|
Arum Cyrenaicum
''Arum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to Europe, northern Africa, and western and central Asia, with the highest species diversity in the Mediterranean region. Frequently called arum lilies, they are not closely related to the true lilies ''Lilium''. Plants in closely related ''Zantedeschia'' are also called "arum lilies". They are rhizomatous, herbaceous perennial plants growing to 20–60 cm tall, with sagittate (arrowhead-shaped) leaves 10–55 cm long. The flowers are produced in a spadix, surrounded by a 10–40 cm long, distinctively coloured spathe, which may be white, yellow, brown, or purple. Some species are scented, others not. The fruit is a cluster of bright orange or red berries. All parts of the plants, including the berries, are poisonous, containing calcium oxalate as raphides. In spite of this, the plant has a history of culinary use among Arab peasants in Palestine who practised leaching the toxins from the plant bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Palaestinum
''Arum palaestinum'' is a species of flowering herbaceous perennial plant in the family Araceae and the genus ''Arum'' (also known as black calla, Solomon's lily, priest's hood, noo'ah loof and kardi) It is native to the Levant and other parts of the Mediterranean Basin, and has been naturalized in North America, North Africa, Europe, Western Asia, and Australia The family Araceae includes other well-known plants such as ''Anthurium, Caladium'', and ''Philodendron''. ''Arum palaestinum'' is perhaps best known for it long history in the Middle East as food and for it use in traditional Middle Eastern medicine. Description It grows high. It blooms in the spring, between the months of March and April, by which time the plant is easily recognized by its dark purplish-black spadix enclosed by a reddish-brown spathe. It is perennial plant. The leaves of ''A. palaestinum'' are light green, narrow, and upright with a purplish-black color. The root is tuberous. Like other members ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
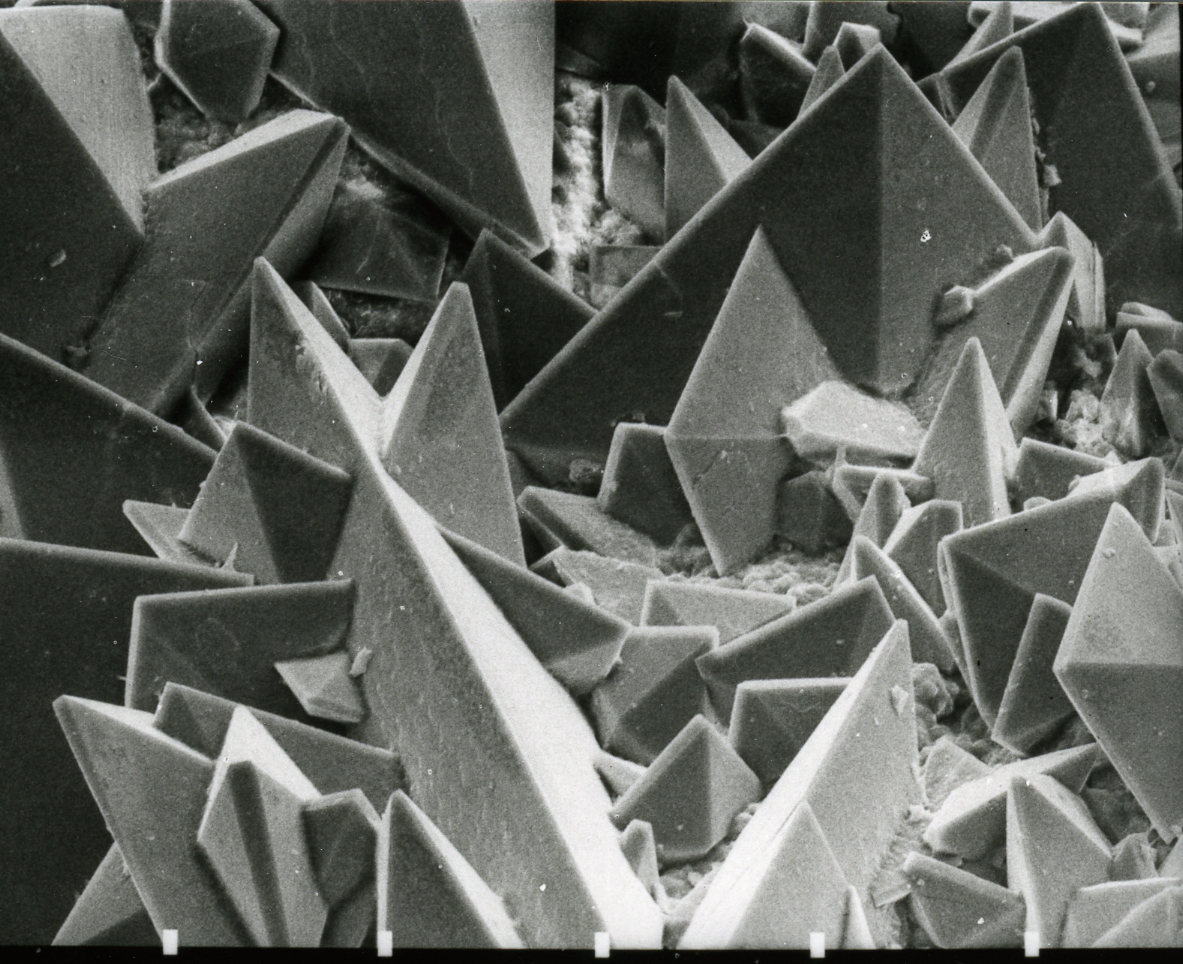
Calcium Oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral weddellite, and trihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral caoxite, are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Tribes with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as in Micronesia, reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them. They are a constituent in 76% of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries. Occurrence Many plants accumu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Besserianum
''Arum besserianum'' is a flowering plant species in the family Araceae. Habitat ''Arum besserianum'' grows in southern Poland and northwest Ukraine Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv .... Taxonomy Within the genus ''Arum'', it belongs to subgenus ''Arum'', section ''Dioscoridea'', and subsection ''Discroochiton''. Its specific status has been considered dubious, but it has been recognized as a valid species in recent studies. References External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q12079258 Flora of Europe Flora of Poland Flora of Ukraine besserianum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Balansanum
''Arum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to Europe, northern Africa, and western and central Asia, with the highest species diversity in the Mediterranean region. Frequently called arum lilies, they are not closely related to the true lilies ''Lilium''. Plants in closely related ''Zantedeschia'' are also called "arum lilies". They are rhizomatous, herbaceous perennial plants growing to 20–60 cm tall, with sagittate (arrowhead-shaped) leaves 10–55 cm long. The flowers are produced in a spadix, surrounded by a 10–40 cm long, distinctively coloured spathe, which may be white, yellow, brown, or purple. Some species are scented, others not. The fruit is a cluster of bright orange or red berries. All parts of the plants, including the berries, are poisonous, containing calcium oxalate as raphides. In spite of this, the plant has a history of culinary use among Arab peasants in Palestine who practised leaching the toxins from the plant bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Apulum
''Arum apulum'', known as Apulian arum, is a flowering plant species in the family Araceae. Description ''Arum apulum'' is a tuberous herbs that spreads clonally through discoid vertically oriented tubers. Flowers are borne on a spadix. Habitat The species is endemic to Italy, where it grows in low scrub at altitudes of 300 to 400 meters in central Apulia. It is threatened by habitat destruction. Taxonomy Within the genus ''Arum'', it belongs to subgenus ''Arum'', section ''Dioscoridea'', and subsection ''Dischroochiton''. ''A. apulum'' is tetraploid, with a chromosome A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ... count of 2n = 56. References External links * Garden plants of Europe Flora of Italy apulum {{Araceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arum Alpinariae
''Arum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to Europe, northern Africa, and western and central Asia, with the highest species diversity in the Mediterranean region. Frequently called arum lilies, they are not closely related to the true lilies ''Lilium''. Plants in closely related ''Zantedeschia'' are also called "arum lilies". They are rhizomatous, herbaceous perennial plants growing to 20–60 cm tall, with sagittate (arrowhead-shaped) leaves 10–55 cm long. The flowers are produced in a spadix, surrounded by a 10–40 cm long, distinctively coloured spathe, which may be white, yellow, brown, or purple. Some species are scented, others not. The fruit is a cluster of bright orange or red berries. All parts of the plants, including the berries, are poisonous, containing calcium oxalate as raphides. In spite of this, the plant has a history of culinary use among Arab peasants in Palestine who practised leaching the toxins from the plant bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciara (fly)
''Sciara'' is a genus of fungus gnats in the family Sciaridae. Species Sciara is among the largest genus in the world, with over 700 species. Species within this genus include: * ''Sciara abbreviata'' * ''Sciara abdita'' * ''Sciara adjuncta'' * ''Sciara aemula'' * ''Sciara aethiops'' * ''Sciara africana'' * ''Sciara albicoxa'' * ''Sciara albifrons'' * ''Sciara amabilis'' * ''Sciara analis'' * ''Sciara angustata'' * ''Sciara antigua'' * ''Sciara antonovae'' * ''Sciara approximata'' * ''Sciara aquila'' * ''Sciara arcuata'' * ''Sciara aspirans'' * ''Sciara atomaria'' * ''Sciara atrata'' * ''Sciara atratula'' * ''Sciara atrifrons'' * ''Sciara attenuata'' * ''Sciara audax'' * ''Sciara aurosa'' * ''Sciara barnardi'' * ''Sciara biformata'' * ''Sciara bispinosa'' * ''Sciara borealis'' * ''Sciara brevifurca'' * ''Sciara brevipetiolata'' * ''Sciara bullastylata'' * ''Sciara cameronensis'' * ''Sciara capensis'' * ''Sciara cavicata'' * ''Sciara cingulata'' * ''Sciara clavata'' * ''Sciara co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychodidae
Psychodidae, called drain flies, sink flies, filter flies, sewer flies, or sewer gnats, is a family of true flies. Some genera have short, hairy bodies and wings giving them a "furry" moth-like appearance, hence one of their common names, moth flies. Members of the sub-family Phlebotominae which are hematophagous (feed on blood) may be called sand flies in some countries, although this term is also used for other unrelated flies. There are more than 2,600 described species worldwide, most of them native to the humid tropics. This makes them one of the most diverse families of their order. Drain flies sometimes inhabit plumbing drains and sewage systems, where they are harmless, but may be a persistent annoyance. Life cycle The larvae of the subfamilies Psychodinae, Sycoracinae and Horaiellinae live in aquatic to semi-terrestrial or sludge-based habitats, including bathroom sinks, where they feed on bacteria and can become problematic. The larvae of the most commonly encou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanide Insensitive Respiration
Cyanide is a naturally occurring, rapidly acting, toxic chemical that can exist in many different forms. In chemistry, a cyanide () is a chemical compound that contains a functional group. This group, known as the cyano group, consists of a carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom. In inorganic cyanides, the cyanide group is present as the anion . Soluble salts such as sodium cyanide (NaCN) and potassium cyanide (KCN) are highly toxic. Hydrocyanic acid, also known as hydrogen cyanide, or HCN, is a highly volatile liquid that is produced on a large scale industrially. It is obtained by acidification of cyanide salts. Organic cyanides are usually called nitriles. In nitriles, the group is linked by a covalent bond to carbon. For example, in acetonitrile (), the cyanide group is bonded to methyl (). Although nitriles generally do not release cyanide ions, the cyanohydrins do and are thus rather toxic. Bonding The cyanide ion is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide and wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermogenesis
Thermogenesis is the process of heat production in organisms. It occurs in all warm-blooded animals, and also in a few species of thermogenic plants such as the Eastern skunk cabbage, the Voodoo lily (''Sauromatum venosum''), and the giant water lilies of the genus ''Victoria''. The lodgepole pine dwarf mistletoe, ''Arceuthobium americanum'', disperses its seeds explosively through thermogenesis.Rolena A.J. deBruyn, Mark Paetkau, Kelly A. Ross, David V. Godfrey & Cynthia Ross Friedman (2015)"Thermogenesis-triggered seed dispersal in dwarf mistletoe" Types Depending on whether or not they are initiated through locomotion and intentional movement of the muscles, thermogenic processes can be classified as one of the following: * Exercise-associated thermogenesis (EAT) * Non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT), energy expended for everything that is not sleeping, eating or sports-like exercise. * Diet-induced thermogenesis (DIT) Shivering One method to raise temperature is thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from the anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed on the axis of a plant. The modifications can involve the length and the nature of the internodes and the phyllotaxis, as well as variations in the proportions, compressions, swellings, adnations, connations and reduction of main and secondary axes. One can also define an inflorescence as the reproductive portion of a plant that bears a cluster of flowers in a specific pattern. The stem holding the whole inflorescence is called a peduncle. The major axis (incorrectly referred to as the main stem) above the peduncle bearing the flowers or secondary branches is called the rachis. The stalk of each flower in the inflorescence is called a pedicel. A flower that is not part of an inflorescence is called a solitary flower and its stalk is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-Brendel_Nr._202-.jpg)