|
Armor (hydrology)
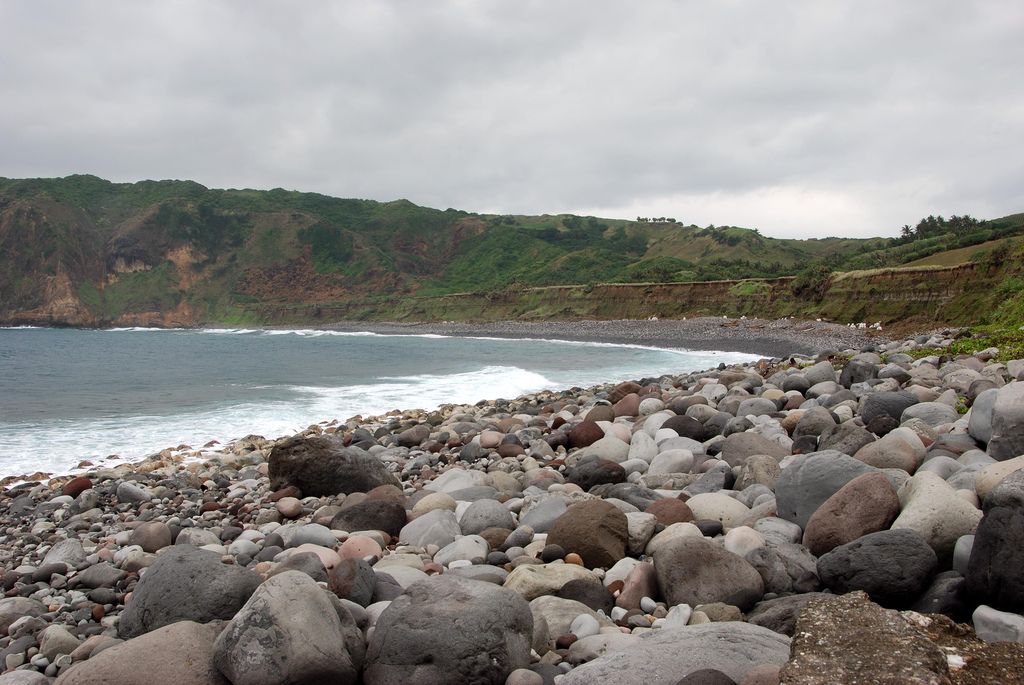
In hydrology and geography, armor is the association of surface pebbles, rocks or boulders with stream beds or beaches. Most commonly hydrological armor occurs naturally; however, a man-made form is usually called riprap, when shorelines or stream banks are fortified for erosion protection with large boulders or sizable manufactured concrete objects. When armor is associated with beaches in the form of pebbles to medium-sized stones grading from two to 200 millimeters across, the resulting landform is often termed a '' shingle beach''. Hydrological modeling indicates that stream armor typically persists in a flood stage environment. Hjulstroms Diagram Bed armor is most often transported through entrainment, and more specifically suspension and saltation. Both of these processes involve moving the sediment both near and around the bed of a river. When a sediment is entrained it is being moved downstream through the forces between the layers of water around it, and once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt Used In Wave Braker Beach The Hague
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shingle Beach
A shingle beach (also referred to as rocky beach or pebble beach) is a beach which is armoured with pebbles or small- to medium-sized cobbles (as opposed to fine sand). Typically, the stone composition may grade from characteristic sizes ranging from diameter. While this beach landform is most commonly found in Europe, examples are found in Bahrain, North America, and a number of other world regions, such as the west coast of New Zealand's South Island, where they are associated with the shingle fans of braided rivers. Though created at shorelines, post-glacial rebound can raise shingle beaches as high as above sea level, as on the High Coast in Sweden. The ecosystems formed by this unique association of rock and sand allow colonization by a variety of rare and endangered species. Formation Shingle beaches are typically steep, because the waves easily flow through the coarse, porous surface of the beach, decreasing the effect of backwash erosion and increasing the formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion Landforms
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion proceed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stream Power
Stream power originally derived by R. A. Bagnold in the 1960s is the amount of energy the water in a river or stream is exerting on the sides and bottom of the river. Stream power is the result of multiplying the density of the water, the acceleration of the water due to gravity, the volume of water flowing through the river, and the slope of that water. There are many forms of the stream power formula with varying utilities such as comparing rivers of various widths or quantify the energy required to move sediment of a certain size. Stream power is closely related to various other criterion such as stream competency and shear stress. Stream power is a valuable measurement for hydrologists and geomorphologist tackling sediment transport issues as well as for civil engineers using it in the planning and construction of roads, bridges, dams, and culverts. History Although many authors had suggested the use of power formulas in sediment transport in the decades preceding Bagnold's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
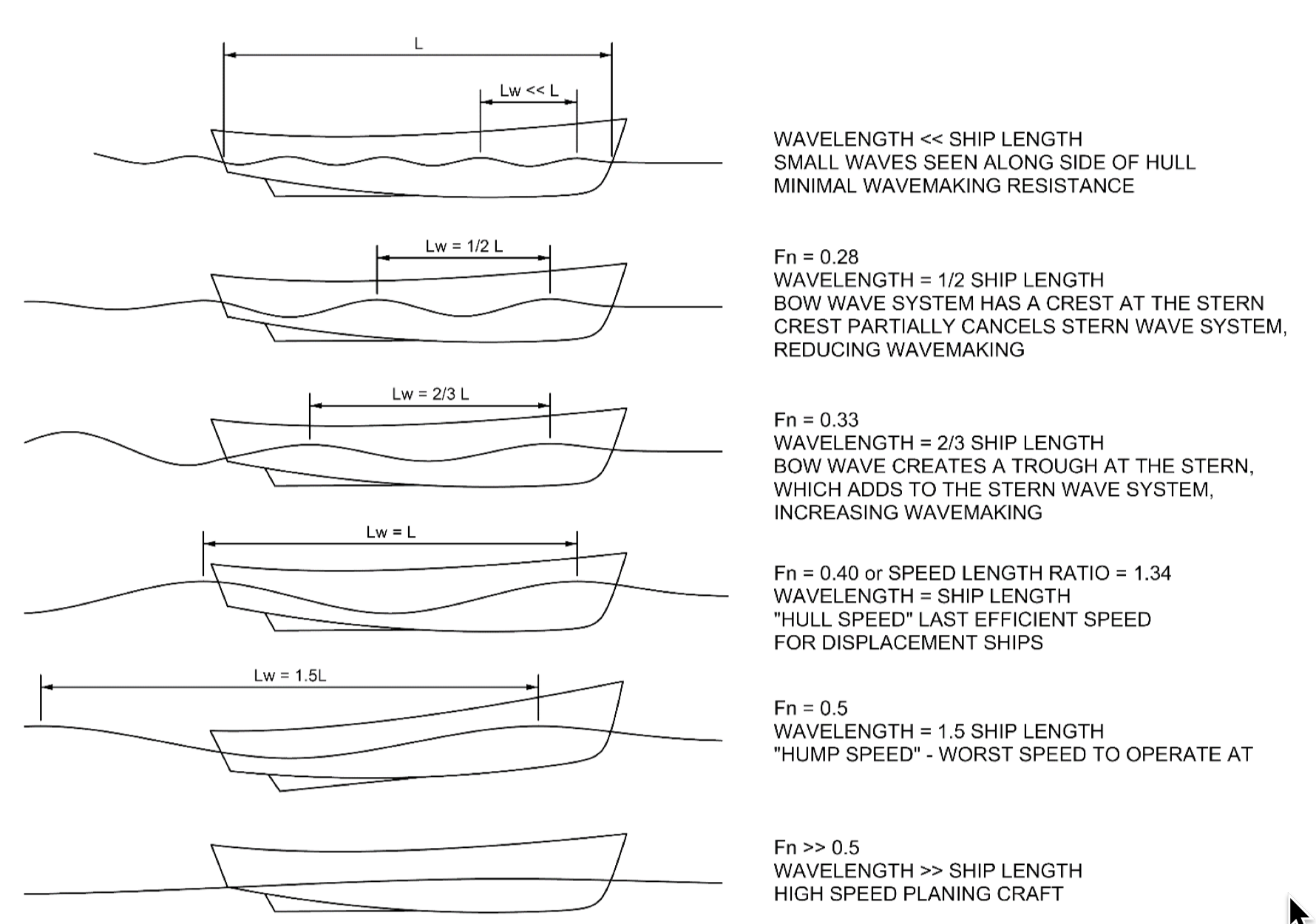
Critical Flow
In continuum mechanics, the Froude number (, after William Froude, ) is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of the flow inertia to the external field (the latter in many applications simply due to gravity). The Froude number is based on the speed–length ratio which he defined as: \mathrm = \frac where is the local flow velocity, is the local external field, and is a characteristic length. The Froude number has some analogy with the Mach number. In theoretical fluid dynamics the Froude number is not frequently considered since usually the equations are considered in the high Froude limit of negligible external field, leading to homogeneous equations that preserve the mathematical aspects. For example, homogeneous Euler equations are conservation equations. However, in naval architecture the Froude number is a significant figure used to determine the resistance of a partially submerged object moving through water. Origins In open channel flows, introduced first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohesion (geology)
Cohesion is the component of Shear strength (soil), shear strength of a Rock (geology), rock or soil that is independent of interparticle friction. In soils, true cohesion is caused by following: # Electrostatic forces in stiff consolidation (soil), overconsolidated clays (which may be lost through weathering) # Cementing by Iron, Fe2Oxygen, O3, Calcium, Ca Carbon, CO3, Sodium, Na Chloride, Cl, etc. There can also be apparent cohesion. This is caused by: # Negative capillary pressure (which is lost upon wetting) # Pore pressure response during undrained loading (which is lost through time) # Root cohesion (which may be lost through logging or fire of the contributing plants, or through Solution (chemistry), solution) Typical values of cohesion Cohesion (alternatively called the cohesive strength) is typically measured on the basis of Mohr–Coulomb theory. Some values for rocks and some common soils are listed in the table below. Apparent cohesion of soil During critical state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hjulström Curve
The Hjulström curve, named after Filip Hjulström (1902–1982), is a graph used by hydrologists and geologists to determine whether a river will erode, transport, or deposit sediment. It was originally published in his doctoral thesis "Studies of the morphological activity of rivers as illustrated by the River Fyris.Hjulstrom, F. (1935). Studies of the morphological activity of rivers as illustrated by the River Fyris, Bulletin. Geological Institute Upsalsa, 25, 221-527." in 1935. The graph takes sediment particle size and water velocity into account.Sediment transportation Last accessed 26 Dec 2011. The upper curve shows the critical erosion velocity in cm/s as a function of particle size in mm, while the lower curve shows the deposition velocity as a function of particle size. Note that the axes are [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood Stage
Flood stage is the water level or stage at which the surface of a body of water has risen to a sufficient level to cause sufficient inundation of areas that are not normally covered by water, causing an inconvenience or a threat to life and property. When a body of water rises to this level, it is considered a flood event. Flood stage does not apply to areal flooding. As areal flooding occurs, by definition, over areas not normally covered by water, the presence of any water at all constitutes a flood. Usually, moderate and major stages are not defined for areal floodplains. Definition Flood stage is the water level, as read by a stream gauge or tide gauge, for a body of water at a particular location, measured from the level at which a body of water threatens lives, property, commerce, or travel. The term "at flood stage" is commonly used to describe the point at which this occurs. "Gauge height" (also referred to as "stream stage", "stage of the ody of water, or simply "stage" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landform
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydrologist. Hydrologists are scientists studying earth or environmental science, civil or environmental engineering, and physical geography. Using various analytical methods and scientific techniques, they collect and analyze data to help solve water related problems such as environmental preservation, natural disasters, and water management. Hydrology subdivides into surface water hydrology, groundwater hydrology (hydrogeology), and marine hydrology. Domains of hydrology include hydrometeorology, surface hydrology, hydrogeology, drainage-basin management, and water quality, where water plays the central role. Oceanography and meteorology are not included because water is only one of many important aspects within those fields. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

