|
Ares (rocket)
{{SIA ...
In terms of rocketry, Ares could mean: *Ares I and Ares V, canceled rockets part of the Constellation program * Ares ICBM, a proposed ICBM and SST launch vehicle *Aerial Regional-scale Environmental Survey (ARES), a proposed Martian rocket airplane *Aries (rocket), a modified LGM-30 Minuteman missile, used to test missile defense systems See also *Ares (other) Ares is the Greek god of war and violence, equivalent of the Roman god ''Mars''. Ares or ARES may also refer to: Technology * Ares (rocket), various proposed and existing launch vehicles and missiles * Aerial Reconfigurable Embedded System, a D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ares I
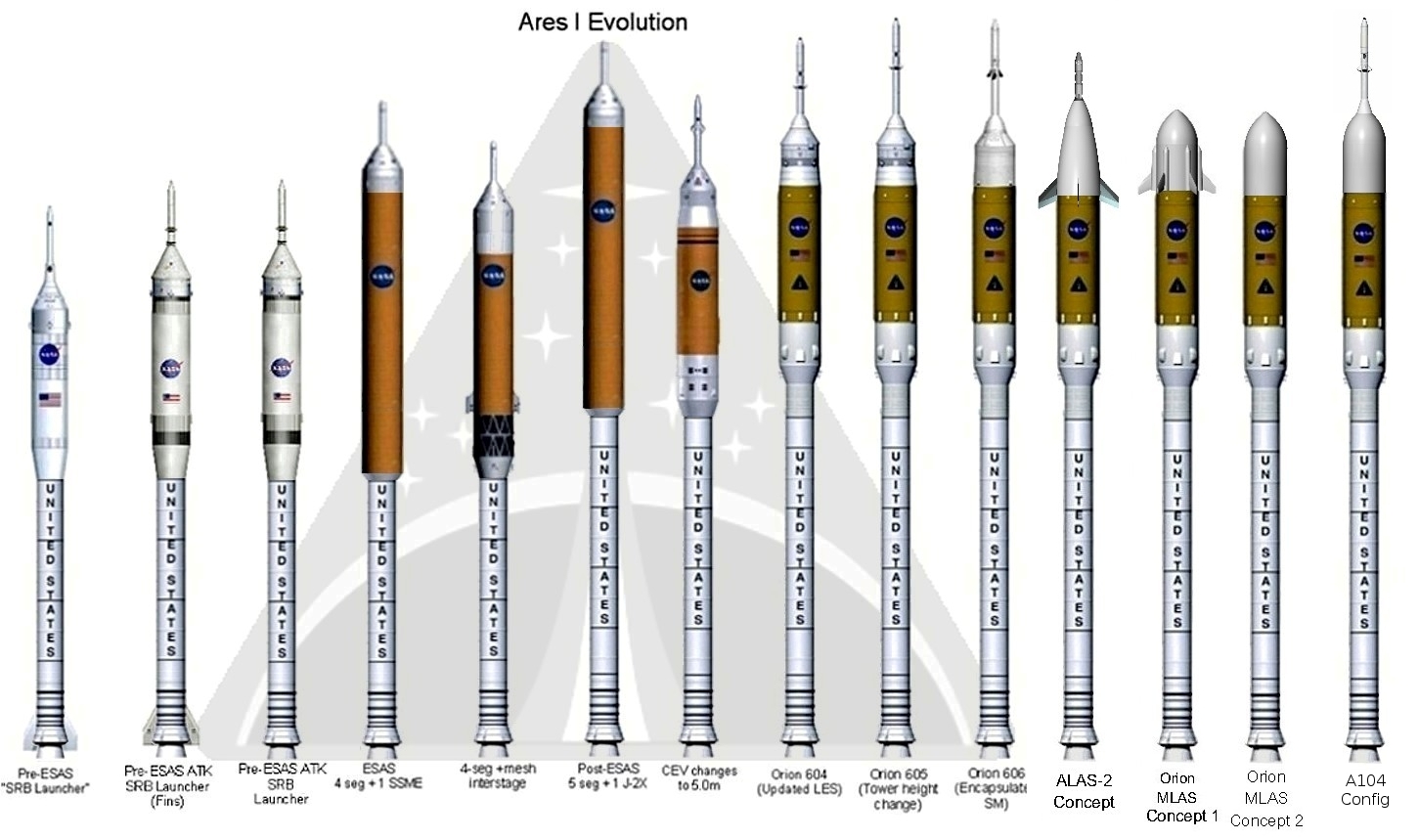
Ares I was the crew launch vehicle that was being developed by NASA as part of the Constellation program. The name "Ares" refers to the Greek deity Ares, who is identified with the Roman god Mars. Ares I was originally known as the "Crew Launch Vehicle" (CLV). NASA planned to use Ares I to launch Orion, the spacecraft intended for NASA human spaceflight missions after the Space Shuttle was retired in 2011. Ares I was to complement the larger, uncrewed Ares V, which was the cargo launch vehicle for Constellation. NASA selected the Ares designs for their anticipated overall safety, reliability and cost-effectiveness. However, the Constellation program, including Ares I, was cancelled by U.S. president Barack Obama in October 2010 with the passage of his 2010 NASA authorization bill. In September 2011, NASA detailed the Space Launch System as its new vehicle for human exploration beyond Earth's orbit. Development Advanced Transportation System Studies In 1995 Lockheed Martin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ares V
The Ares V (formerly known as the Cargo Launch Vehicle or CaLV) was the planned cargo launch component of the cancelled NASA Constellation program, which was to have replaced the Space Shuttle after its retirement in 2011. Ares V was also planned to carry supplies for a human presence on Mars. Ares V and the smaller Ares I were named after Ares, the Greek god of war. The Ares V was to launch the Earth Departure Stage and Altair lunar lander for NASA's return to the Moon, which was planned for 2019. It would also have served as the principal launcher for missions beyond the Earth-Moon system, including the program's ultimate goal, a crewed mission to Mars. The uncrewed Ares V would complement the smaller, and human-rated Ares I rocket for the launching of the 4–6 person Orion spacecraft. Both rockets, deemed safer than the then-current Space Shuttle, would have employed technologies developed for the Apollo program, the Shuttle program, and the Delta IV EELV program. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation Program
The Constellation program (abbreviated CxP) was a crewed spaceflight program developed by NASA, the space agency of the United States, from 2005 to 2009. The major goals of the program were "completion of the International Space Station" and a "return to the Moon no later than 2020" with a crewed flight to the planet Mars as the ultimate goal. The program's logo reflected the three stages of the program: the Earth (ISS), the Moon, and finally Mars—while the Mars goal also found expression in the name given to the program's booster rockets: Ares (the Greek equivalent of the Roman god Mars). The technological aims of the program included the regaining of significant astronaut experience beyond low Earth orbit and the development of technologies necessary to enable sustained human presence on other planetary bodies. Constellation began in response to the goals laid out in the Vision for Space Exploration under NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and President George W. Bush. O'Keef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ares ICBM
The Ares was a proposed intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) derived from the Titan II missile. It was a single-stage rocket with a high-performance engine to increase the rocket's specific impulse. Both Aerojet Aerojet was an American rocket and missile propulsion manufacturer based primarily in Rancho Cordova, California, with divisions in Redmond, Washington, Orange and Gainesville in Virginia, and Camden, Arkansas. Aerojet was owned by GenCorp. ... and Rocketdyne carried out engine design studies for the project, but Ares was ultimately cancelled in favour of solid-fuel ICBMs, which were safer to store and could be launched with much less notice. The Ares missile series was canceled due to the inconvenience of using liquid fuel. Some reasons included extensive protection from corrosion within the silos, as well as the liquid fuel propellant, ideally used in the proposed Ares missiles, being more expensive to maintain. Thus making the transition to use the Min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Regional-scale Environmental Survey
The Aerial Regional-scale Environmental Survey (ARES) was a proposal by NASA's Langley Research Center to build a robotic, rocket-powered airplane that would fly one mile above the surface of Mars, in order to investigate the atmosphere, surface, and sub-surface of the planet. The ARES team, headed by Dr. Joel S. Levine, sought to be selected and funded as a NASA Mars Scout Mission for a 2011 or 2013 launch window. ARES was chosen as one of four finalists in the program, out of 25 potential programs. However, the Phoenix mission was ultimately chosen instead. ARES would have traveled to Mars compactly folded into a protective aeroshell; upon entry in the thin atmosphere, the capsule would have deployed a parachute to decelerate, followed by ARES release at altitude. As well as the aforementioned goals, the aircraft would also have investigated the atmosphere of Mars and its weak magnetic field. Goals ARES would have been able to measure the crustal magnetization, spatia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aries (rocket)
Aries is an American sounding rocket and target rocket, developed by Space Vector Corporation from retired LGM-30 Minuteman I intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) stages for use by the United States Air Force and NASA. Taken over by Orbital Sciences Corporation, Aries, as the Target Test Vehicle, remains in use. Design and development In the late 1960s, the retirement of the LGM-30 Minuteman I ICBM resulted in the opportunity to produce a high-performance sounding rocket from the surplus solid-propellant rockets that became available; the Naval Research Laboratory awarded a contract to Space Vector Corporation in 1971Parsch 2005 to develop the "Fat Albert" rocket using the surplus Minuteman I first stages; before the first launch, the name of the rocket was changed to the "more dignified" Aries.Dickson 2009, pp. 24–25. Aries consisted of an Aerojet M56 solid-fuel rocket, the second stage of the Minuteman I, fitted with an aerodynamic nose cone and four tail fins, taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |