|
Arthur Richard Dillon
Arthur Richard Dillon (1721–1806) was archbishop of Narbonne in France. He was the youngest son of Arthur Dillon (1670–1733), who came to France with Mountcashel's Irish Brigade. At the French Revolution he refused the civil constitution of the clergy and fled first to Coblenz and then to London. Birth and origins Arthur Richard was born on 15 September 1721 at the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye in France. He was the youngest of the five sons of Arthur Dillon and his wife Christina Sheldon. His father was born in 1670 in Ireland, had fought for the Jacobites in the Williamite War and had gone to France as the colonel of Dillon's Regiment with the Irish Brigade in April 1690 when Irish troops were sent to France in exchange for French troops sent to Ireland with Lauzun. He was a younger son of the 7th Viscount Dillon. His father's family was Old English Irish and descended from Sir Henry Dillon who came to Ireland with Prince John in 1185. Henry's mother was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Holy Spirit
The Order of the Holy Spirit (french: Ordre du Saint-Esprit; sometimes translated into English as the Order of the Holy Ghost), is a French order of chivalry founded by Henry III of France in 1578. Today, it is a dynastic order under the House of France. It should not be confused with the Holy Ghost Fathers, Congregation of the Holy Ghost or with the religious Order of the Holy Ghost. It was the senior chivalric order of France by precedence, although not by age, since the Order of Saint Michael was established more than a century earlier. Although officially abolished by the government authorities in 1830 following the July Revolution, its activities carried on. It is still recognised by the International Commission on Orders of Chivalry. History Prior to the creation of the Order of the Holy Spirit in 1578 by King Henri III, the senior order of chivalry in France had been the Order of Saint Michael. The idea flashed to him in Venice, where he had seen the original manuscript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
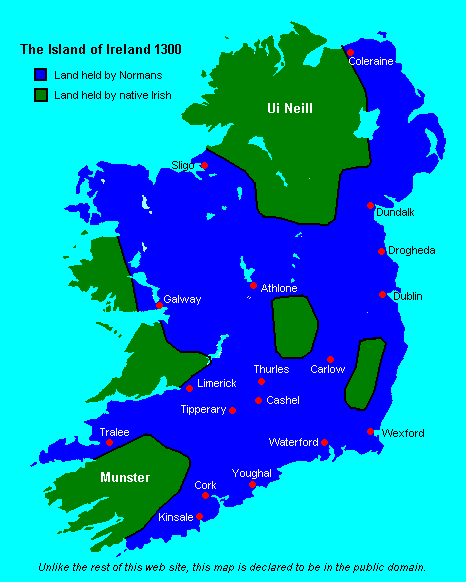
Normans In Ireland
From the 12th century onwards, a group of Normans invaded and settled in Gaelic Ireland. These settlers later became known as Norman Irish or Hiberno-Normans. They originated mainly among Cambro-Norman families in Wales and Anglo-Normans from England, who were loyal to the Kingdom of England, and the English state supported their claims to territory in the various realms then comprising Ireland. During the High Middle Ages and Late Middle Ages the Hiberno-Normans constituted a feudal aristocracy and merchant oligarchy, known as the Lordship of Ireland. In Ireland, the Normans were also closely associated with the Gregorian Reform of the Catholic Church in Ireland. Over time the descendants of the 12th-century Norman settlers spread throughout Ireland and around the world, as part of the Irish diaspora; they ceased, in most cases, to identify as Norman, Cambro-Norman or Anglo-Norman. The dominance of the Norman Irish declined during the 16th century, after a new English Protest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscount Dillon
Viscount Dillon, of Barony of Costello, Costello-Gallen (barony), Gallen in the County Mayo, County of Mayo, is a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created in 1622 for Theobald Dillon, 1st Viscount Dillon, Theobald Dillon, Lord President of Connaught. The Dillons were a Hiberno-Normans, Hiberno-Norman landlord family from the 13th century in a part of County Westmeath called 'Dillon's Country'. His great-grandson, the seventh Viscount, was a supporter of the Catholic James II of England, King James II of England and was outlawed after the Glorious Revolution. He founded 'Dillon Regiment, Dillon's Regiment' of the Irish Brigade (French)#Formation, Irish Brigade in the French Army, which was supported by the Flight of the Wild Geese, Wild Geese and achieved success at Battle of Fontenoy, Fontenoy in 1745. However, his son Henry, the eighth Viscount, managed to obtain a reversal of the outlawry in 1694 and later served as Lord Lieutenant of Roscommon, Lord Lieutenant of Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henriette-Lucy, Marquise De La Tour Du Pin Gouvernet
Henriette-Lucy, Marquise de La Tour-du-Pin-Gouvernet (25 February 1770, Paris – 2 April 1853, Pisa) (also known as Lucie) was a French aristocrat famous for her posthumously published memoirs entitled ''Journal d'une femme de 50 ans''. The memoirs are a first-hand account of her life through the Ancien Régime, the French Revolution, and the Imperial court of Napoleon, ending in March 1815 with Napoleon's return from exile on Elba. Her memoirs serve as unique testimony to much unchronicled history. Life Early life Henriette-Lucy Dillon was born into a prominent Irish Wild Geese Jacobite military family in France. She was daughter of Arthur Dillon, colonel-proprietor of the Dillon Regiment, and the lady-in-waiting Thérèse-Lucy de Rothe (1751–1782). Her father had been born in England, so she was often regarded in France as English. However the family, of Norman descent, was linked to the Dillons of Costello-Gallen and the lords of Drumraney in Ireland, who were grante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Dillon, 13th Viscount Dillon
Henry Augustus Dillon-Lee, 13th Viscount Dillon (1777–1832), was an Irish politician, soldier and writer. Despite being a Protestant, he supported Catholic emancipation in Ireland and wrote on the topic. He sat as MP for Harwich in England in the last parliament of Great Britain and the first parliament of the United Kingdom. In the second parliament of the United Kingdom he sat for County Mayo in Ireland. He was the colonel of a regiment and wrote on military subjects. He wrote fiction publishing two historical novels. Birth and origins Henry Augustus was born on 28 October 1777 at Brussels, then the capital of the Austrian Netherlands. He was the eldest son of Charles Dillon-Lee and his first wife Henrietta Maria Phipps. His father was the 12th Viscount Dillon, who had in 1767 conformed to the established religion. Henry Augustus's mother was the daughter of Constantine John Phipps, 1st Baron Mulgrave. Her family was Anglo-Irish. Thus both p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thérèse-Lucy De Dillon
Thérèse-Lucy de Dillon née ''de Rothe'' (1751 – September 1782), was a French countess and courtier, lady-in-waiting to queen Marie Antoinette of France in 1780–82. She belonged to the intimate circle of friends of the queen and was for a while known as one of her favorites. Life She was the maternal niece of the Archbishop of Narbonne, Arthur Richard Dillon, and married her second cousin count Arthur Dillon (1750–1794) in 1768, and became the mother of Henriette-Lucy, Marquise de La Tour du Pin Gouvernet. Dillon was described as a beauty and became one of the favorite companions of Marie Antoinette and one of the close confidants she invited to her ''petit cabinets''. To keep Dillon near her, the queen appointed her ''dame du palais surnuméraire'' in 1780, a step which created great jealousy at court, and for a while, she was reportedly always in the queen's presence. Like the other favorite Princesse de Lamballe, who was regarded to be affiliated with Palais Royal, Dil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Dillon, 12th Viscount Dillon
Charles Dillon-Lee, 12th Viscount Dillon, KP, PC (Ire) (1745–1813) conformed to the established religion in 1767. Birth and origins Charles was born on 6 November 1745 in London. He was the eldest child of Henry Dillon and his wife Charlotte Lee. His father was the 11th Viscount Dillon. Charles's mother was the eldest daughter of George Lee, 2nd Earl of Lichfield. His parents had married on 26 October 1744 in London. Early life In January 1766 Pope Clement XIII ended the Catholic Church's support for the Jacobites and recognised the Hanoverian Dynasty as the rightful rulers of England. On 4 December 1767, in Dublin, Charles conformed to the established church. In that same year he was also elected a Fellow of the Royal Society. Charles, in his youth, liked racing and gambling and made huge debts. He moved to Brussels to avoid his debtors. In 1770 he was elected MP for the Westbury Borough constituency in Wiltshire, England. In 1776 Charles changed his surn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Cary, 6th Viscount Falkland
Lucius Henry Cary, 6th Viscount Falkland (27 August 1687 – 31 December 1730) was a Scottish peer and Jacobite. Cary was the son of Edward Cary (1656–1692), of Caldicot, Monmouthshire, and his wife Anne, the eldest daughter of Charles Lucas, 2nd Baron Lucas. In 1694, he succeeded as Viscount Falkland upon the death of his third cousin once removed, Anthony Cary, 5th Viscount Falkland. Early in life, his guardian sued on his behalf to obtain the estate of Stanwell, Middlesex. Upon the death of Falkland's first cousin once removed, John Cary, in 1686, he had left that estate in trust to his great-niece, Elizabeth Willoughby, provided that she would marry Lord Guilford within three years of his death; the inheritance was otherwise to go to the 5th Viscount and his heirs, then to Edward Cary and his heirs. Elizabeth's trustees came to an agreement with Falkland and Edward Cary to allow her to enjoy the estate for life, notwithstanding her failure to marry Lord Guilford, and she af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Dillon, 11th Viscount Dillon
Henry Dillon, 11th Viscount Dillon (1705–1787) was an Irish peer and a soldier in French service. He was the colonel proprietor of Dillon's Regiment, an Irish regiment of foot in French service, in 1741–1744 and again in 1747–1767. In the War of the Polish Succession (1733–1735), he fought at the sieges of Kehl and Philippsburg. In the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748), he was present at the Battle of Dettingen in 1743, on the French side, while King George II was present on the English side. He then resigned from the colonelcy, left France and married the rich English heiress Charlotte Lee, daughter of George Lee, 2nd Earl of Lichfield, acquiring lands in Oxfordshire, England, in addition to his Irish lands. During his second term as colonel he was absent and the regiment was led by hired soldiers. Birth and origins Henry was born in 1705, most likely at the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France, where the Jacobite court w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Dillon, 8th Viscount Dillon
Henry Dillon, 8th Viscount Dillon (died 1714) was an Irish soldier and politician. In 1689 he sat in the Patriot Parliament. He fought for the Jacobites during the Wiiliamite War, defending Galway against Ginkel and surrendering it in 1691 after a short siege. He obtained the reversal of his father's attainder in 1696 recovering his father's lands. Birth and origins Henry was born about 1665, probably at his parents' house at Kilmore, County Roscommon, Ireland. He was the second but eldest surviving of the three sons of Theobald Dillon and his wife Mary Talbot. At that time his father was heir apparent of Lucas Dillon, 6th Viscount Dillon of Costello-Gallen, a remote cousin. His father's family was Old English and descended from Sir Henry Dillon who had come to Ireland with Prince John in 1185. Henry's mother was a daughter of Sir Henry Talbot of Templeogue. The Talbots also were an Old English family. Both his parents were Catholic. He had two brothers, which are list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James II Of England
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Revolution of 1688. He was the last Catholic monarch of England, Scotland, and Ireland. His reign is now remembered primarily for conflicts over religious tolerance, but it also involved struggles over the principles of absolutism and the divine right of kings. His deposition ended a century of political and civil strife in England by confirming the primacy of the English Parliament over the Crown. James succeeded to the thrones of England, Ireland, and Scotland following the death of his brother with widespread support in all three countries, largely because the principles of eligibility based on divine right and birth were widely accepted. Tolerance of his personal Catholicism did not extend to tolerance of Catholicism in general, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Of Modena
Mary of Modena ( it, Maria Beatrice Eleonora Anna Margherita Isabella d'Este; ) was Queen of England, Scotland and Ireland as the second wife of James II and VII. A devout Roman Catholic, Mary married the widower James, who was then the younger brother and heir presumptive of Charles II. She was uninterested in politics and devoted to James and their children, two of whom survived to adulthood: the Jacobite claimant to the thrones, James Francis Edward, and Louisa Maria Teresa. Born a princess of the northwestern Italian Duchy of Modena, Mary is primarily remembered for the controversial birth of James Francis Edward, her only surviving son. It was widely rumoured that he was smuggled into the birth chamber in a warming pan in order to perpetuate her husband's Catholic Stuart dynasty. James Francis Edward's birth was a contributing factor to the "Glorious Revolution", the revolution which deposed James II and VII, and replaced him with Mary II, a Protestant, James II's eld ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |