|
Arterial Resistivity Index
The arterial resistivity index (also called as Resistance index, abbreviated as RI), developed by Léandre Pourcelo is a measure of pulsatile blood flow that reflects the Vascular resistance, resistance to blood flow caused by microvascular bed distal to the site of measurement. It is primarily used in ultrasound imaging to evaluate artery, arteries and organ (biology), solid organ damage. Calculation The formula used to calculate resistance index is: :RI = \frac Description The RI is altered not by vascular resistance alone but by the combination of vascular resistance and vascular compliance. Normal mean renal artery RI for an adult is 0.6 with 0.7 the upper limit of normal. In children, RI commonly exceeds 0.7 through 12 months of age and can remain above 0.7 through 4 years of age.American Journal of Roentgenology. 2003;180: 885-892. 10.2214/ajr.180.4.1800885 Medical uses It is used in Medical ultrasonography, ultrasound testing of umbilical artery for placental insuffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Laser Doppler Imaging
Laser Doppler imaging (LDI) is an imaging method that uses a laser beam to image live tissue. When the laser light reaches the tissue, the moving blood cells generate Doppler components in the reflected ( backscattered) light. The light that comes back is detected using a photodiode that converts it into an electrical signal. Then the signal is processed to calculate a signal that is proportional to the tissue perfusion in the imaged area. When the process is completed, the signal is processed to generate an image that shows the perfusion on a screen. The laser Doppler effect was first used to measure microcirculation by Stern M.D. in 1975. It is used widely in medicine, some representative research work about it are these: Use in ophthalmology The eye offers a unique opportunity for the non-invasive exploration of cardiovascular diseases. LDI by digital holography can measure blood flow in the retina and choroid. In particular, the choroid is a highly vascularized tissue supply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to insulin's effects. Classic symptoms include polydipsia (excessive thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (excessive hunger), weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the cardiovascular system, eye, kidney, and nerves. Diabetes accounts for approximately 4.2 million deaths every year, with an estimated 1.5 million caused by either untreated or poorly treated diabetes. The major types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. The most common treatment for type 1 is insulin replacement therapy (insulin injections), while anti-diabetic medications (such as metformin and semaglutide) and lifestyle modificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis. The underlying mechanisms vary depending on the disease. It is estimated that dietary risk factors are associated with 53% of CVD deaths. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease involve atherosclerosis. This may be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep, among other things. High blood pressure is estimated to account for approximately 13% of CVD deaths, while tobacco accounts for 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pulsatility Index
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. Blood flow ensures the transportation of nutrients, hormones, metabolic waste products, oxygen, and carbon dioxide throughout the body to maintain cell-level metabolism, the regulation of the pH, osmotic pressure and temperature of the whole body, and the protection from microbial and mechanical harm. Blood is a non-Newtonian fluid, and is most efficiently studied using rheology rather than hydrodynamics. Because blood vessels are not rigid tubes, classic hydrodynamics and fluids mechanics based on the use of classical viscometers are not capable of explaining haemodynamics. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hemodynamics
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. Blood flow ensures the transportation of nutrients, hormones, metabolic waste products, oxygen, and carbon dioxide throughout the body to maintain cell-level metabolism, the regulation of the pH, osmotic pressure and temperature of the whole body, and the protection from microbial and mechanical harm. Blood is a non-Newtonian fluid, and is most efficiently studied using rheology rather than hydrodynamics. Because blood vessels are not rigid tubes, classic hydrodynamics and fluids mechanics based on the use of classical viscometers are not capable of explaining haemodynamics. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
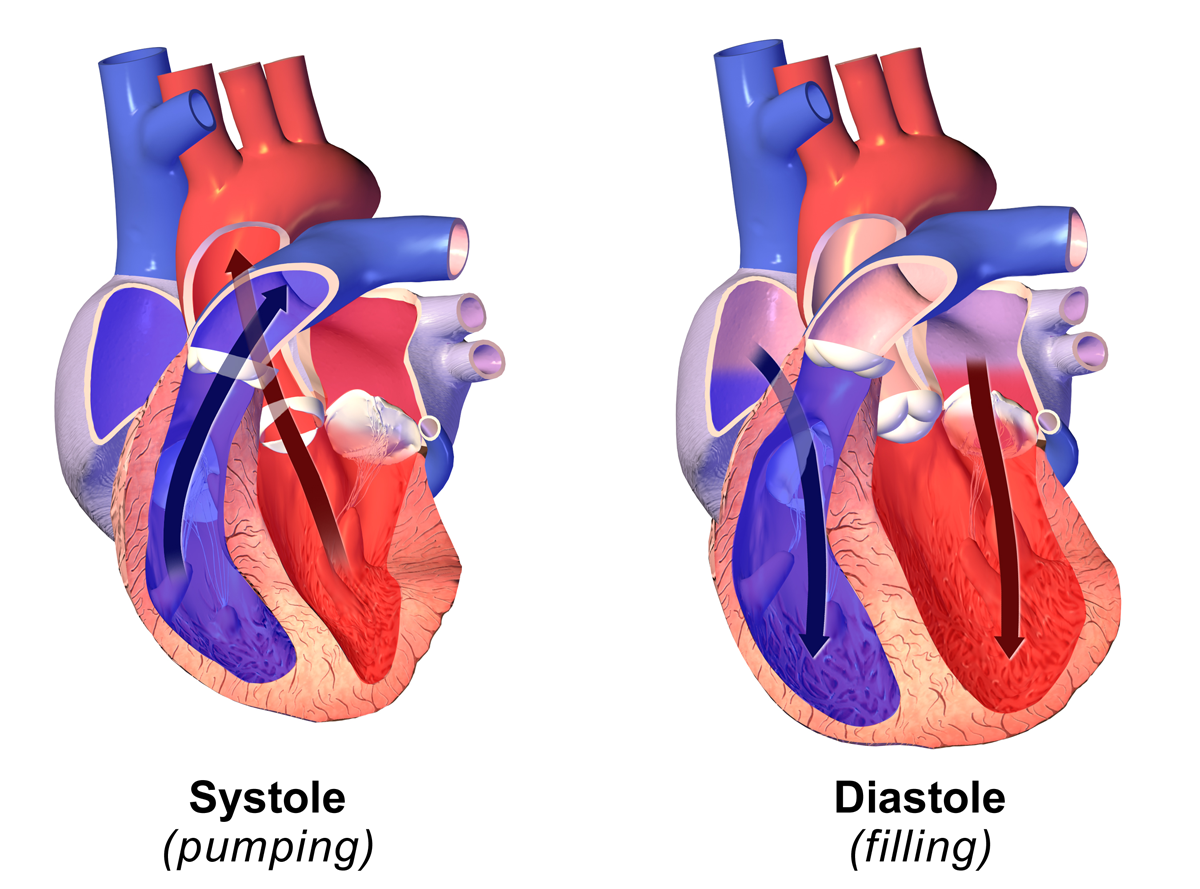
Diastole
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles. The term originates from the Greek word (''diastolē''), meaning "dilation", from (''diá'', "apart") + (''stéllein'', "to send"). Role in cardiac cycle A typical heart rate is 75 beats per minute (bpm), which means that the cardiac cycle that produces one heartbeat, lasts for less than one second. The cycle requires 0.3 sec in ventricular systole (contraction)—pumping blood to all body systems from the two ventricles; and 0.5 sec in diastole (dilation), re-filling the four chambers of the heart, for a total of 0.8 sec to complete the cycle. Early ventricular diastole During early ventricular diastole, pressure in the two ventricles begins to drop from the peak reached during systole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. Its contrasting phase is diastole, the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. Etymology The term originates, via Neo-Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. Terminology, general explanation The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Transplant Rejection
Transplant rejection occurs when transplanted tissue is rejected by the recipient's immune system, which destroys the transplanted tissue. Transplant rejection can be lessened by determining the molecular similitude between donor and recipient and by use of immunosuppressant drugs after transplant. Types Transplant rejection can be classified into three types: hyperacute, acute, and chronic. These types are differentiated by how quickly the recipient's immune system is activated and the specific aspect or aspects of immunity involved. Hyperacute rejection Hyperacute rejection is a form of rejection that manifests itself in the minutes to hours following transplantation. It is caused by the presence of pre-existing antibodies in the recipient that recognize antigens in the donor organ. These antigens are located on the endothelial lining of blood vessels within the transplanted organ and, once antibodies bind, will lead to the rapid activation of the complement system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
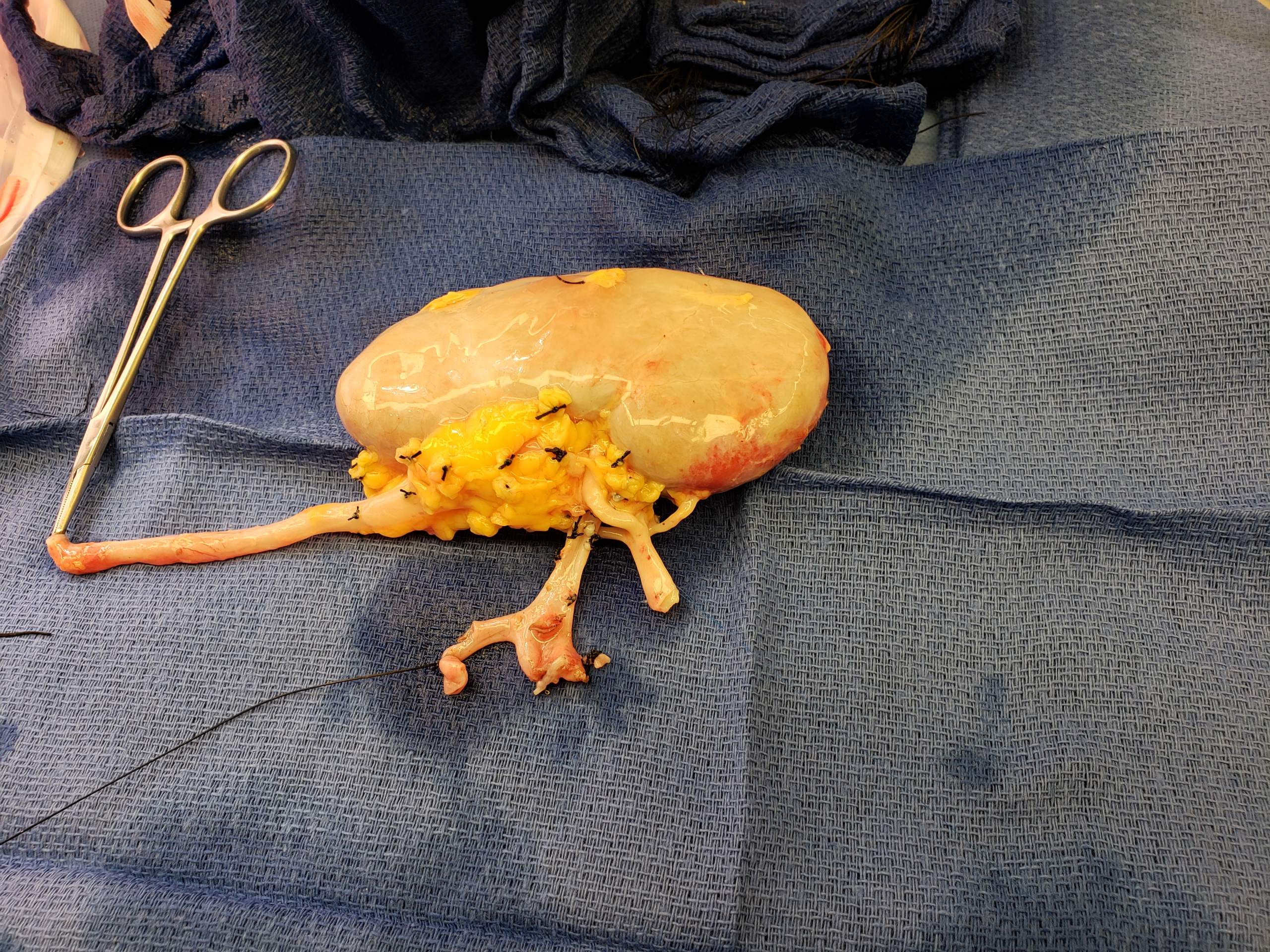
Kidney Transplantation
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor kidney transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 by a team including Joseph Murray, the recipient's surgeon, and Hartwell Harrison, surgeon for the donor. Murray was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1990 for this and other work. In 2018, an estimated 95,479 kidney transplants were performed worldwide, 36% of which came from living donors. Before receiving a kidney transplant, a person with ESRD must undergo a thorough medical evaluat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kidneys
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vascular Resistance
Vascular resistance is the resistance that must be overcome for blood to flow through the circulatory system. The resistance offered by the systemic circulation is known as the systemic vascular resistance or may sometimes be called by another term total peripheral resistance, while the resistance caused by the pulmonary circulation is known as the pulmonary vascular resistance. Vasoconstriction (i.e., decrease in the diameter of arteries and arterioles) increases resistance, whereas vasodilation (increase in diameter) decreases resistance. Blood flow and cardiac output are related to blood pressure and inversely related to vascular resistance. Measurement The measurement of vascular resistance is challenging in most situations. The standard method is by the use of a Pulmonary artery catheter. This is common in ICU settings but impractical is most other settings. Units for measuring Units for measuring vascular resistance are dyn·s·cm−5, pascal seconds per cubic metre (Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |