|
Aritomo Yamagata
'' Gensui'' Prince , also known as Prince Yamagata Kyōsuke, was a senior-ranking Japanese military commander, twice-elected Prime Minister of Japan, and a leading member of the ''genrō'', an élite group of senior statesmen who dominated Japan after the Meiji Restoration. As the Imperial Japanese Army's inaugural Chief of Staff, he was the chief architect of the Empire of Japan's military and its reactionary ideology. For this reason, some historians consider Yamagata to be the “father” of Japanese militarism. During the latter part of the Meiji Era, Yamagata vied against Marquess Itō Hirobumi for control over the nation's policies. After Itō was assassinated in 1909, he became the most powerful figure in Japan save for the Emperor himself. Henceforth, Prince Yamagata oversaw all policymaking within the empire until a falling-out with the Imperial family resulted in him losing power shortly before his death in February 1922. Early career Yamagata Tatsunosuke was born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gensui (Imperial Japanese Army)
, formal rank designations: was the highest title in the pre-war Imperial Japanese military. The title originated from the Chinese title ''yuanshuai'' (元帥). The term ''gensui'', which was used for both the Imperial Japanese Army and the Imperial Japanese Navy, was at first a rank held by Saigō Takamori as the Commander of the Armies (陸軍元帥 Rikugun-gensui) in 1872. However, in May 1873 Saigō was "demoted" to general, with ''gensui'' thereafter no longer a rank as such, but a largely honorific title awarded for extremely meritorious service to the Emperor - thus similar in concept to the French title of Marshal of France. Equivalent to a five-star rank (OF-10), it is similar to Field Marshal in the British Army and General of the Army in the United States Army. While ''gensui'' would retain their actual ranks of general or admiral, they were entitled to wear an additional enamelled breast badge, depicting paulownia leaves between crossed army colors and a naval en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
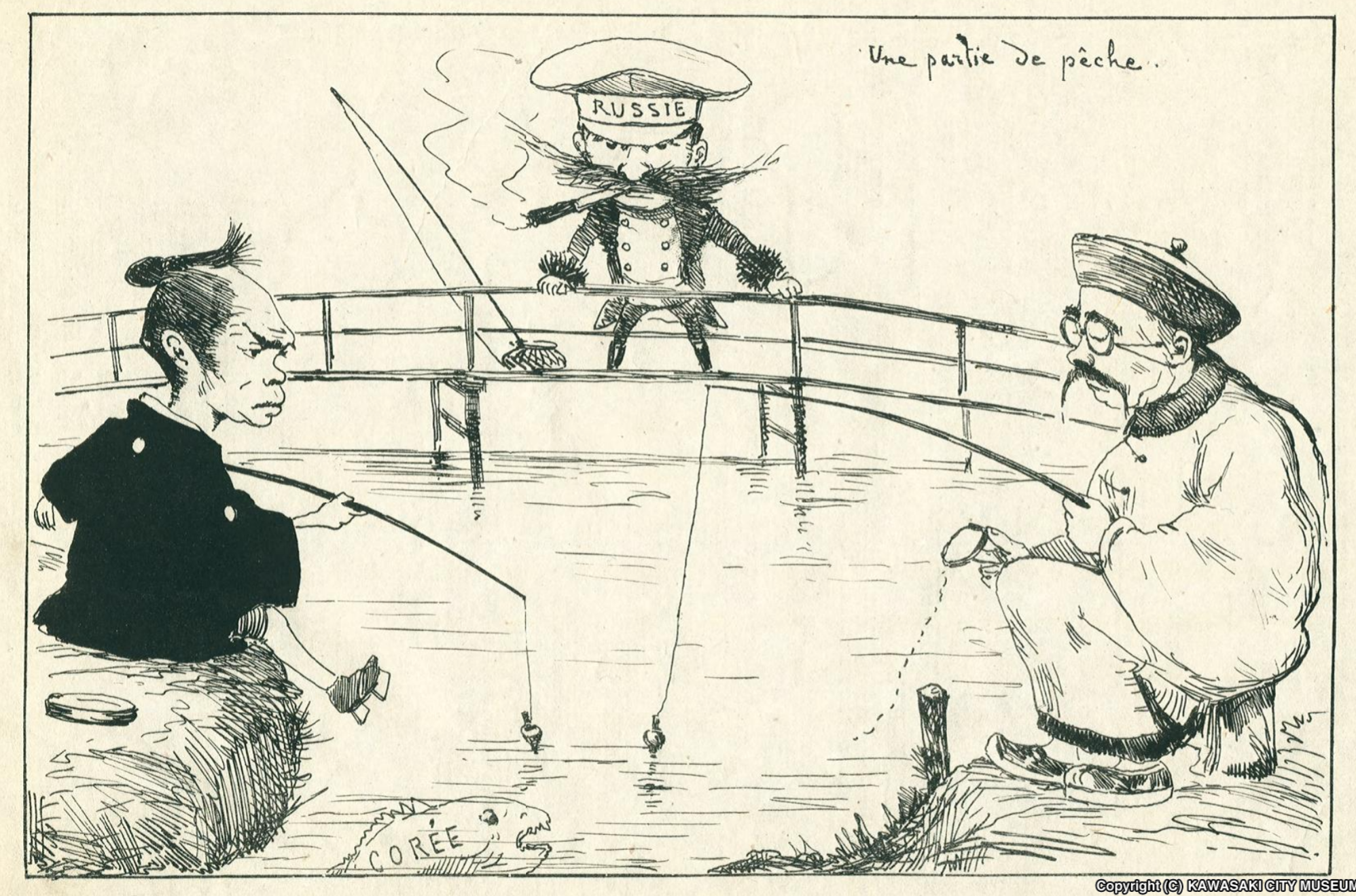
Empire Of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories. Under the slogans of and following the Boshin War and restoration of power to the Emperor from the Shogun, Japan underwent a period of industrialization and militarization, the Meiji Restoration, which is often regarded as the fastest modernisation of any country to date. All of these aspects contributed to Japan's emergence as a great power and the establishment of a colonial empire following the First Sino-Japanese War, the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s, including the Great Depression, led to the rise of militarism, nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Jiuliancheng
The Battle of Jiuliancheng (九連城之戰) was a land battle of the First Sino-Japanese War between the forces of Meiji Japan and Qing China. It is sometimes referred to as the , thus creating confusion with the previous naval conflict of the same name of 17 September, and the subsequent naval and ground battles of the Russo-Japanese War, with the same name and occurring at much the same location. Background After their defeat at the Battle of Pyongyang, the Beiyang Army made its next stand at the crossing of the Yalu River, the border between Korea and China. On the Chinese side, Qing general Song Qing established his headquarters at the walled town of Jiuliancheng (九連城), and fortified the banks of the Yalu River south to the local district capital of Dandong and north to the village of Hushan (虎山) for about 16 kilometers in either direction with over a hundred redoubts and trenches manned by around 23,000 troops. On the Korean side of the Yalu River, Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the port of Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895. The war demonstrated the failure of the Qing dynasty's attempts to modernize its military and fend off threats to its sovereignty, especially when compared with Japan's successful Meiji Restoration. For the first time, regional dominance in East Asia shifted from China to Japan; the prestige of the Qing dynasty, along with the classical tradition in China, suffered a major blow. The humiliating loss of Korea as a tributary state sparked an unprecedented public outcry. Within China, the defeat was a catalyst for a series of political upheavals led by Sun Yat-sen and Kang Youwei, culminating in the 1911 Xinhai Revolution. The war is commonly known in China as the War of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
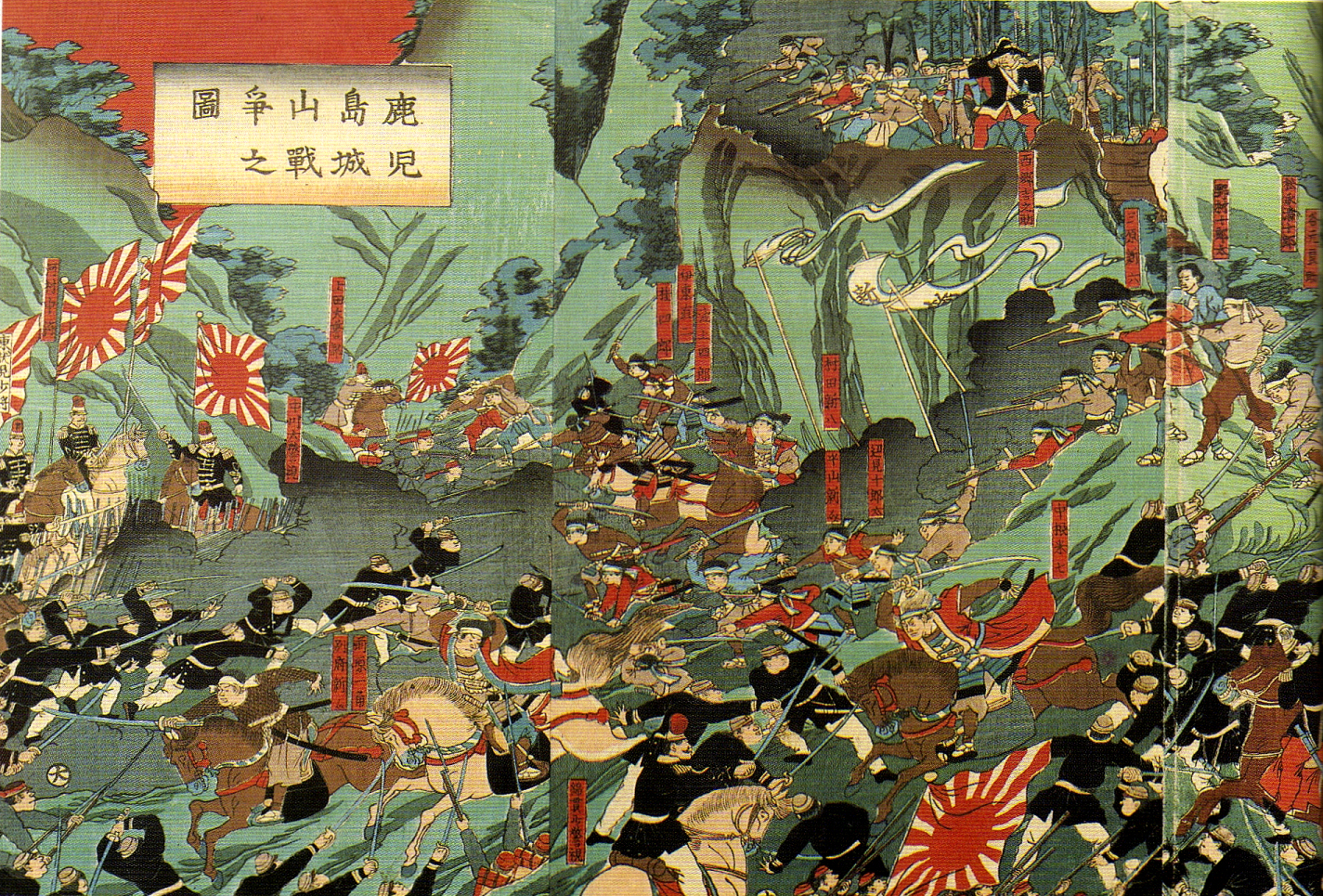
Battle Of Shiroyama
The took place on 24 September 1877, in Kagoshima, Japan. It was the final battle of the Satsuma Rebellion, where the heavily outnumbered samurai under Saigō Takamori made their last stand against Imperial Japanese Army troops under the command of General Yamagata Aritomo and Admiral Kawamura Sumiyoshi. The battle culminated in the annihilation of Saigō and his army, marking the end of the Satsuma Rebellion. The Imperial Army's victory consolidated their power, and the Satsuma Rebellion was the last instance of internal mutiny seen in the Empire of Japan. Battle Following their defeat at the Siege of Kumamoto Castle and in other battles in central Kyūshū, the surviving remnants of the samurai forces loyal to Saigō Takamori fled back to Satsuma, seizing the hill of Shiroyama overlooking Kagoshima on 1 September 1877. Imperial army troops under the command of General Yamagata Aritomo and marines under the command of Admiral Kawamura Sumiyoshi began arriving soon after, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tabaruzaka
The Battle of Tabaruzaka was a major battle of the Satsuma Rebellion. It took place in March 1877, on the island of Kyushu, Japan, concurrently to the Siege of Kumamoto Castle. Summary The Battle of Tabaruzaka began on March 3, 1877 when troops loyal to the Imperial Meiji government seeking to break the Siege of Kumamoto Castle met rebel Satsuma samurai forces seeking to capture the main road out of Kumamoto. The battle eventually spread across a 6.5 mile line from Tabaruzaka to the Ariake Sea. Skirmishes occurred for the first of several days of the battle, as both sides continued to bring additional support troops to the area. In the end, Saigō Takamori's forces would number 15,000, and the Imperial Japanese Army, led by Arisugawa Taruhito and Yamagata Aritomo, numbered 90,000. The first days of the battle were marked by heavy rain, which hampered the rebel's ability to resupply. As a result of low ammunition supplies, and water damage to their antiquated muzzle-loading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Kumamoto Castle
The from February 19 to April 12, 1877, in Kumamoto, Japan, was a major battle of the Satsuma Rebellion. Summary After the opening of hostilities between Satsuma and the Meiji government, Satsuma military leader Saigō Takamori announced his intention of marching on Tokyo to speak with Emperor Meiji and to rid the government of corrupt and venial politicians. The route to Tokyo was via Kumamoto, the site of a historic castle, and the primary garrison town for the Imperial Japanese Army in Kyūshū. The leaders of the Meiji government were aware that the loss of Kumamoto meant that all of Kyūshū would fall to Satsuma forces, and this loss would fan a rebellion across other parts of Japan as well. The Satsuma vanguard crossed into Kumamoto Prefecture on February 14 and the Commandant of Kumamoto Castle, Major General Tani Tateki sent word to Satsuma governor Oyama that any attempt by Satsuma soldiers to cross Kumamoto would be met by force. Tani had 3,800 soldiers and 600 police ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satsuma Rebellion
The Satsuma Rebellion, also known as the was a revolt of disaffected samurai against the new imperial government, nine years into the Meiji Era. Its name comes from the Satsuma Domain, which had been influential in the Restoration and became home to unemployed samurai after military reforms rendered their status obsolete. The rebellion lasted from January 29, 1877, until September of that year, when it was decisively crushed, and its leader, Saigō Takamori, was shot and mortally wounded. Saigō's rebellion was the last and most serious of a series of armed uprisings against the new government of the Empire of Japan, the predecessor state to modern Japan. The rebellion was very expensive for the government, which forced it to make numerous monetary reforms including leaving the gold standard. The conflict effectively ended the samurai class and ushered in modern warfare fought by conscript soldiers instead of military nobles. Background Although Satsuma had been one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hokuetsu
The was a battle of the Boshin War of the Meiji Restoration, which occurred in 1868 in the northwestern part of Japan, in the area of modern Niigata Prefecture. Background The Boshin War erupted in 1868 between troops favourable to the restoration of political authority to the Emperor and the government of the Tokugawa shogunate. The new Meiji government defeated the forces of Shōgun Tokugawa Yoshinobu (mostly from the western domains of Satsuma and Chōshū) at the Battle of Toba–Fushimi, and afterwards divided into three armies to advance on the Shogun’s capital of Edo. The imperial army marching up the coast of the Sea of Japan was commanded by Yamagata Aritomo and Kuroda Kiyotaka. Summary Makino Tadakuni, the ''daimyō'' of Nagaoka, in Echigo Province (modern day Niigata Prefecture) was a supporter of the Tokugawa shogunate, and refused to submit to the new government even after the fall of Edo Castle to the imperial armies. With the assistance of two Prussian busin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hatchōoki
The was an ambush in the middle of the Battle of Hokuetsu in the Boshin War by forces of Nagaoka Domain on forces loyal to the Imperial Court. The battle occurred in what is now the city of Nagaoka, in Niigata Prefecture. Background At the final years of the Tokugawa shogunate, the army of Nagaoka Domain underwent reformation. Under the leadership of senior retainer Kawai Tsugunosuke, the Nagaoka army was organized based on the British Army at the time. When fighting broke out in the Battle of Toba-Fushimi on January 27, 1868, over 60 Nagaoka soldiers were stationed to protect Tamatsu bridge near Osaka Castle. However, at the defeat of the shogunate's forces in the battle, these soldiers were among those who returned to their respective domains. After the battle, Kawai went to Edo. Planning to amass enough strength to counter the pro-imperial forces, he purchased large numbers of firearms for Nagaoka troops. Moreover, being influenced by the Monroe Doctrine from the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Aizu
The Battle of Aizu (Japanese: 会津戦争, "War of Aizu") was fought in northern Japan from October to November in autumn 1868, and was part of the Boshin War. History Aizu was known for its martial skill, and maintained at any given time a standing army of over 5000. It was often deployed to security operations on the northern fringes of the country, as far north as southern Sakhalin. Also, in the period immediately before, during, and after Commodore Perry's arrival, Aizu had a presence in security operations around Edo Bay. During the tenure of the 9th generation lord Matsudaira Katamori, the domain deployed massive amounts of their troops to Kyoto, where Katamori served as Kyoto Shugoshoku. Earning the hatred of the Chōshū domain, and alienating his ally, the Satsuma domain, Katamori retreated with the shōgun Tokugawa Yoshinobu in 1868. Though the Satchōdo controlled Imperial Court, following Yoshinobu's resignation, called for the punishment of Katamori and Aizu as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boshin War
The , sometimes known as the Japanese Revolution or Japanese Civil War, was a civil war in Japan fought from 1868 to 1869 between forces of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate and a clique seeking to seize political power in the name of the Imperial Court. The war stemmed from dissatisfaction among many nobles and young samurai with the shogunate's handling of foreigners following the opening of Japan during the prior decade. Increasing Western influence in the economy led to a decline similar to that of other Asian countries at the time. An alliance of western samurai, particularly the domains of Chōshū, Satsuma, and Tosa, and court officials secured control of the Imperial Court and influenced the young Emperor Meiji. Tokugawa Yoshinobu, the sitting ''shōgun'', realizing the futility of his situation, abdicated and handed over political power to the emperor. Yoshinobu had hoped that by doing this the House of Tokugawa could be preserved and participate in the future gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |