|
Artificial Demand
Artificial demand constitutes demand for something that, in the absence of exposure to the vehicle of creating demand, would not exist. It has controversial applications in microeconomics (pump and dump strategy) and advertising. A demand is usually seen as artificial when it increases consumer utility very inefficiently; for example, a physician prescribing unnecessary surgeries would create artificial demand. Government spending with the primary purpose of providing jobs (rather than delivering any other end product) has been labelled "artificial demand". Similarly Noam Chomsky has suggested that unchecked militarism is a type of government-created artificial demand, a "system of state planning ... oriented toward military production, in effect, the production of high technology waste", with military Keynesianism or a powerful military industrial complex amounts to the "creation of state-guaranteed markets for high technology waste (armaments)." Vehicles Vehicles of creating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. The relationship between price and quantity demand is also called the demand curve. Demand for a specific item is a function of an item's perceived necessity, price, perceived quality, convenience, available alternatives, purchasers' disposable income and tastes, and many other options. Factors influencing demand Innumerable factors and circumstances affect a consumer's willingness or to buy a good. Some of the common factors are: The price of the commodity: The basic demand relationship is between potential prices of a good and the quantities that would be purchased at those prices. Generally, the relationship is negative, meaning that an increase in price will induce a decrease in the quantity demanded. This negative relationship is embodied in the downward slope of the consumer demand curve. The assumption of a negative relationship is reaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Share Price
A share price is the price of a single share of a number of saleable equity shares of a company. In layman's terms, the stock price is the highest amount someone is willing to pay for the stock, or the lowest amount that it can be bought for. Behaviour of share prices In economics and financial theory, analysts use random walk techniques to model behavior of asset prices, in particular share prices on stock markets. This practice has its basis in the presumption that investors act rationally and without biases, and that at any moment they estimate the value of an asset based on future expectations. Under these conditions, all existing information affects the price, which changes only when new information comes out. By definition, new information appears randomly and influences the asset price randomly. Empirical studies have demonstrated that prices do not completely follow random walks. Low serial correlations (around 0.05) exist in the short term, and slightly stronger correl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advertising
Advertising is the practice and techniques employed to bring attention to a product or service. Advertising aims to put a product or service in the spotlight in hopes of drawing it attention from consumers. It is typically used to promote a specific good or service, but there are wide range of uses, the most common being the commercial advertisement. Commercial advertisements often seek to generate increased consumption of their products or services through "branding", which associates a product name or image with certain qualities in the minds of consumers. On the other hand, ads that intend to elicit an immediate sale are known as direct-response advertising. Non-commercial entities that advertise more than consumer products or services include political parties, interest groups, religious organizations and governmental agencies. Non-profit organizations may use free modes of persuasion, such as a public service announcement. Advertising may also help to reassure employees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planned Obsolescence
In economics and industrial design, planned obsolescence (also called built-in obsolescence or premature obsolescence) is a policy of planning or designing a product with an artificially limited useful life or a purposely frail design, so that it becomes obsolete after a certain pre-determined period of time upon which it decrementally functions or suddenly ceases to function, or might be perceived as unfashionable. The rationale behind this strategy is to generate long-term sales volume by reducing the time between repeat purchases (referred to as "shortening the replacement cycle"). It is the deliberate shortening of a lifespan of a product to force people to purchase functional replacements. Planned obsolescence tends to work best when a producer has at least an oligopoly. Before introducing a planned obsolescence, the producer has to know that the customer is at least somewhat likely to buy a replacement from them (see brand loyalty). In these cases of planned obsolescence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overconsumption
Overconsumption describes a situation where a consumer overuses their available goods and services to where they can't, or don't want to, replenish or reuse them. In microeconomics, this may be described as the point where the marginal cost of a consumer is greater than their marginal utility. The term overconsumption is quite controversial in use and does not necessarily have a single unifying definition. When used to refer to natural resources to the point where the environment is negatively affected, is it synonymous with the term overexploitation. However, when used in the broader economic sense, overconsumption can refer to all types of goods and services, including manmade ones, e.g. "the overconsumption of alcohol can lead to alcohol poisoning". Overconsumption is driven by several factors of the current global economy, including forces like consumerism, planned obsolescence, economic materialism, and other unsustainable business models and can be contrasted with sustaina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Manipulation
In economics and finance, market manipulation is a type of market abuse where there is a deliberate attempt to interfere with the free and fair operation of the market; the most blatant of cases involve creating false or misleading appearances with respect to the price of, or market for, a product, security or commodity. Market manipulation is prohibited in most countries, in particular, it is prohibited in the United States under Section 9(a)(2) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, in the European Union under Article 12 of the ''Market Abuse Regulation'', in Australia under Section 1041A of the Corporations Act 2001, and in Israel under Section 54(a) of the securities act of 1968. In the US, market manipulation is also prohibited for wholesale electricity markets under Section 222 of the Federal Power Act and wholesale natural gas markets under Section 4A of the Natural Gas Act. The US Securities Exchange Act defines market manipulation as "transactions which create an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Bubble
An economic bubble (also called a speculative bubble or a financial bubble) is a period when current asset prices greatly exceed their intrinsic valuation, being the valuation that the underlying long-term fundamentals justify. Bubbles can be caused by overly optimistic projections about the scale and sustainability of growth (e.g. dot-com bubble), and/or by the belief that intrinsic valuation is no longer relevant when making an investment (e.g. Tulip mania). They have appeared in most asset classes, including equities (e.g. Roaring Twenties), commodities (e.g. Uranium bubble), real estate (e.g. 2000s US housing bubble), and even esoteric assets (e.g. Cryptocurrency bubble). Bubbles usually form as a result of either excess liquidity in markets, and/or changed investor psychology. Large multi-asset bubbles (e.g. 1980s Japanese asset bubble and the 2020–21 Everything bubble), are attributed to central banking liquidity (e.g. overuse of the Fed put). In the early stages o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Beers
De Beers Group is an international corporation that specializes in diamond mining, diamond exploitation, diamond retail, diamond trading and industrial diamond manufacturing sectors. The company is active in open-pit, large-scale alluvial and coastal mining. It operates in 35 countries and mining takes place in Botswana, Namibia, South Africa, Canada and Australia. From its inception in 1888 until the start of the 21st century, De Beers controlled 80% to 85% of rough diamond distribution and was considered a monopoly. Competition has since dismantled the complete monopoly; the De Beers Group now sells approximately 29.5% of the world's rough diamond production by value through its global sightholder and auction sales businesses. The company was founded in 1888 by British businessman Cecil Rhodes, who was financed by the South African diamond magnate Alfred Beit and the London-based N M Rothschild & Sons bank. In 1926, Ernest Oppenheimer, a German immigrant to Britain and later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartel
A cartel is a group of independent market participants who collude with each other in order to improve their profits and dominate the market. Cartels are usually associations in the same sphere of business, and thus an alliance of rivals. Most jurisdictions consider it anti-competitive behavior and have outlawed such practices. Cartel behavior includes price fixing, bid rigging, and reductions in output. The doctrine in economics that analyzes cartels is cartel theory. Cartels are distinguished from other forms of collusion or anti-competitive organization such as corporate mergers. Etymology The word ''cartel'' comes from the Italian word '' cartello'', which means a "leaf of paper" or "placard", and is itself derived from the Latin ''charta'' meaning "card". The Italian word became ''cartel'' in Middle French, which was borrowed into English. In English, the word was originally used for a written agreement between warring nations to regulate the treatment and exchange of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial scarcity is scarcity of items despite the technology for production or the sufficient capacity for sharing. The most common causes are monopoly pricing structures, such as those enabled by laws that restrict competition or by high fixed costs in a particular marketplace. The inefficiency associated with artificial scarcity is formally known as a deadweight loss. Background In a capitalist system, an enterprise is judged to be successful and efficient if it is profitable. To obtain maximum profits, producers may be restricting production rather than ensuring the maximum utilisation of resources. This strategy of restricting production by firms in order to obtain profits in a capitalist system or mixed economy is known as creating artificial scarcity. Artificial scarcity essentially describes situations where the producers or owners of a good restrict its availability to others beyond what is strictly necessary. Ideas and information are prime examples of unnecessaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
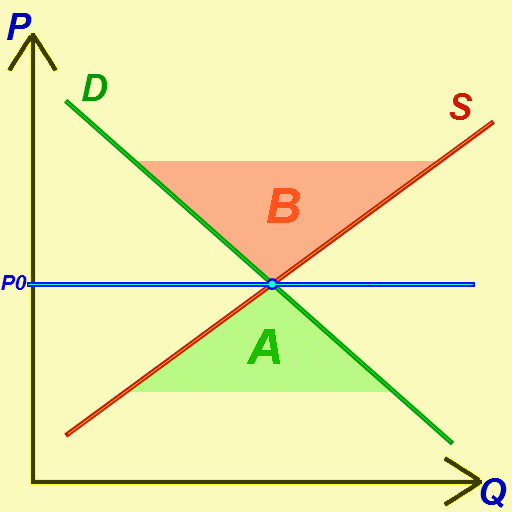
Market Equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the ( equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. But the concept of ''equilibrium'' in economics also applies to imperfectly competitive markets, where it takes the form of a Nash equilibrium. Understanding economic equilibriu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trader (finance)
A trader is a person, firm, or entity in finance who buys and sells financial instruments, such as forex, cryptocurrencies, stocks, bonds, commodities, derivatives, and mutual funds in the capacity of agent, hedger, arbitrageur, or speculator. Duties and types Traders buy and sell financial instruments traded in the stock markets, derivatives markets and commodity markets, comprising the stock exchanges, derivatives exchanges, and the commodities exchanges. Several categories and designations for diverse kinds of traders are found in finance, including: *Bond trader *Floor trader *Hedge fund trader *High-frequency trader *Market maker *Pattern day trader * Principal trader * Proprietary trader *Rogue trader *Scalper *Stock trader Income According to the Wall Street Journal in 2004, a managing director convertible bond trader was earning between $700,000 and $900,000 on average. See also *Commodities exchange *Commodity market *Derivatives market *List of commodity traders *Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |