|
Articulavirales
''Articulavirales'' is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect invertebrates and vertebrates. It includes the family of influenza viruses which infect humans. It is the only order of viruses in the monotypic class ''Insthoviricetes''. The order contains two families and eight genera. Etymology The order name ''Articulavirales'' derives from Latin meaning "segmented" (alluding to the segmented genome of member viruses) added to the suffix for virus orders ''-virales''. The class name ''Insthoviricetes'' is a portmanteau of member viruses "''in''fluenza, i''s''avirus, and ''tho''gotovirus" added to the suffix ''-viricetes'' for virus classes. Genome Member viruses have segmented, negative-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes. Classification The order ''Articulavirales'' contains two families and eight genera: * '' Amnoonviridae'' ** '' Tilapinevirus'' * '' Orthomyxoviridae'' ** ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' ** ''Betainfluenzavirus'' ** '' Deltainfluenzaviru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
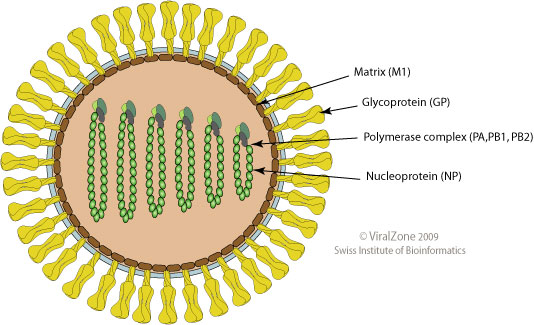
Orthomyxoviridae
''Orthomyxoviridae'' (from Greek ὀρθός, ''orthós'' 'straight' + μύξα, ''mýxa'' 'mucus') is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes seven genera: ''Alphainfluenzavirus'', ''Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', '' Deltainfluenzavirus'', ''Isavirus'', ''Thogotovirus'', and ''Quaranjavirus''. The first four genera contain viruses that cause influenza in birds (see also avian influenza) and mammals, including humans. Isaviruses infect salmon; the thogotoviruses are arboviruses, infecting vertebrates and invertebrates (such as ticks and mosquitoes). The Quaranjaviruses are also arboviruses, infecting vertebrates (birds) and invertebrates (arthropods). The four genera of Influenza virus that infect vertebrates, which are identified by antigenic differences in their nucleoprotein and matrix protein, are as follows: * ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' infects humans, other mammals, and birds, and causes all flu pandemics * ''Betainfluenzavirus'' infects h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative-strand RNA Virus
Negative-strand RNA viruses (−ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized by the viral enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). During replication of the viral genome, RdRp synthesizes a positive-sense antigenome that it uses as a template to create genomic negative-sense RNA. Negative-strand RNA viruses also share a number of other characteristics: most contain a viral envelope that surrounds the capsid, which encases the viral genome, −ssRNA virus genomes are usually linear, and it is common for their genome to be segmented. Negative-strand RNA viruses constitute the phylum ''Negarnaviricota'', in the kingdom ''Orthornavirae'' and realm ''Riboviria''. They are descended from a common ancestor that was a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) virus, and they are considered to be a sister clade of reoviru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphainfluenzavirus
'' A virus'' (''IAV'') causes influenza in birds and some mammals, and is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. Strains of all subtypes of influenza A virus have been isolated from wild birds, although disease is uncommon. Some isolates of influenza A virus cause severe disease both in domestic poultry and, rarely, in humans. Occasionally, viruses are transmitted from wild aquatic birds to domestic poultry, and this may cause an outbreak or give rise to human influenza pandemics. Influenza A viruses are negative-sense, single-stranded, segmented RNA viruses. The several subtypes are labeled according to an H number (for the type of hemagglutinin) and an N number (for the type of neuraminidase). There are 18 different known H antigens (H1 to H18) and 11 different known N antigens (N1 to N11). H17N10 was isolated from fruit bats in 2012. H18N11 was discovered in a Peruvian bat in 2013. Each virus subtype has mutated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thogotovirus
''Thogotovirus'' is a genus of enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. Their single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome has six or seven segments. Thogotoviruses are distinguished from most other orthomyxoviruses by being arboviruses – viruses that are transmitted by arthropods, in this case usually ticks. Thogotoviruses can replicate in both tick cells and vertebrate cells; one subtype has also been isolated from mosquitoes. A consequence of being transmitted by blood-sucking vectors is that the virus must spread systemically in the vertebrate host – unlike influenza viruses, which are transmitted by respiratory droplets and are usually confined to the respiratory system. The genus contains the species '' Thogoto thogotovirus'' and ''Dhori virus'' (DHOV), and the latter's subtype Batken virus, as well as the species or strains Araguari virus, Aransas Bay virus (ABV), Bourbon virus, Jos virus (JOSV) and Upolu virus (UPOV), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaranjavirus
''Quaranjavirus'' is a genus of viral envelope, enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. The genome is single-stranded, sense (molecular biology), negative-sense segmented RNA, generally with six segments. The genus contains two species: ''Johnston Atoll virus'' and ''Quaranfil virus''; it has been proposed to contain species or strains including Cygnet River virus, Lake Chad virus, Tyulek virus and Wellfleet Bay virus. Quaranjaviruses predominantly infect arthropods and birds; , ''Quaranfil quaranjavirus'' is the only member of the genus to have been shown to infect humans. The ''Quaranfil'' and ''Johnston Atoll'' viruses are transmitted between vertebrates by ticks, resembling members of ''Thogotovirus'', another genus of ''Orthomyxoviridae''. History ''Quaranfil virus'' was first isolated from humans in Egypt in 1953. ''Johnston Atoll virus'' and Lake Chad virus were first isolated from birds in 1964 and 1969, respectively. In 1989, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isavirus
Infectious salmon anemia (ISA) is a viral disease of Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') caused by ''Salmon isavirus''. It affects fish farms in Canada, Norway, Scotland and Chile, causing severe losses to infected farms. ISA has been a World Organisation for Animal Health notifiable disease since 1990. In the EU, it is classified as a non-exotic disease, and is monitored by the European Community Reference Laboratory for Fish Diseases. Virology ISA is caused by the infectious salmon anemia virus (ISAV). ISAV, a segmented RNA virus that is the only species in the genus "Isavirus", which is in the family Orthomyxoviridae, and therefore related to the influenza viruses. The genome encodes at least 10 proteins. There are several distinct strains of the virus. The most common are a European strain and a North American strain. Pathology ISA virus causes severe anemia in infected fish. Unlike the mature red blood cells of mammals, the mature red blood cells of fish contain DNA, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betainfluenzavirus
''Influenza B virus'' is the only species in the genus ''Betainfluenzavirus'' in the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. Influenza B virus is known only to infect humans and seals. This limited host range is apparently responsible for the lack of associated influenza pandemics in contrast with those caused by the morphologically similar influenza A virus as both mutate by both antigenic drift and reassortment. There are two known circulating lineages of Influenza B virus based on the antigenic properties of the surface glycoprotein hemagglutinin. The lineages are termed B/Yamagata/16/88-like and B/Victoria/2/87-like viruses. The quadrivalent influenza vaccine licensed by the CDC is currently designed to protect against both co-circulating lineages and has been shown to have greater effectiveness in prevention of influenza caused by Influenza B virus than the previous trivalent vaccine. Further diminishing the impact of this virus, "in humans, influenza B viruses evolve slo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilapinevirus
''Tilapia tilapinevirus'', or Tilapia lake virus (TiLV), is a negative-strand RNA virus that infects both wild and aquacultured populations of tilapia. It is the only species in the monotypic genus ''Tilapinevirus'', which in turn is the only genus in the family ''Amnoonviridae''. Thus far it has been recorded in various regions across Asia, Africa, and South America. The virus was first discovered and identified in 2014 when the Sea of Galilee (Kinneret Lake) in Israel experienced a major noticeable decline in tilapia catch quantities. Classification Tilapia lake virus is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. It belongs to Group V of the Baltimore Classification System of viruses. Structure Electron microscopy has revealed tilapia lake virus to be an enveloped icosahedral particle that is 55–100 nm in diameter. Further information of the viral structure is not yet available, however, as TiLV is described to be an orthomyxo-like virus it may share similar st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amnoonviridae
''Tilapia tilapinevirus'', or Tilapia lake virus (TiLV), is a negative-strand RNA virus that infects both wild and aquacultured populations of tilapia. It is the only species in the monotypic genus ''Tilapinevirus'', which in turn is the only genus in the family ''Amnoonviridae''. Thus far it has been recorded in various regions across Asia, Africa, and South America. The virus was first discovered and identified in 2014 when the Sea of Galilee (Kinneret Lake) in Israel experienced a major noticeable decline in tilapia catch quantities. Classification Tilapia lake virus is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. It belongs to Group V of the Baltimore Classification System of viruses. Structure Electron microscopy has revealed tilapia lake virus to be an enveloped icosahedral particle that is 55–100 nm in diameter. Further information of the viral structure is not yet available, however, as TiLV is described to be an orthomyxo-like virus it may share similar st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of wordsGarner's Modern American Usage , p. 644. in which parts of multiple words are combined into a new word, as in ''smog'', coined by blending ''smoke'' and ''fog'', or ''motel'', from ''motor'' and ''hotel''. In , a portmanteau is a single morph that is analyzed as representing two (or more) underlying morphemes. When portmanteaus shorten established [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |