II included the BM-13 launcher, light BM-8, and heavy BM-31. Today, the nickname ''Katyusha'' is also applied to newer truck-mounte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Safeguards
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Safeguards are a system of inspection and verification of the peaceful uses of nuclear materials as part of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), supervised by the International Atomic Energy Agency. Department of Safeguards Safeguards activities are undertaken and by the Department of Safeguards, a separate department within the International Atomic Energy Agency. The Department is headed by Deputy Director General and Head of the Department of Safeguards Massimo Aparo. The mission statement of the Department of Safeguards is: "The primary role of the Department is to administer and implement IAEA safeguards. It also contributes to nuclear arms control and disarmament, by responding to requests for verification and technical assistance associated with related agreements and arrangements." The Department is organized into operations divisions, which include the inspectors that conduct safeguards inspections in the IAEA's member st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arms Control
Arms control is a term for international restrictions upon the development, production, stockpiling, proliferation and usage of small arms, conventional weapons, and weapons of mass destruction. Arms control is typically exercised through the use of diplomacy which seeks to impose such limitations upon consenting participants through international treaties and agreements, although it may also comprise efforts by a nation or group of nations to enforce limitations upon a non-consenting country. Enactment Arms control treaties and agreements are often seen as a way to avoid costly arms races which could prove counter-productive to national aims and future peace. Some are used as ways to stop the spread of certain military technologies (such as nuclear weaponry or missile technology) in return for assurances to potential developers that they will not be victims of those technologies. Additionally, some arms control agreements are entered to limit the damage done by warfare, es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, in the American southwest. Best known for its central role in helping develop the first atomic bomb, LANL is one of the world's largest and most advanced scientific institutions. Los Alamos was established in 1943 as Project Y, a top-secret site for designing nuclear weapons under the Manhattan Project during World War II.The site was variously called Los Alamos Laboratory and Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory. Chosen for its remote yet relatively accessible location, it served as the main hub for conducting and coordinating nuclear research, bringing together some of the world's most famous scientists, among them numerous Nobel Prize winners. The town of Los Alamos, directly north of the lab, grew extensively through this period. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Alamos, New Mexico
Los Alamos is an census-designated place in Los Alamos County, New Mexico, United States, that is recognized as the development and creation place of the atomic bomb—the primary objective of the Manhattan Project by Los Alamos National Laboratory during World War II. The town is located on four mesas of the Pajarito Plateau, and had a population of about 13,200 as of 2020. It is the county seat and one of two population centers in the county known as census-designated places (CDPs); the other is White Rock. History The ruins of permanent Puebloan settlements, such as those located in nearby Bandelier National Monument and Tsankawi, and numerous other sites such as cliff dwellings indicate that the area has been inhabited during various eras since around 1150 AD. The first settlers on the plateau are thought to be Keres speaking Native Americans around the 10th century. Around 1300, Tewa settlers immigrated from the Four Corners Region and built large cities but were driven o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister City
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties. While there are early examples of international links between municipalities akin to what are known as sister cities or twin towns today dating back to the 9th century, the modern concept was first established and adopted worldwide during World War II. Origins of the modern concept The modern concept of town twinning has its roots in the Second World War. More specifically, it was inspired by the bombing of Coventry on 14 November 1940, known as the Coventry Blitz. First conceived by the then Mayor of Coventry, Alfred Robert Grindlay, culminating in his renowned telegram to the people of Stalingrad (now Volgograd) in 1942, the idea emerged as a way of establishing solidarity links between cities in allied countries that went through similar devastating events. The comradesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Mordovia
The Republic of Mordovia (russian: Респу́блика Мордо́вия, r=Respublika Mordoviya, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə mɐrˈdovʲɪjə; mdf, Мордовия Республиксь, ''Mordovija Respublikś''; myv, Мордовия Республикась, ''Mordovija Respublikaś'') is a republic of Russia, located in Eastern Europe. Its capital is the city of Saransk. As of the 2010 Census, the population of the republic was 834,755. Ethnic Russians (53.1%) and Mordvins (39.8%) account for the majority of the population. History Early history The earliest archaeological signs of modern humans in the area of Mordovia are from the Neolithic era. Mordvins are mentioned in written sources from the 6th century. Later, Mordvins were under the influence of both Volga Bulgaria and the Kievan Rus. Mordvin princes sometimes raided Muroma and Volga Bulgaria and often despoiled each other's holdings. Mongol rule The Mongols conquered vast areas of Eastern Europe in the 13th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temnikovsky District
Temnikovsky District (russian: Те́мниковский райо́н; mdf, Темникавонь аймак, ''Temnikavoń ajmak''; myv, Чополтбуе, ''Čopoltbuje'') is an administrativeConstitution of the Republic of Mordovia, Article 63 and municipalLaw #124-Z district (raion), one of the twenty-two in the Republic of Mordovia, Russia. It is located in the northwest of the republic. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the town of Temnikov.Law #7-Z As of the 2010 Census, the total population of the district was 17,261, with the population of Temnikov accounting for 42.0% of that number. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative divisions, Temnikovsky District is one of the twenty-two in the republic. It is divided into one town of district significance ( Temnikov) and sixteen selsoviets, all of which comprise ninety-six rural localities. As a municipal division, the district is incorporated as Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət ), colloquially shortened to Nizhny, from the 13th to the 17th century Novgorod of the Lower Land, formerly known as Gorky (, ; 1932–1990), is the administrative centre of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast and the Volga Federal District. The city is located at the confluence of the Oka and the Volga rivers in Central Russia, with a population of over 1.2 million residents, up to roughly 1.7 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Nizhny Novgorod is the sixth-largest city in Russia, the second-most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. It is an important economic, transportation, scientific, educational and cultural center in Russia and the vast Volga-Vyatka economic region, and is the main center of river tourism in Russia. In the historic part of the city there are many universities, theaters, museums and churches. The city w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarov Airport
Sarov Airport (also called Mius Airfield; airport code XUDM/ЬУДМ) is an airport in Russia located in the town of Sarov, north of downtown, within the closed city area. It is a mixed use utilitarian airfield with an unusually wide runway for a small airfield of this type. The airport consists of Runway 01/19 (1920m, or 2500m including displaced thresholds) without taxiways, a small airport apron with an adjacent car park, and a small terminal/administration building located 200 meters away from the apron. Satellite imagery from Google Earth on 2018-04-15 show major runway work underway. An additional image from 2018-09-06 reveals the work is a completely resurfacing, with the prior overruns being included to bring the fully operational length to 2500 Meters. In addition, the image shows substantial work on the apron area, perhaps doubling the former surface area. This airport was used for experimental aircraft as well as for commercial and government flights to Moscow's By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
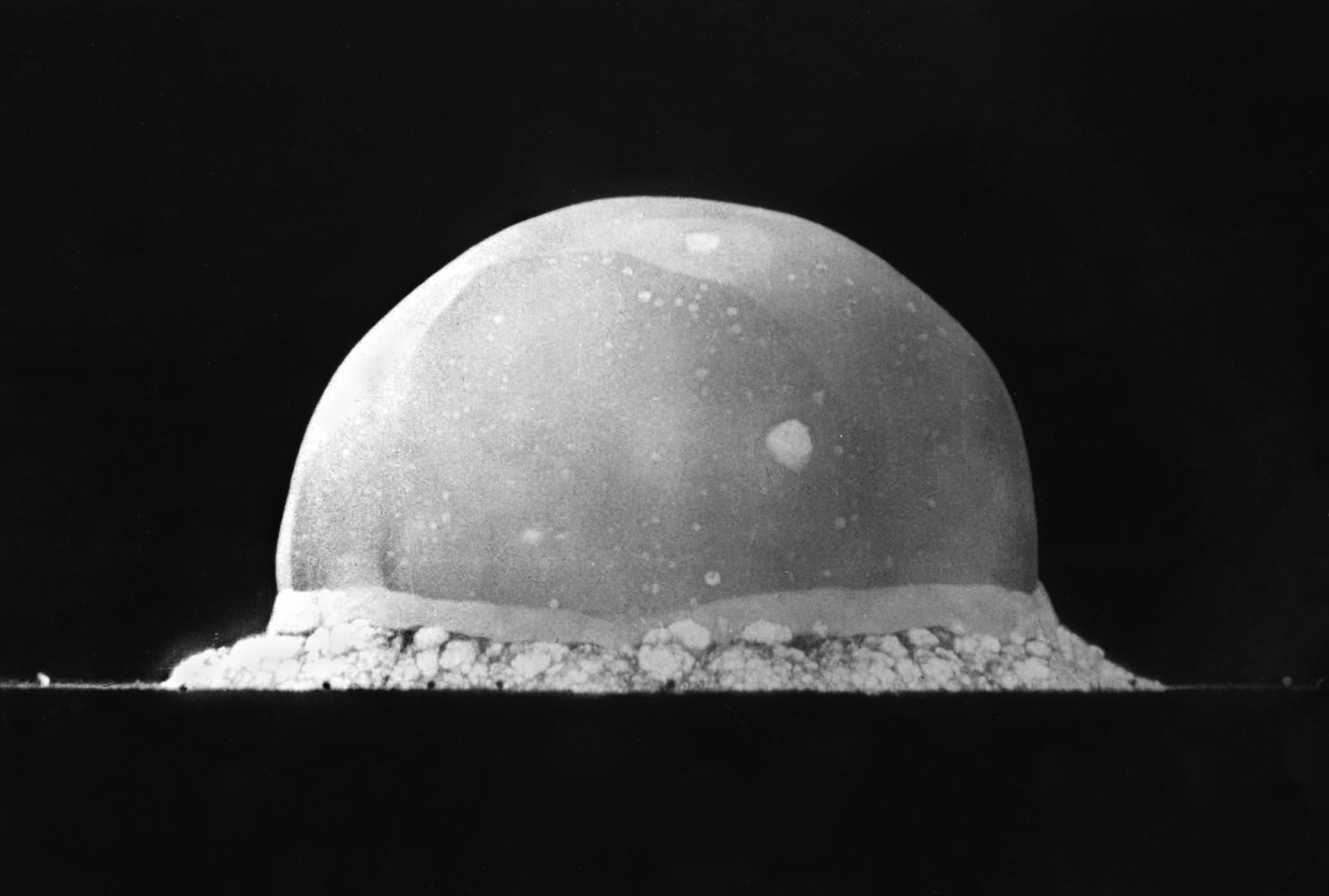
Tsar Bomba Revised
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official (the Pope or the Ecumenical Patriarch)—but was usually considered by western Europeans to be equivalent to "king". It lends its name to a system of government, tsarist autocracy or tsarism. "Tsar" and its variants were the official titles of the following states: * Bulgarian Empire ( First Bulgarian Empire in 681–1018, Second Bulgarian Empire in 1185–1396), and also used in Tsardom of Bulgaria, in 1908–1946 * Serbian Empire, in 1346–1371 * Tsardom of Russia, in 1547–1721 (replaced in 1721 by '' imperator'' in Russian Empire The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)


